
The point $\left( 12,-5 \right)$ is on the terminal side of an angle in standard position, how do you determine the exact values of the trigonometric functions of the angle ?
Answer
541.8k+ views
Hint: For these kinds of questions, we need to use the definitions of all the six trigonometric functions. First we mark the point given to us. Then we construct the triangle with the given specifications. And then we locate the position of $\theta $ according to the question. Thereafter, we use the definitions of the trigonometric ratios or functions to find out their values. We should be very careful with the sign of their values.
Complete step by step answer:
In trigonometry, angles are always measured taking the $x$- axis as the initial line and in counter-clockwise direction.
If not mentioned, the vertex is always taken to be the origin and one side is always taken on the positive $x$- axis. This side or sometimes ray is called the initial side of the angle as we measure our angle starting from here. An angle can be represented with two sides. Angle is nothing but the space between them.
We already have only one side. Now the other side is called the terminal side. And this positioning of the angle is called the standard position.
So in this question, we are given the point where the terminal side terminates.
Now let us construct a triangle $\Delta ABC$ whose vertex is at the origin and the other side terminates at $\left( 12,-5 \right)$.
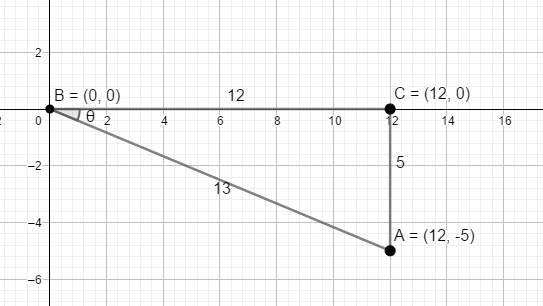
As we can see, $\angle ABC=\theta $.
We know the length of the sides from the question. They are $AC=5,BC=12$ .
From this we calculate the length of the side $AB$ using Pythagoras Theorem.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}={{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AC \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}=144+25 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}=169 \\
& \Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{169}=13 \\
\end{align}$
Now let us calculate the trigonometric ratios.
$\sin \theta = \dfrac{opposite}{hypotenuse}=\dfrac{-5}{13}$
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{adjacent}{hypotenuse}=\dfrac{12}{13}$
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{opposite}{adjacent}=\dfrac{-5}{12}$
$\cot \theta = \dfrac{adjacent}{opposite}=\dfrac{12}{-5}$
$\cos ec\theta = \dfrac{hypotenuse}{opposite}=\dfrac{13}{-5}$
$\sec \theta = \dfrac{hypotenuse}{adjacent}=\dfrac{13}{12}$
Note: We have to understand the technical terms in the question or else we cannot proceed forward. It is very important to remember the definitions of all the trigonometric functions so as to solve the question quickly. It is equally important to remember all the trigonometric identities and formulae. We should be aware of the signs each trigonometric function has in each quadrant. And write the value of each function accordingly or our answer would be wrong.
Complete step by step answer:
In trigonometry, angles are always measured taking the $x$- axis as the initial line and in counter-clockwise direction.
If not mentioned, the vertex is always taken to be the origin and one side is always taken on the positive $x$- axis. This side or sometimes ray is called the initial side of the angle as we measure our angle starting from here. An angle can be represented with two sides. Angle is nothing but the space between them.
We already have only one side. Now the other side is called the terminal side. And this positioning of the angle is called the standard position.
So in this question, we are given the point where the terminal side terminates.
Now let us construct a triangle $\Delta ABC$ whose vertex is at the origin and the other side terminates at $\left( 12,-5 \right)$.

As we can see, $\angle ABC=\theta $.
We know the length of the sides from the question. They are $AC=5,BC=12$ .
From this we calculate the length of the side $AB$ using Pythagoras Theorem.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}={{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AC \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}=144+25 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}=169 \\
& \Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{169}=13 \\
\end{align}$
Now let us calculate the trigonometric ratios.
$\sin \theta = \dfrac{opposite}{hypotenuse}=\dfrac{-5}{13}$
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{adjacent}{hypotenuse}=\dfrac{12}{13}$
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{opposite}{adjacent}=\dfrac{-5}{12}$
$\cot \theta = \dfrac{adjacent}{opposite}=\dfrac{12}{-5}$
$\cos ec\theta = \dfrac{hypotenuse}{opposite}=\dfrac{13}{-5}$
$\sec \theta = \dfrac{hypotenuse}{adjacent}=\dfrac{13}{12}$
Note: We have to understand the technical terms in the question or else we cannot proceed forward. It is very important to remember the definitions of all the trigonometric functions so as to solve the question quickly. It is equally important to remember all the trigonometric identities and formulae. We should be aware of the signs each trigonometric function has in each quadrant. And write the value of each function accordingly or our answer would be wrong.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




