
The primary and secondary valencies of chromium in the complex ion, dichloro di oxalato chromium (lll), respectively are:
(A) 3, 4
(B) 4, 3
(C) 3, 6
(D) 6, 3
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: Primary valency is the oxidation state of the metal ion and secondary valency is the coordination number of the metal ion in the given complex. Also, the number given in the bracket of IUPAC names of complex ions is the oxidation number of central metal.
Complete step by step answer:
-First of all we will talk about primary and secondary valencies.
According to Werner’s explanation of coordination complexes, the metal ion in a coordination complex will exhibit 2 types of valencies: primary and secondary.
Primary valency is basically the oxidation number of the metal ion (positive charge).
Secondary valency is the coordination number of the metal ion or say the number of atoms or ligands directly bonded to the metal ion.
-We will now write down the formula of the coordination compound named dichloro dioxalato chromium (lll). From the name we can see that chromium is attached to 2 chlorine atoms (dichloro) and 2 oxalato groups (dioxalato). It also tells us that the oxidation state of chromium here is (+3).
The formula for oxalate is ${({C_2}{O_4})^{ - 2}}$ and hence we know it is a bidentate ligand, while that of chlorine is $C{l^ - }$ which is a monodentate ligand.
Let the oxidation state of entire complex be = x
x = (O.S. of Cr) + (O.S. of 2 chlorine) + (O.S. of 2 oxalate)
= (+3) + 2(-1) + 2(-2)
= +3 -2 -4
= (-3)
So, the oxidation state of the entire complex is (-3).
The molecular formula of the complex can be written as: ${\left[ {Cr{{({C_2}{O_4})}_2}{{(Cl)}_2}} \right]^{ - 3}}$ and a structure as shown below:
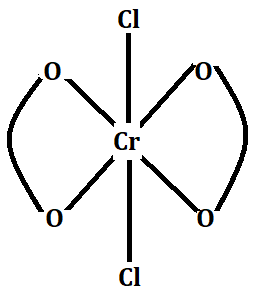
-Now we have already seen that the oxidation state of Cr atom is (+3), so the primary valency will be = (+3).
-Also 2 bidentate ligands (oxalate) and 2 monodentate ligands (chlorine) are attached to Cr atom, coordination number of Cr will be = 2(2) + 2(1) = 6
Hence the secondary valency will be = 6.
The primary and secondary valencies are: 3 and 6.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Remember that the coordination number for 1 bidentate ligand will be 2 because it has 2 binding sites or say it binds to the metal atom from 2 places. While, a monodentate ligand forms a coordination number of 1 since it has only 1 binding site. Similarly 1 tridentate ligand will have 3 binding sites and will form a coordination number of 3 and so on.
Complete step by step answer:
-First of all we will talk about primary and secondary valencies.
According to Werner’s explanation of coordination complexes, the metal ion in a coordination complex will exhibit 2 types of valencies: primary and secondary.
Primary valency is basically the oxidation number of the metal ion (positive charge).
Secondary valency is the coordination number of the metal ion or say the number of atoms or ligands directly bonded to the metal ion.
-We will now write down the formula of the coordination compound named dichloro dioxalato chromium (lll). From the name we can see that chromium is attached to 2 chlorine atoms (dichloro) and 2 oxalato groups (dioxalato). It also tells us that the oxidation state of chromium here is (+3).
The formula for oxalate is ${({C_2}{O_4})^{ - 2}}$ and hence we know it is a bidentate ligand, while that of chlorine is $C{l^ - }$ which is a monodentate ligand.
Let the oxidation state of entire complex be = x
x = (O.S. of Cr) + (O.S. of 2 chlorine) + (O.S. of 2 oxalate)
= (+3) + 2(-1) + 2(-2)
= +3 -2 -4
= (-3)
So, the oxidation state of the entire complex is (-3).
The molecular formula of the complex can be written as: ${\left[ {Cr{{({C_2}{O_4})}_2}{{(Cl)}_2}} \right]^{ - 3}}$ and a structure as shown below:

-Now we have already seen that the oxidation state of Cr atom is (+3), so the primary valency will be = (+3).
-Also 2 bidentate ligands (oxalate) and 2 monodentate ligands (chlorine) are attached to Cr atom, coordination number of Cr will be = 2(2) + 2(1) = 6
Hence the secondary valency will be = 6.
The primary and secondary valencies are: 3 and 6.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Remember that the coordination number for 1 bidentate ligand will be 2 because it has 2 binding sites or say it binds to the metal atom from 2 places. While, a monodentate ligand forms a coordination number of 1 since it has only 1 binding site. Similarly 1 tridentate ligand will have 3 binding sites and will form a coordination number of 3 and so on.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




