
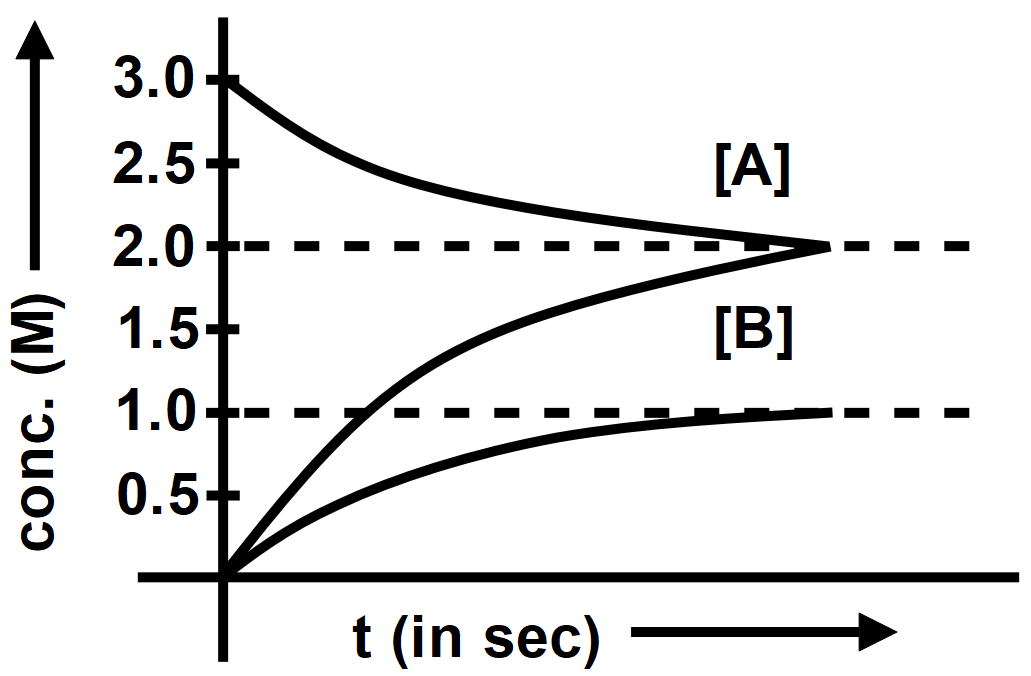
The progress of reaction $ {{A}_{\left( g \right)}}\rightleftharpoons x{{B}_{\left( g \right)}}+y{{C}_{\left( g \right)}} $ with time is presented in figure. What is the value of $ K_{c}^{0} $ at $ ~300K $ ?
(A) $ 1 $
(B) $ 2 $
(C) $ 3 $
(D) $ 4 $

Answer
507.9k+ views
Hint: We know that the concentration of the product is zero. Still, with time, the concentration of the product increases and the concentration of the reactant decreases as it is getting consumed. After some time, the concentration does not change any further.
Complete answer:
As we know the equilibrium concentration equation, you need to know the formula for equilibrium constant $ {{K}_{c}}. $ When the chemical is in equilibrium, the ratio of the products to the reactants is called the equilibrium constant. We say that equilibrium has been reached when the reverse and forward reactions are proceeding at the same rate. For different reactions, those rates will become equal at various places in the transformation of reactant into a product. Therefore, it is not necessary for the equilibrium concentration of reactants and products to be the same. Changes in the concentrations of chemicals will shift chemical equilibrium according to Le Chatelier’s Principle.
When the concentration of a reactant is increased, the chemical equilibrium will shift towards the products. When the concentration of a product increases, the chemical equilibrium will shift towards the reactants. The concentration of A and B are the same and the same decrease in concentration of $ 2 $ M and the graphs show that condition so the value of equilibrium constant is $ 2. $
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
Remember that the temperature increases, molecules gain energy and move faster and faster. Therefore, the greater the temperature, the higher the probability that molecules will be moving with the necessary activation energy for a reaction to occur upon collision.
Complete answer:
As we know the equilibrium concentration equation, you need to know the formula for equilibrium constant $ {{K}_{c}}. $ When the chemical is in equilibrium, the ratio of the products to the reactants is called the equilibrium constant. We say that equilibrium has been reached when the reverse and forward reactions are proceeding at the same rate. For different reactions, those rates will become equal at various places in the transformation of reactant into a product. Therefore, it is not necessary for the equilibrium concentration of reactants and products to be the same. Changes in the concentrations of chemicals will shift chemical equilibrium according to Le Chatelier’s Principle.
When the concentration of a reactant is increased, the chemical equilibrium will shift towards the products. When the concentration of a product increases, the chemical equilibrium will shift towards the reactants. The concentration of A and B are the same and the same decrease in concentration of $ 2 $ M and the graphs show that condition so the value of equilibrium constant is $ 2. $
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
Remember that the temperature increases, molecules gain energy and move faster and faster. Therefore, the greater the temperature, the higher the probability that molecules will be moving with the necessary activation energy for a reaction to occur upon collision.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




