
The $ p{K_{{a_1}}},p{K_{{a_2}}},p{K_{{a_3}}} $ values for the amino acid cysteine
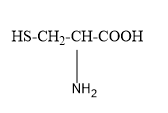
are respectively $ 1.8,8.3{\text{ and 10}}{\text{.8}} $ . What is the isoelectric point of cysteine amino acid?

Answer
511.8k+ views
Hint :Isoelectric point can be defined as that point or that pH at which there is no or overall zero charge on the amino acids. At an isoelectric point the molecule is electrically in a stable form as it has overall zero charge on it.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Generally, there are two $ p{K_a} $ values for the amino acids, one the $ p{K_{{a_1}}} $ for the carboxylic acid and other $ p{K_{{a_2}}} $ for the amine group. These $ p{K_a} $ values are determined by the protonation and the deprotonation of the carboxylic and the amine group in the solution at a particular ph.
So, generally isoelectric point is measure by taking the average mean of the two $ p{K_a} $ values i.e. $ p{K_{{a_1}}} $ and $ p{K_{{a_2}}} $ .
Thus the formula can be written as:
$ pI = \dfrac{{p{K_{{a_1}}} + p{K_{{a_2}}}}}{2} $
However, the amino acid cysteine is the exception to all the general amino acids, as the cysteine isoelectric point is determined by the $ p{K_a} $ values of the carboxylic group and the side chain group.
So, from the above discussion we are very clear which two $ p{K_a} $ values we have to consider while calculating the isoelectric point of the amino acid cysteine.
Thus, in the question, it is given,
$ p{K_{{a_1}}} $ $ = 1.8 $
$ p{K_{{a_2}}} $ $ = 8.3 $
$ p{K_{{a_3}}} = 10.8 $
Thus, the isoelectric point of amino acid cysteine is, $ pI = \dfrac{{p{K_{{a_2}}} + p{K_{{a_3}}}}}{2} $
$ pI = \dfrac{{8.3 + 10.8}}{2} $
$ pI = 8.85 $
Thus, the isoelectric point of cysteine amino acid is $ 8.85 $ .
Note :
Isoelectric point is of very significance in the laboratories as it is the point at which solubility of the amino acid is minimal. And also at this point the mobility in an electro-focussing system is zero, which means the amino acid will collect or precipitate at this isoelectric point.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Generally, there are two $ p{K_a} $ values for the amino acids, one the $ p{K_{{a_1}}} $ for the carboxylic acid and other $ p{K_{{a_2}}} $ for the amine group. These $ p{K_a} $ values are determined by the protonation and the deprotonation of the carboxylic and the amine group in the solution at a particular ph.
So, generally isoelectric point is measure by taking the average mean of the two $ p{K_a} $ values i.e. $ p{K_{{a_1}}} $ and $ p{K_{{a_2}}} $ .
Thus the formula can be written as:
$ pI = \dfrac{{p{K_{{a_1}}} + p{K_{{a_2}}}}}{2} $
However, the amino acid cysteine is the exception to all the general amino acids, as the cysteine isoelectric point is determined by the $ p{K_a} $ values of the carboxylic group and the side chain group.
So, from the above discussion we are very clear which two $ p{K_a} $ values we have to consider while calculating the isoelectric point of the amino acid cysteine.
Thus, in the question, it is given,
$ p{K_{{a_1}}} $ $ = 1.8 $
$ p{K_{{a_2}}} $ $ = 8.3 $
$ p{K_{{a_3}}} = 10.8 $
Thus, the isoelectric point of amino acid cysteine is, $ pI = \dfrac{{p{K_{{a_2}}} + p{K_{{a_3}}}}}{2} $
$ pI = \dfrac{{8.3 + 10.8}}{2} $
$ pI = 8.85 $
Thus, the isoelectric point of cysteine amino acid is $ 8.85 $ .
Note :
Isoelectric point is of very significance in the laboratories as it is the point at which solubility of the amino acid is minimal. And also at this point the mobility in an electro-focussing system is zero, which means the amino acid will collect or precipitate at this isoelectric point.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




