
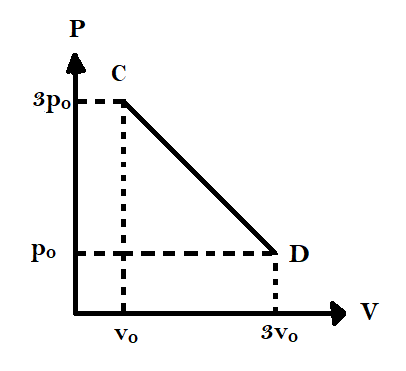
The process $CD$ is shown in the diagram. As the system is taken from $C$ to $D$, what happens to the temperature of the system?
A. Temperature first decreases and then increases
B. Temperature first increases and then decreases
C. Temperature decreases continuously
D. Temperature increases continuously

Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint:With the data given to us, we can easily calculate the conditions at both the ends of $CD$ using the ideal gas relations. However, to find what happens during the process, we can arbitrarily choose a point, such as the midpoint of $CD$ and evaluate the conditions at that point.
Formulas used: $PV = nRT$
Where $P$ is the pressure, $V$ is the volume, $n$ is the number of moles, $R$ is the universal gas constant and $T$ is the absolute temperature.
Complete step by step answer:
-From the ideal gas law, we have:
\[PV = nRT \Rightarrow T = \dfrac{{PV}}{{nR}}\]
Where $P$ is the pressure, $V$ is the volume, $n$ is the number of moles, $R$ is the universal gas constant and $T$ is the absolute temperature.
-At point $C$, we have $P = 3{p_0}$ and $V = {v_0}$
Substituting these values, we have:
${T_C} = \dfrac{{3{p_0}{v_0}}}{{nR}}$ ………………… (1)
Where ${T_C}$ is the temperature at the point $C$
-At point $D$, we have $P = {p_0}$ and $V = 3{v_0}$
Substituting these values, we get:
${T_D} = \dfrac{{3{p_0}{v_0}}}{{nR}}$ ……………..…. (2)
Where ${T_D}$ is the temperature at the point $D$
Now let us evaluate the temperature at the midpoint of $CD$.
-As we are choosing the midpoint, both pressure and volume at the midpoint will be the average of pressure and volume at the two ends of $CD$
-Therefore, at the midpoint, $P = \dfrac{{3{p_0} + {p_0}}}{2}$
On solving this, we get:
$P = \dfrac{{4{p_0}}}{2} = 2{p_0}$
Similarly, volume at the midpoint, $V = \dfrac{{{v_0} + 3{v_0}}}{2}$
On solving this, we get:
$V = \dfrac{{4{v_0}}}{2} = 2{v_0}$
Substituting these values, we get:
${T_{{{midpoint}}}} = \dfrac{{2{p_0} \times 2{v_0}}}{{nR}} = \dfrac{{4{p_0}{v_0}}}{{nR}}$ ………………… (3)
From equations (1), (2) and (3) we can clearly see that temperatures at $C$ and $D$ are equal and the temperature at the midpoint is higher than either of these.
Hence, temperature first increases from $C$ till the midpoint and then decreases till $D$.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: Note that we have taken the conditions at the midpoint as the average value of both the ends of $CD$ only because the process $CD$ is seen to be a linear function, that is, a straight line. If the shape of the graph were to be different, we would have to use integral methods to evaluate the conditions at the midpoint. The initial increase in temperature is due to the fact that the pressure is continuously reducing and the volume is continuously increasing, till they reach a maximum at the midpoint. After the midpoint, the fall in pressure is drastic and this leads to decrease in temperature.
Formulas used: $PV = nRT$
Where $P$ is the pressure, $V$ is the volume, $n$ is the number of moles, $R$ is the universal gas constant and $T$ is the absolute temperature.
Complete step by step answer:
-From the ideal gas law, we have:
\[PV = nRT \Rightarrow T = \dfrac{{PV}}{{nR}}\]
Where $P$ is the pressure, $V$ is the volume, $n$ is the number of moles, $R$ is the universal gas constant and $T$ is the absolute temperature.
-At point $C$, we have $P = 3{p_0}$ and $V = {v_0}$
Substituting these values, we have:
${T_C} = \dfrac{{3{p_0}{v_0}}}{{nR}}$ ………………… (1)
Where ${T_C}$ is the temperature at the point $C$
-At point $D$, we have $P = {p_0}$ and $V = 3{v_0}$
Substituting these values, we get:
${T_D} = \dfrac{{3{p_0}{v_0}}}{{nR}}$ ……………..…. (2)
Where ${T_D}$ is the temperature at the point $D$
Now let us evaluate the temperature at the midpoint of $CD$.
-As we are choosing the midpoint, both pressure and volume at the midpoint will be the average of pressure and volume at the two ends of $CD$
-Therefore, at the midpoint, $P = \dfrac{{3{p_0} + {p_0}}}{2}$
On solving this, we get:
$P = \dfrac{{4{p_0}}}{2} = 2{p_0}$
Similarly, volume at the midpoint, $V = \dfrac{{{v_0} + 3{v_0}}}{2}$
On solving this, we get:
$V = \dfrac{{4{v_0}}}{2} = 2{v_0}$
Substituting these values, we get:
${T_{{{midpoint}}}} = \dfrac{{2{p_0} \times 2{v_0}}}{{nR}} = \dfrac{{4{p_0}{v_0}}}{{nR}}$ ………………… (3)
From equations (1), (2) and (3) we can clearly see that temperatures at $C$ and $D$ are equal and the temperature at the midpoint is higher than either of these.
Hence, temperature first increases from $C$ till the midpoint and then decreases till $D$.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: Note that we have taken the conditions at the midpoint as the average value of both the ends of $CD$ only because the process $CD$ is seen to be a linear function, that is, a straight line. If the shape of the graph were to be different, we would have to use integral methods to evaluate the conditions at the midpoint. The initial increase in temperature is due to the fact that the pressure is continuously reducing and the volume is continuously increasing, till they reach a maximum at the midpoint. After the midpoint, the fall in pressure is drastic and this leads to decrease in temperature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




