
The plot that depicts the behavior of the mean free time $\tau $ (Time between two successive collisions) for the molecules of an ideal gas as a function of temperature (T). Qualitatively, is: (Graphs are schematic and not drawn to scale)
A.
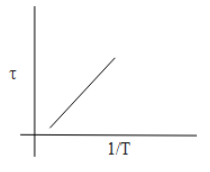
B.
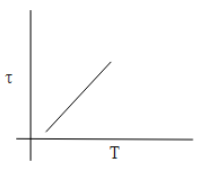
C.
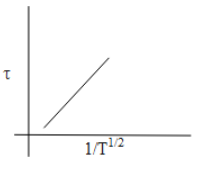
D.
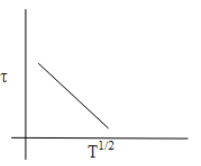


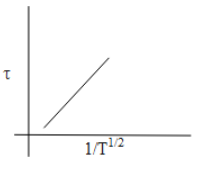
Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: The mean free time of a molecule is the average time between the collisions of successive collisions. For collision, the molecule has to cover a certain distance that is named as a mean free path. Materials in different states (solid, liquid, and gas) have different mean free path values
Complete step by step solution:
The mean free time of molecules is given by the ratio of the mean free path and average speed of the molecule. The mean free path of the molecule is the distance between the two molecules and the average speed is the ratio of the distance and time in which the molecule can cover that distance.
Mathematically,
$\tau =\dfrac{\sqrt{n}}{\sqrt{2\pi {{d}^{2}}}{{n}_{v}}\sqrt{T}}\quad ....\left( 1 \right)$
This can also be written as,
$\tau =\dfrac{k}{\sqrt{T}}$
So, if we consider $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{T}}$ as $x$ and $\tau $ as $y$. The above equation can be as,
$y=kx$
This is an equation of a straight.
From equation (1) we can say that the mean free time is directly proportional to $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{T}}$ .
$\tau \propto \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{T}}$
So as the value of $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{T}}$ increases the mean free time will also increase.
When we plot a graph of mean free time concerning the change in temperature will be as follows,
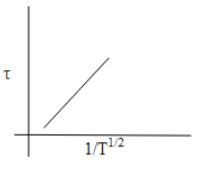
Thus, from the above discussion, we can say that the option which shows the correct graphical representation of mean free time concerning the increase in temperature is Option C.
Note:
The mean free path of the molecule is calculated by the product of mean free time and the average speed of the molecule. This concept is used for the study of the kinetic theory of gases to find coefficients such as velocity. In the case of gases, the mean free path of the can be quite large as compared to the liquid, and thus the mean free time can also be large.
Complete step by step solution:
The mean free time of molecules is given by the ratio of the mean free path and average speed of the molecule. The mean free path of the molecule is the distance between the two molecules and the average speed is the ratio of the distance and time in which the molecule can cover that distance.
Mathematically,
$\tau =\dfrac{\sqrt{n}}{\sqrt{2\pi {{d}^{2}}}{{n}_{v}}\sqrt{T}}\quad ....\left( 1 \right)$
This can also be written as,
$\tau =\dfrac{k}{\sqrt{T}}$
So, if we consider $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{T}}$ as $x$ and $\tau $ as $y$. The above equation can be as,
$y=kx$
This is an equation of a straight.
From equation (1) we can say that the mean free time is directly proportional to $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{T}}$ .
$\tau \propto \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{T}}$
So as the value of $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{T}}$ increases the mean free time will also increase.
When we plot a graph of mean free time concerning the change in temperature will be as follows,
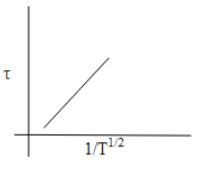
Thus, from the above discussion, we can say that the option which shows the correct graphical representation of mean free time concerning the increase in temperature is Option C.
Note:
The mean free path of the molecule is calculated by the product of mean free time and the average speed of the molecule. This concept is used for the study of the kinetic theory of gases to find coefficients such as velocity. In the case of gases, the mean free path of the can be quite large as compared to the liquid, and thus the mean free time can also be large.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




