
The process of blood clotting does not require
(a) Sodium ions
(b) Calcium ions
(c) Prothrombin
(d) Vitamin K
(e) Platelets
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: The process of blood clotting or blood coagulation occurs when there is any damage to the blood vessels in order to stop the loss of blood from the body before shock and possible death may occur. Clotting is done by converting liquid blood to solid gel-like to prevent its flow.
Complete Answer:
Blood clotting is a mechanism to prevent excessive loss of blood from the body. A clot or coagulum is formed as the place of injury to act as a plug to prevent the flow of blood outside. This coagulum is formed by a network of threads known as fibrins which are converted from inactive fibrinogen to active fibrins by the enzyme thrombin.
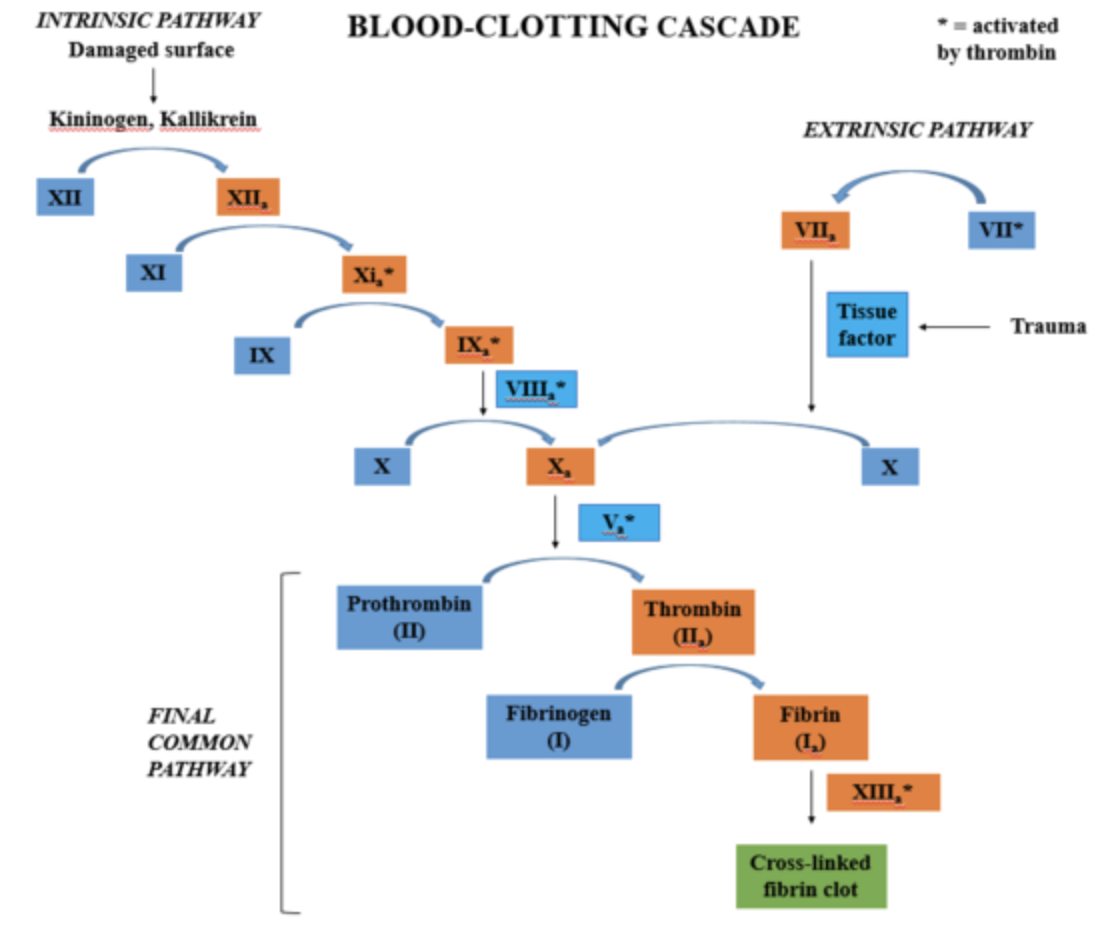
Thrombin is again converted from inactive prothrombin by the enzyme thrombokinase and calcium ions. This prothrombin is produced by platelets in the presence of vitamin K. Hence, the process of blood clotting does not require sodium ions.
Additional information: Let us know more about the process of blood clotting.
- The process of blood clotting takes place in a series of reactions known as the cascade process.
- The cascade process consists of two pathways known as the intrinsic pathway and the extrinsic pathway.
- The intrinsic pathway is initiated by Hageman’s factor or factor XII when there is damage within the walls of the blood vessels. The factors for this pathway are released by platelets and endothelium of blood vessels.
- The extrinsic pathway is initiated by the release of factors from the damaged tissue. This is because the cells of the damaged tissue show a surface protein known as tissue factor.
So, the correct option is ‘(a) Sodium ions’.
Note:
- The body contains 13 clotting factors for the process of blood coagulation.
- Fibrinogen is known as factor 1, prothrombin is known as factor 2, thromboplastin is factor 3, and calcium ions are factor 4.
- Deficiency of vitamin K in the body can affect the coagulation process and one tiny cut can result in the death of the person. Subject: Biology
Complete Answer:
Blood clotting is a mechanism to prevent excessive loss of blood from the body. A clot or coagulum is formed as the place of injury to act as a plug to prevent the flow of blood outside. This coagulum is formed by a network of threads known as fibrins which are converted from inactive fibrinogen to active fibrins by the enzyme thrombin.

Thrombin is again converted from inactive prothrombin by the enzyme thrombokinase and calcium ions. This prothrombin is produced by platelets in the presence of vitamin K. Hence, the process of blood clotting does not require sodium ions.
Additional information: Let us know more about the process of blood clotting.
- The process of blood clotting takes place in a series of reactions known as the cascade process.
- The cascade process consists of two pathways known as the intrinsic pathway and the extrinsic pathway.
- The intrinsic pathway is initiated by Hageman’s factor or factor XII when there is damage within the walls of the blood vessels. The factors for this pathway are released by platelets and endothelium of blood vessels.
- The extrinsic pathway is initiated by the release of factors from the damaged tissue. This is because the cells of the damaged tissue show a surface protein known as tissue factor.
So, the correct option is ‘(a) Sodium ions’.
Note:
- The body contains 13 clotting factors for the process of blood coagulation.
- Fibrinogen is known as factor 1, prothrombin is known as factor 2, thromboplastin is factor 3, and calcium ions are factor 4.
- Deficiency of vitamin K in the body can affect the coagulation process and one tiny cut can result in the death of the person. Subject: Biology
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




