
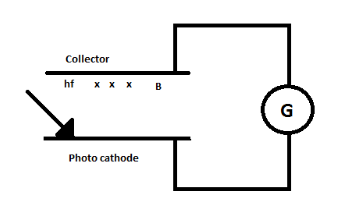
The photo cathode and collector plate are kept $ 10cm $ and connected through a galvanometer without a battery. A magnetic field $ B $ exists parallel to the plates. The work function of the emitter is $ 2.39eV $ and the light incident on it has wavelength $ 400 $ to $ 600nm $ . Find the minimum value of $ B $ so that the galvanometer shows null deflection.

Answer
539.4k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we are going to first consider the condition at which the galvanometer is going to show no deflection at all. After that, taking Einstein's equation, we are going to find the value of maximum kinetic energy, after which the value of the minimum magnetic field is found.
According to the Einstein’s equation,
$ \left( {KE} \right)\max = hf - \phi $
The radius for the revolution is given by
$ r = \dfrac{{mv}}{{qB}} $
Complete step by step solution:
The galvanometer will indicate zero deflection if the electrons complete the semi-circular path before reaching the plate $ P $ . The photoelectric effect is seen only for the wavelength $ 400nm $ .
Now, according to the Einstein’s equation,
$ \left( {KE} \right)\max = hf - \phi $
Where, $ hf $ is the energy and $ \phi $ is the work function of the emitter which is equal to $ 2.39eV $
Putting these in the equation above, we get
$ \left( {KE} \right)\max = 6.626 \times {10^{ - 34}} \times 400 \times {10^{ - 9}} - 2.39eV \\
\Rightarrow \left( {KE} \right)\max = 3.1eV - 2.39eV \\
\Rightarrow \left( {KE} \right)\max = 0.71eV \\ $
Now as we know that the radius for the revolution is given by
$ r = \dfrac{{mv}}{{qB}} $
Calculating the magnetic field from this, we get
$ B = \dfrac{{\sqrt {2 \times 9.1 \times {{10}^{ - 31}} \times 0.71 \times 1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}} }}{{1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}} \times 1}} \\
B = 2.842 \times {10^{ - 5}}T \\$
Thus, the minimum value of $ B $ for which the galvanometer shows no deflection is $ 2.842 \times {10^{ - 5}}T $.
Note:
The energy of the photons is given corresponding to the light of the wavelength $ 400nm $ and $ 600nm $ . The photoelectric emission is possible only with the wavelength $ {\lambda _1} $ . Photoelectrons experience magnetic force and move along a circular path and the zero deflection is seen when the electron is in the middle of the path.
According to the Einstein’s equation,
$ \left( {KE} \right)\max = hf - \phi $
The radius for the revolution is given by
$ r = \dfrac{{mv}}{{qB}} $
Complete step by step solution:
The galvanometer will indicate zero deflection if the electrons complete the semi-circular path before reaching the plate $ P $ . The photoelectric effect is seen only for the wavelength $ 400nm $ .
Now, according to the Einstein’s equation,
$ \left( {KE} \right)\max = hf - \phi $
Where, $ hf $ is the energy and $ \phi $ is the work function of the emitter which is equal to $ 2.39eV $
Putting these in the equation above, we get
$ \left( {KE} \right)\max = 6.626 \times {10^{ - 34}} \times 400 \times {10^{ - 9}} - 2.39eV \\
\Rightarrow \left( {KE} \right)\max = 3.1eV - 2.39eV \\
\Rightarrow \left( {KE} \right)\max = 0.71eV \\ $
Now as we know that the radius for the revolution is given by
$ r = \dfrac{{mv}}{{qB}} $
Calculating the magnetic field from this, we get
$ B = \dfrac{{\sqrt {2 \times 9.1 \times {{10}^{ - 31}} \times 0.71 \times 1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}} }}{{1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}} \times 1}} \\
B = 2.842 \times {10^{ - 5}}T \\$
Thus, the minimum value of $ B $ for which the galvanometer shows no deflection is $ 2.842 \times {10^{ - 5}}T $.
Note:
The energy of the photons is given corresponding to the light of the wavelength $ 400nm $ and $ 600nm $ . The photoelectric emission is possible only with the wavelength $ {\lambda _1} $ . Photoelectrons experience magnetic force and move along a circular path and the zero deflection is seen when the electron is in the middle of the path.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




