
The potential difference between A & B in the given branch of a circuit is
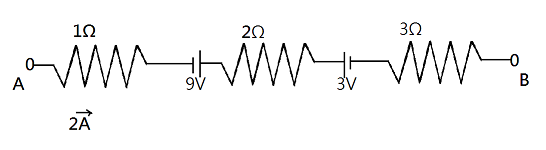
A. $6\,V$
B. $12\,V$
C. $9\,V$
D. $0\,V$

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: We need to find the potential difference between two given points. There are three resistors given and the values of each resistor is also given. Two voltages are also mentioned in the figure. We will apply Kirchhoff’s voltage law to find the resultant potential difference between the two points.
Complete step by step answer:
Kirchhoff gave two laws for any closed circuit; Kirchhoff’s current law and Kirchhoff’s voltage law. Kirchhoff's voltage law states that the sum of all the voltages around any closed loop in a circuit must equal zero.
In the given problem, the direction of the flow of current is given. The current is flowing from left to right as shown in the diagram above. Now, we will calculate the potential drops while moving from point A to point B. This will be given as:
As we cross the first resistance of $1\Omega $ there will be drop in voltage which will be current multiplied by resistance given as $ - 2 \times 1V$
Now, as we move further the $9V$ battery has negative terminal at left so the potential will be $ - 9V$
Then we have $2\Omega $ resistance, the drop of potential will be current multiplied by resistance $ - 2 \times 2 = - 4V$
The $3V$ battery has positive terminal towards left so it will be taken as positive
Next $3\Omega $ resistance will lead to potential drop of $ - 3 \times 2 = - 6V$
As a result, the potential difference across A & B ${V_{AB}}$ will be given as:
${V_{AB}} = 2 \times 1 - 9 + 2 \times 2 + 3 + 3 \times 2$
$ \Rightarrow {V_{AB}} = 6\,V$
The potential difference is of $6\,V$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
For this question, there is potential drop across resistances. Be careful while observing the positive and negative terminal of the battery.
The potential drop across resistance is the multiplication of the current flowing through the resistance with the resistance. The value of this is taken to be negative which indicates drop in potential.
Complete step by step answer:
Kirchhoff gave two laws for any closed circuit; Kirchhoff’s current law and Kirchhoff’s voltage law. Kirchhoff's voltage law states that the sum of all the voltages around any closed loop in a circuit must equal zero.
In the given problem, the direction of the flow of current is given. The current is flowing from left to right as shown in the diagram above. Now, we will calculate the potential drops while moving from point A to point B. This will be given as:
As we cross the first resistance of $1\Omega $ there will be drop in voltage which will be current multiplied by resistance given as $ - 2 \times 1V$
Now, as we move further the $9V$ battery has negative terminal at left so the potential will be $ - 9V$
Then we have $2\Omega $ resistance, the drop of potential will be current multiplied by resistance $ - 2 \times 2 = - 4V$
The $3V$ battery has positive terminal towards left so it will be taken as positive
Next $3\Omega $ resistance will lead to potential drop of $ - 3 \times 2 = - 6V$
As a result, the potential difference across A & B ${V_{AB}}$ will be given as:
${V_{AB}} = 2 \times 1 - 9 + 2 \times 2 + 3 + 3 \times 2$
$ \Rightarrow {V_{AB}} = 6\,V$
The potential difference is of $6\,V$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
For this question, there is potential drop across resistances. Be careful while observing the positive and negative terminal of the battery.
The potential drop across resistance is the multiplication of the current flowing through the resistance with the resistance. The value of this is taken to be negative which indicates drop in potential.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




