
The product formed should be:
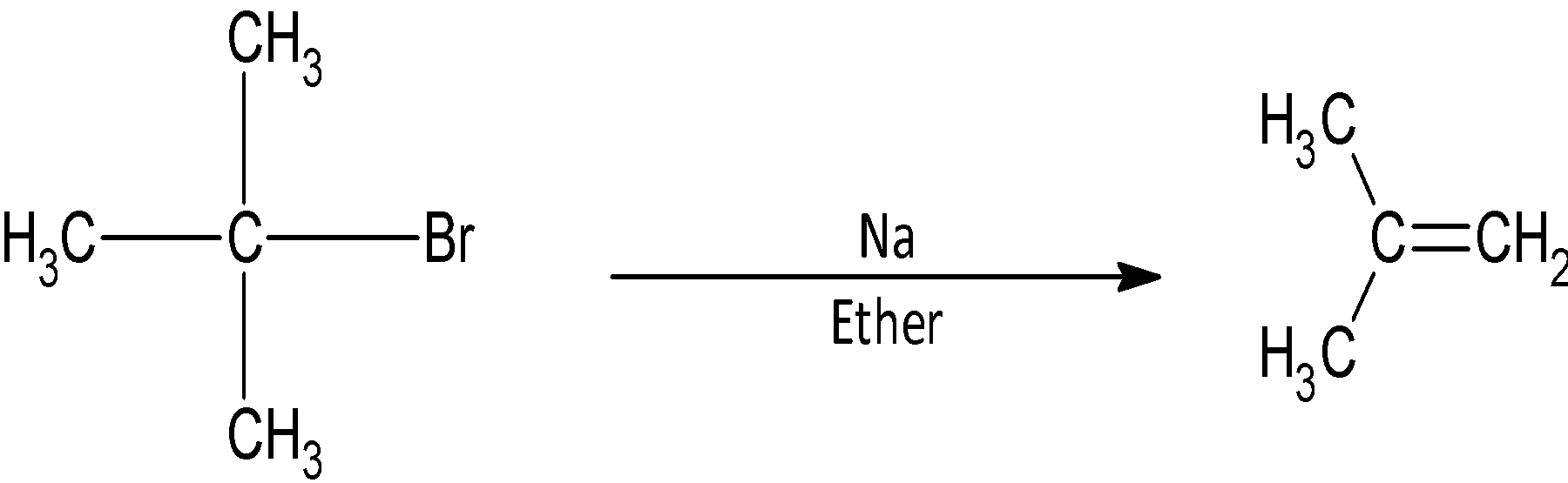
(A)
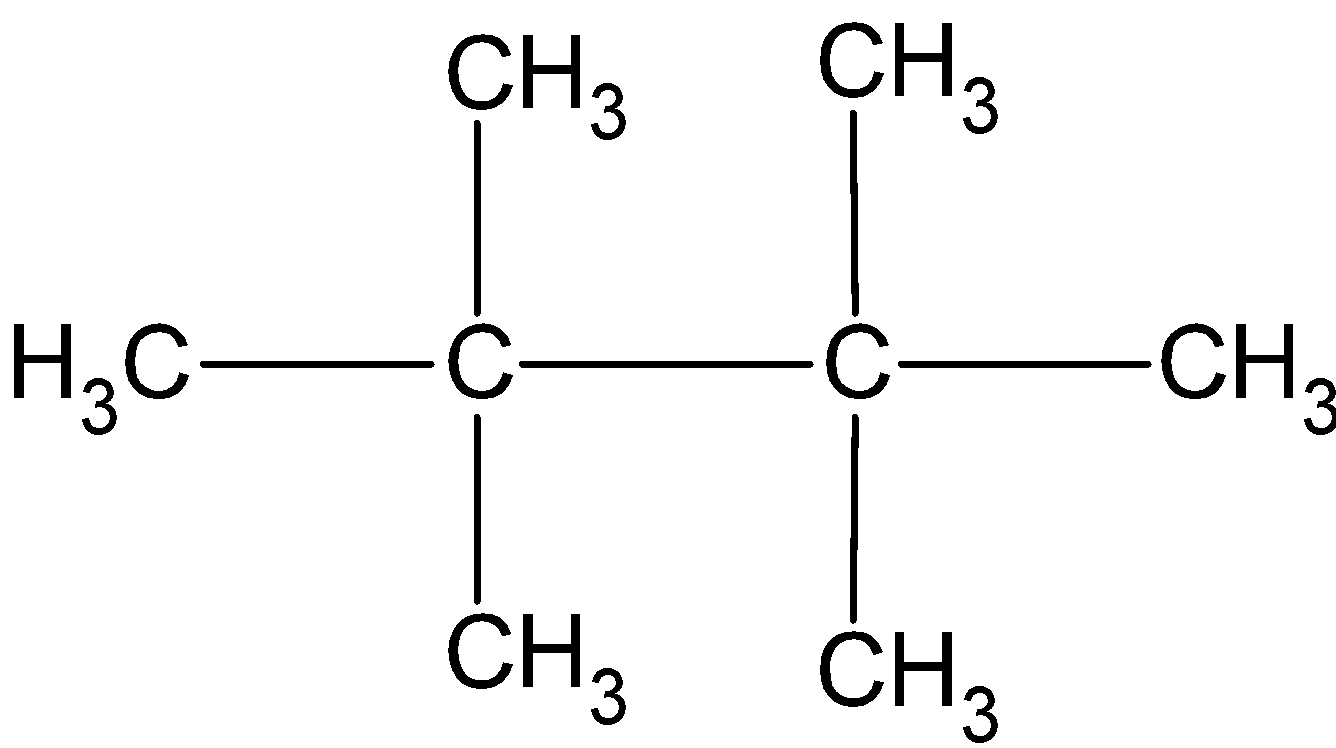
(B)
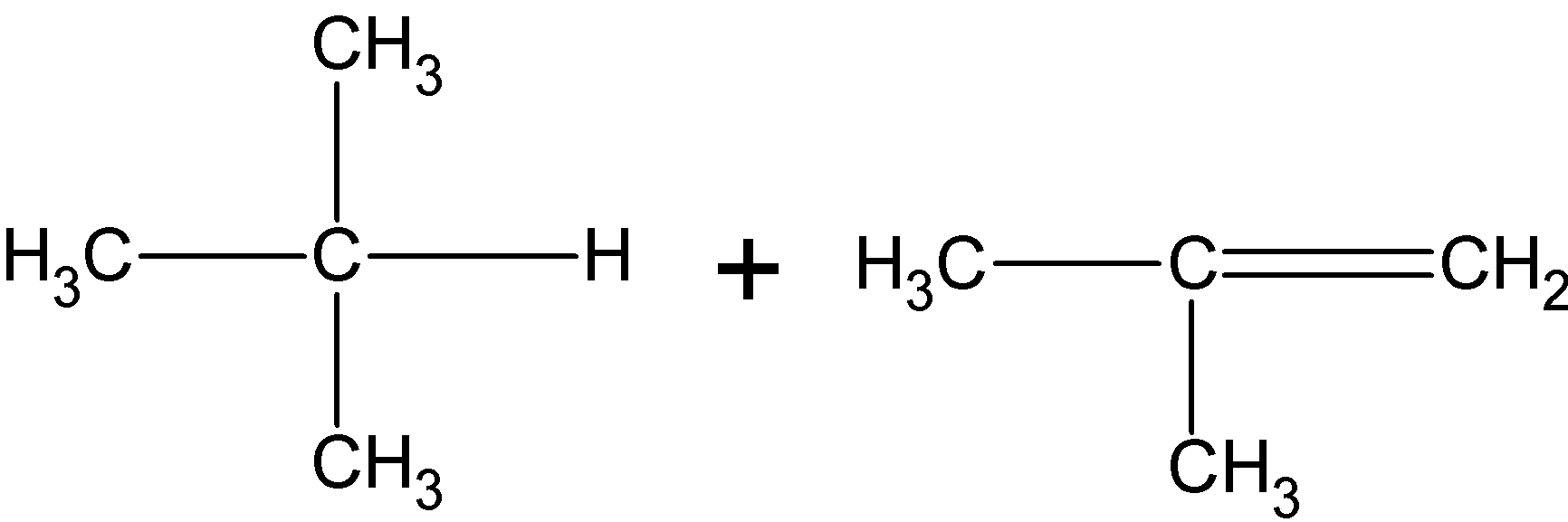
(C)
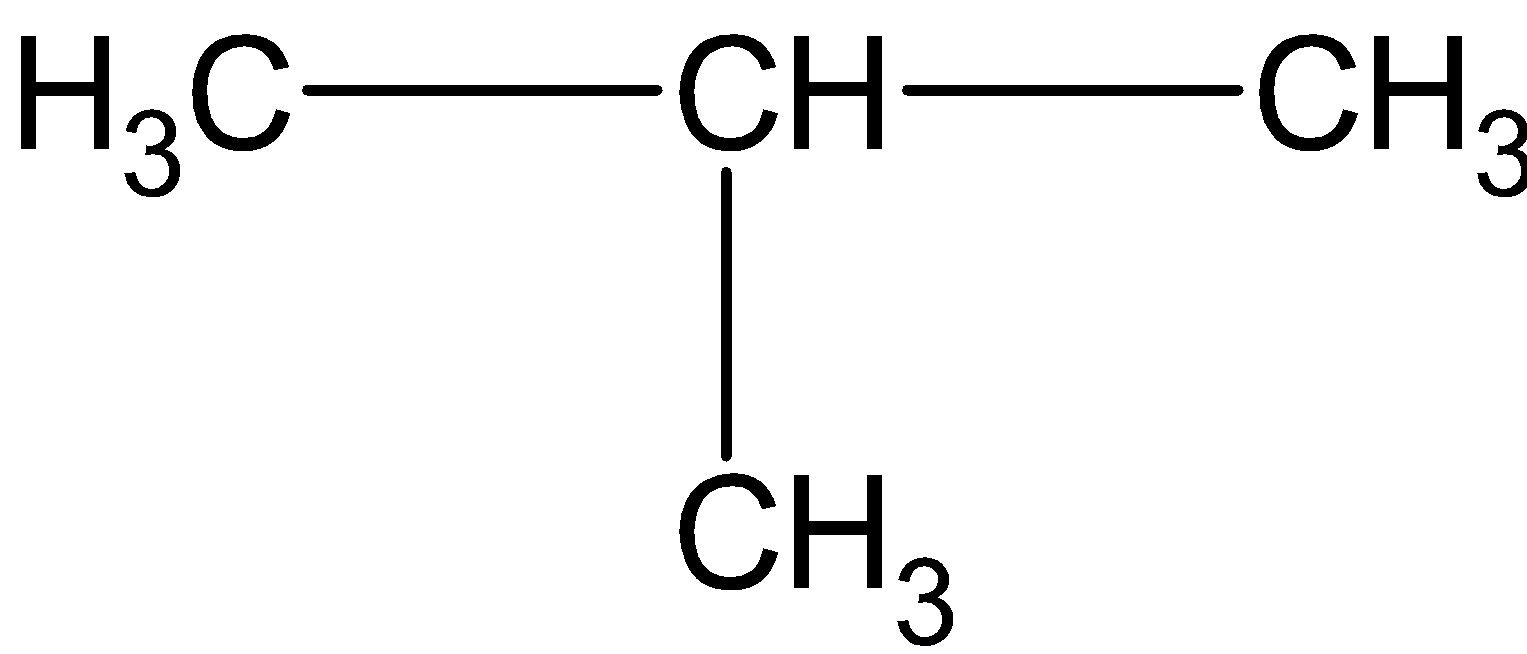
(D)




Answer
551.7k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you must recall the reaction occurring when certain reagents are reacted with organic compounds. When an alkyl bromide is reacted with sodium in presence of ether, electrophilic substitution reaction occurs and this is a name reaction, known as the Williamson’s synthesis. You must also recall the tendencies of primary, secondary or tertiary halides to undergo substitution or electrophilic reactions.
