
The potential energy in the joule of a particle of mass 1 kg moving in x-y plane obeys the law,\[\phi =3x+4y\] . Here x and y are in meters. If the particle is at rest at (6m, 8m) at time\[t=0\], then, the work done by the conservative force on the particle from the initial position to the instant when it crosses the x-axis is:
A. 25 J
B. -25 J
C. 50 J
D. -50 J
Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: In the beginning, the particle was at rest, thus, the particle will move in the direction of the force. As the particle crosses the x-axis at the origin, thus, the sum of the initial kinetic energy and the internal energy equals the sum of the final kinetic energy and the internal energy. Using this, we will find the value of the work done.
Formula used:
\[\overset{\to }{\mathop{F}}\,=-\left( \dfrac{\partial \phi }{\partial x}i+\dfrac{\partial \phi }{\partial y}j \right)\]
Complete answer:
From the given information, we have the data as follows.
The potential energy in the joule of a particle of mass 1 kg moving in x-y plane obeys the law,\[\phi =3x+4y\] . The particle is at rest at (6m, 8m) at time\[t=0\].
The force is given as follows.
\[\overset{\to }{\mathop{F}}\,=-\left( \dfrac{\partial \phi }{\partial x}i+\dfrac{\partial \phi }{\partial y}j \right)\]
The component of ‘i’ represents the x-coordinate and the component of ‘j’ represents the y-coordinate.
Substitute the values in the above formula.
\[\begin{align}
& \overset{\to }{\mathop{F}}\,=-\left( 3i+4j \right) \\
& \therefore \overset{\to }{\mathop{F}}\,=-3i-4j \\
\end{align}\]
The diagrammatic representation of these values is given as follows.
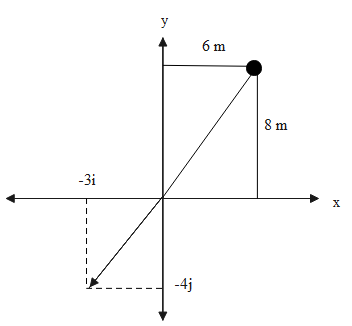
As the particle crosses the x-axis at origin, thus, the sum of the initial kinetic energy and the initial internal energy equals the sum of the final kinetic energy and the final internal energy. The mathematical representation of the same is,
\[K{{E}_{i}}+{{U}_{i}}=K{{E}_{f}}+{{U}_{f}}\]
Substitute the values in the above formula.
\[\begin{align}
& 0+(3\times 6+4\times 8)=K{{E}_{f}}+(3\times 0+4\times 0) \\
& \Rightarrow K{{E}_{f}}=18+32 \\
& \therefore K{{E}_{f}}=50\,J \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \] The work done by the conservative force on the particle from the initial position to the instant when it crosses the x-axis is 50 J.
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note:
In the beginning, the particle was at rest, thus, the particle will move in the direction of the force. As the particle crosses the x-axis at the origin, thus, the sum of the initial kinetic energy and the internal energy equals the sum of the final kinetic energy and the internal energy.
Formula used:
\[\overset{\to }{\mathop{F}}\,=-\left( \dfrac{\partial \phi }{\partial x}i+\dfrac{\partial \phi }{\partial y}j \right)\]
Complete answer:
From the given information, we have the data as follows.
The potential energy in the joule of a particle of mass 1 kg moving in x-y plane obeys the law,\[\phi =3x+4y\] . The particle is at rest at (6m, 8m) at time\[t=0\].
The force is given as follows.
\[\overset{\to }{\mathop{F}}\,=-\left( \dfrac{\partial \phi }{\partial x}i+\dfrac{\partial \phi }{\partial y}j \right)\]
The component of ‘i’ represents the x-coordinate and the component of ‘j’ represents the y-coordinate.
Substitute the values in the above formula.
\[\begin{align}
& \overset{\to }{\mathop{F}}\,=-\left( 3i+4j \right) \\
& \therefore \overset{\to }{\mathop{F}}\,=-3i-4j \\
\end{align}\]
The diagrammatic representation of these values is given as follows.

As the particle crosses the x-axis at origin, thus, the sum of the initial kinetic energy and the initial internal energy equals the sum of the final kinetic energy and the final internal energy. The mathematical representation of the same is,
\[K{{E}_{i}}+{{U}_{i}}=K{{E}_{f}}+{{U}_{f}}\]
Substitute the values in the above formula.
\[\begin{align}
& 0+(3\times 6+4\times 8)=K{{E}_{f}}+(3\times 0+4\times 0) \\
& \Rightarrow K{{E}_{f}}=18+32 \\
& \therefore K{{E}_{f}}=50\,J \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \] The work done by the conservative force on the particle from the initial position to the instant when it crosses the x-axis is 50 J.
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note:
In the beginning, the particle was at rest, thus, the particle will move in the direction of the force. As the particle crosses the x-axis at the origin, thus, the sum of the initial kinetic energy and the internal energy equals the sum of the final kinetic energy and the internal energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




