
The period of oscillation of a simple pendulum of length L suspended from the roof of a rocket acceleration upwards with a constant acceleration (g) is given by?
(A) Infinity
(B) Zero
(C) $2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{L}{{2g}}} $
(D) $2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{L}{g}} $
Answer
491.1k+ views
Hint: First we need to draw a free body diagram representing all the parameters required to solve this problem. Now by taking the rocket as the frame of reference we can find the effective acceleration acting on the pendulum which is acting downward. Now applying the time period formula we can find the solution to this problem.
Complete step by step answer:
As per the problem we know that a simple pendulum of length L suspended from the roof of a rocket accelerates upwards with a constant acceleration (g).
Now we need to find the time period of the simple pendulum.
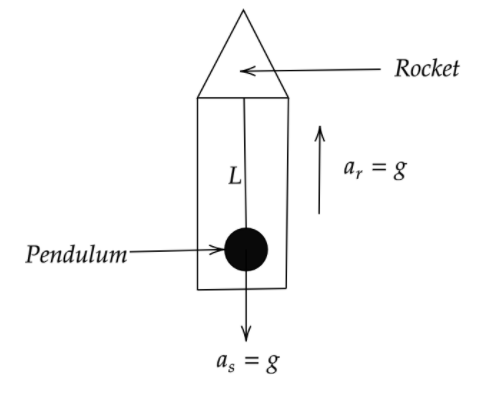
Here in this problem the rocket accelerates with a constant acceleration of g in the upward direction. From the figure we can say that a rocket is an acceleration frame of reference. As we know that Newton's law is not applicable in the acceleration frame of reference hence if we want to use Newton's law of motion in the acceleration frame of reference then we have to use a pseudo acceleration that is acting on the pendulum.
Since the rocket is accelerating in an upward direction same as that of the acceleration due to gravity and the pendulum bob experiences downward pseudo acceleration which is also equal to g.
Therefore the effective acceleration acting on the pendulum is equals to,
${a_{eff}} = {a_r} - {a_s}$
Where,
${a_{eff}}$ is the effective acceleration of the pendulum.
${a_r}$ is the acceleration due to the frame of reference that is g.
And ${a_s}$ is the pseudo acceleration that is –g.
Now putting the respective values we will get,
${a_{eff}} = g - \left( { - g} \right) = 2g$
We know the periodic time of a simple pendulum as,
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{L}{{{a_{eff}}}}} $
$ \Rightarrow T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{L}{{2g}}} $
Therefore the correct option is (C).
Note: Remember that here the pseudo force acting on the pendulum is opposite to the direction of acceleration of the frame of reference and the pseudo force or acceleration is always equal to the magnitude of the reference acceleration or force. Note that pseudo force or acceleration is an apparent force that acts on all the masses whose motion is described using a non-inertial frame of reference.
Complete step by step answer:
As per the problem we know that a simple pendulum of length L suspended from the roof of a rocket accelerates upwards with a constant acceleration (g).
Now we need to find the time period of the simple pendulum.

Here in this problem the rocket accelerates with a constant acceleration of g in the upward direction. From the figure we can say that a rocket is an acceleration frame of reference. As we know that Newton's law is not applicable in the acceleration frame of reference hence if we want to use Newton's law of motion in the acceleration frame of reference then we have to use a pseudo acceleration that is acting on the pendulum.
Since the rocket is accelerating in an upward direction same as that of the acceleration due to gravity and the pendulum bob experiences downward pseudo acceleration which is also equal to g.
Therefore the effective acceleration acting on the pendulum is equals to,
${a_{eff}} = {a_r} - {a_s}$
Where,
${a_{eff}}$ is the effective acceleration of the pendulum.
${a_r}$ is the acceleration due to the frame of reference that is g.
And ${a_s}$ is the pseudo acceleration that is –g.
Now putting the respective values we will get,
${a_{eff}} = g - \left( { - g} \right) = 2g$
We know the periodic time of a simple pendulum as,
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{L}{{{a_{eff}}}}} $
$ \Rightarrow T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{L}{{2g}}} $
Therefore the correct option is (C).
Note: Remember that here the pseudo force acting on the pendulum is opposite to the direction of acceleration of the frame of reference and the pseudo force or acceleration is always equal to the magnitude of the reference acceleration or force. Note that pseudo force or acceleration is an apparent force that acts on all the masses whose motion is described using a non-inertial frame of reference.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