Complete step by step solution:
When alkyl halides undergo Williamson’s synthesis, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction occurs and an ether is obtained as the product. The reacting species is sodium ethoxide. It is a one- step reaction and the addition of the nucleophile and removal of the bromide ion takes place in the same step.
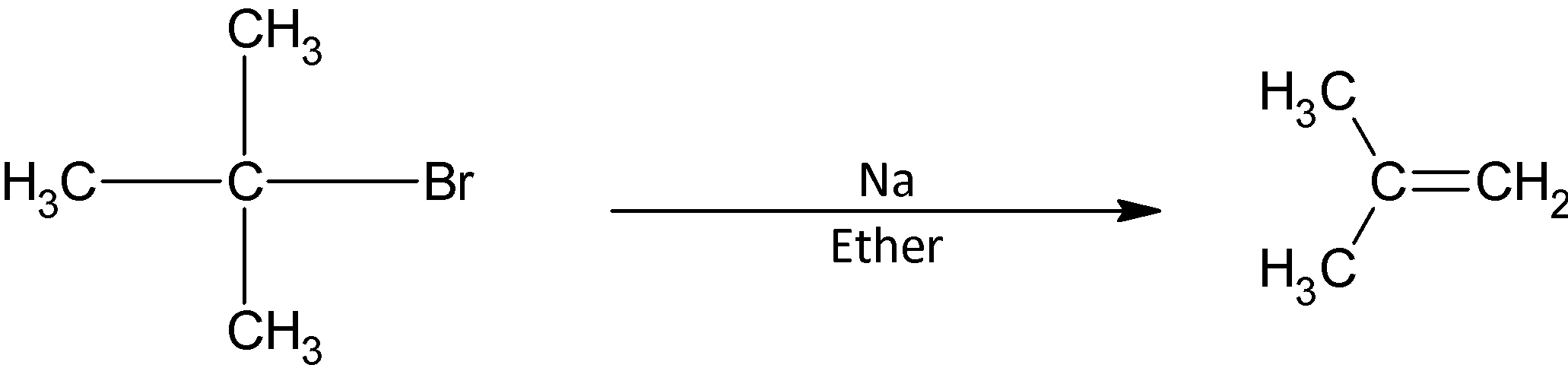
However, in the given question, we have tertiary butoxide. We know that tertiary alkyl halides do not undergo bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction. There are three bulky methyl groups attached to the carbon atom susceptible to attack. The incoming ethoxide nucleophile is repelled by from the front side attack by the leaving bromide ion and its back side attack is hindered by the bulky methyl groups.
