
The position and size of the image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed between the focus F and optical centre O are:
(A) On the same side of lens and enlarged
(B) On the same side of lens and diminished
(C) On opposite side of lens and enlarged
(D) On opposite side of lens and diminished
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint
When the observer looks at any object through a lens, the light rays travelling from that object incident at different points depending upon the location of the object. This location is also responsible for the apparent increase or decrease in size of the image visible to the observer.
Complete step by step answer
A convex lens is also known as a converging lens, as the parallel light rays from an object passing through it tend to converge at its principal focus. It is thicker in the middle as compared to its sides.
According to the question, we place the object between the optical centre O and the Focus of the lens F as shown below:
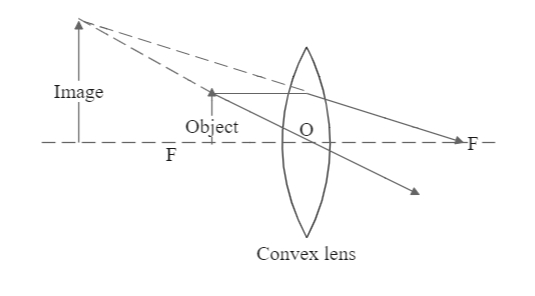
Now to understand the image formation in this alignment, we draw light rays coming out of the object parallel to the principal axis. As the object is very close to the lens, this light ray gets refracted inside the lens and converges on the focus on the other side. Another light ray from the same point of the object will travel straight through the optical centre without any refraction. We can see that these two lines are divergent in nature. To find the point of image formation, we need to find the place where they converge.
So, we extend them backwards and see that they meet at a point on the same side of the lens as the object. We can also see that this enlarges the image as compared to the original size.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note
The converging convex lens, and the diverging concave lens are readily used for correcting eyesight. The convex lens is used for correcting far-sightedness or hypermetropia, while the concave lens is used for correcting short-sightedness or myopia.
When the observer looks at any object through a lens, the light rays travelling from that object incident at different points depending upon the location of the object. This location is also responsible for the apparent increase or decrease in size of the image visible to the observer.
Complete step by step answer
A convex lens is also known as a converging lens, as the parallel light rays from an object passing through it tend to converge at its principal focus. It is thicker in the middle as compared to its sides.
According to the question, we place the object between the optical centre O and the Focus of the lens F as shown below:

Now to understand the image formation in this alignment, we draw light rays coming out of the object parallel to the principal axis. As the object is very close to the lens, this light ray gets refracted inside the lens and converges on the focus on the other side. Another light ray from the same point of the object will travel straight through the optical centre without any refraction. We can see that these two lines are divergent in nature. To find the point of image formation, we need to find the place where they converge.
So, we extend them backwards and see that they meet at a point on the same side of the lens as the object. We can also see that this enlarges the image as compared to the original size.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note
The converging convex lens, and the diverging concave lens are readily used for correcting eyesight. The convex lens is used for correcting far-sightedness or hypermetropia, while the concave lens is used for correcting short-sightedness or myopia.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