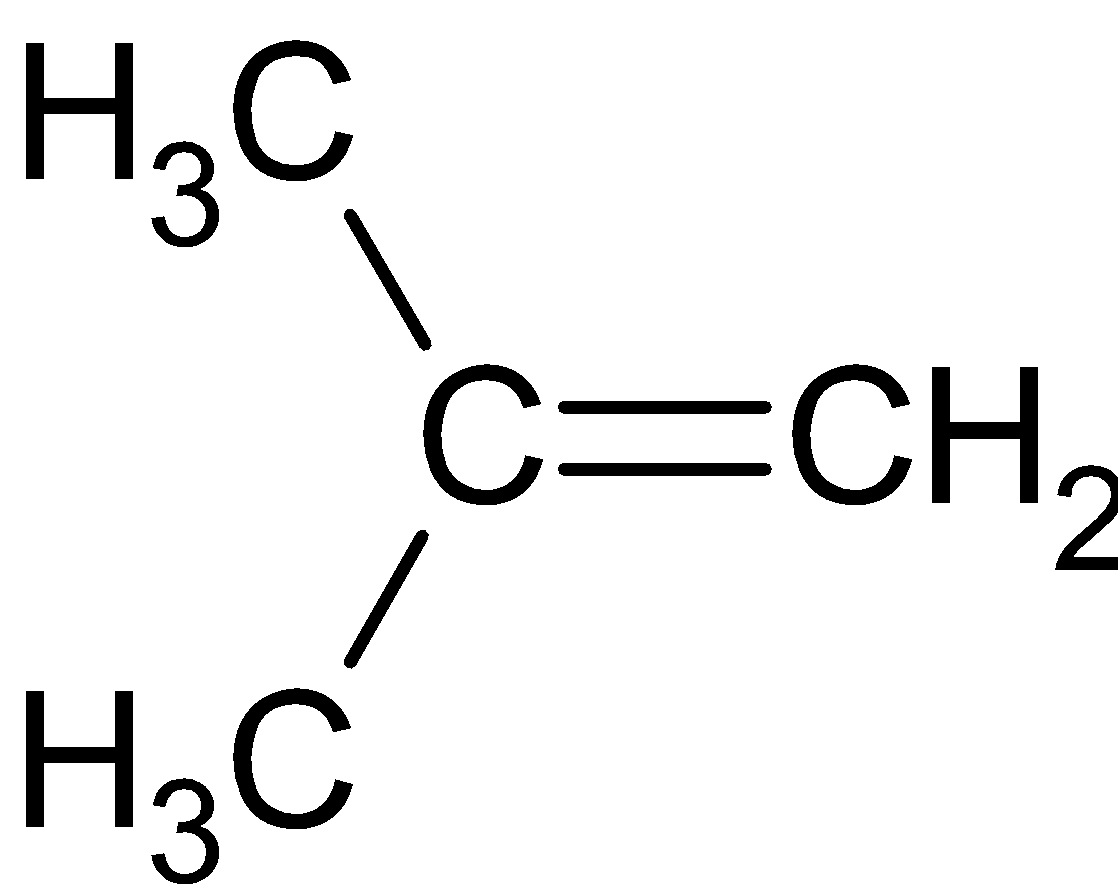
As a result, the ethoxide ion acts as a base in case of tertiary substrates. It removes a hydrogen ion from the adjacent methyl group. As a result, a double bond is formed between the two carbon atoms and the product obtained is an alkene. The product formed in case of tertiary butyl bromide.
The correct answer is (D).
Note:
Williamson's synthesis is a common reaction used for the preparation of ethers. Both symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers can be prepared easily using this reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
When alkyl halides undergo Williamson’s synthesis, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction occurs and an ether is obtained as the product. The reacting species is sodium ethoxide. It is a one- step reaction and the addition of the nucleophile and removal of the bromide ion takes place in the same step.
However, in the given question, we have tertiary butoxide. We know that tertiary alkyl halides do not undergo bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction. There are three bulky methyl groups attached to the carbon atom susceptible to attack. The incoming ethoxide nucleophile is repelled by from the front side attack by the leaving bromide ion and its back side attack is hindered by the bulky methyl groups.
As a result, the ethoxide ion acts as a base in case of tertiary substrates. It removes a hydrogen ion from the adjacent methyl group. As a result, a double bond is formed between the two carbon atoms and the product obtained is an alkene. The product formed in case of tertiary butyl bromide.

The correct answer is (D).
Note:
Williamson's synthesis is a common reaction used for the preparation of ethers. Both symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers can be prepared easily using this reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




