
The perimeter of an isosceles triangle is equal to 14cm. The ratio of the lateral side to the base is 5:4. The area of the triangle is
[a] $\dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt{21}c{{m}^{2}}$
[b] $\dfrac{3}{2}\sqrt{21}c{{m}^{2}}$
[c] $\sqrt{21}c{{m}^{2}}$
[d] $2\sqrt{21}c{{m}^{2}}$
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: Assume that the base is of length x centimetres. Use the fact that the ratio of the lateral side to the base is 5:4 to find the length of the lateral side in terms of x. Use the fact that the perimeter of a triangle is the sum of its sides and hence find the perimeter of the triangle in terms of x. Equate this expression to 14 and hence find the value of x and hence the length of the sides of the triangle. Use heron's formula, i.e. $\Delta =\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}$, where the symbols have their usual meanings to find the area of the triangle.
Complete step by step solution:
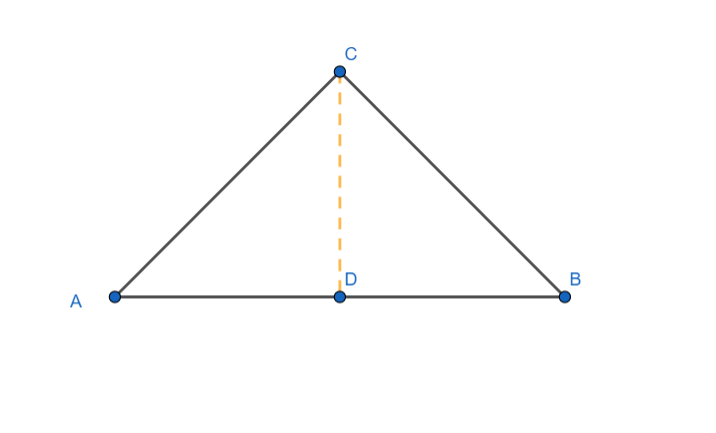
Given: ABC is an isosceles triangle with AC = BC. The perimeter of the triangle is 14cm and AC: AB = 5:4
To determine: Area of the triangle ABC.
Construction: Draw CD perpendicular to AB
Let AB = x centimeters.
Now, we have
AC:AB = 5:4.
Since in a proportion product of means is equal to the product of extremes, we have
4AC = 5AB
Hence, we have
4AC = 5x
Dividing both sides by 4, we get
$AC=\dfrac{5}{4}x$
Now, we have the perimeter of ABC= AB+BC+AC $=x+\dfrac{5x}{4}+\dfrac{5x}{4}=\dfrac{4x+5x+5x}{4}=\dfrac{7x}{2}$
But given that the perimeter is 14cm.
Hence, we have
$\dfrac{7x}{2}=14$
Multiplying by 2 on both sides, we get
7x= 28
Dividing by 7 on both sides, we get
x = 4cm.
Hence the length of the base AB = 4cm.
Hence, we have
$AC=BC=\dfrac{5x}{4}=5cm$
Since ABC is an isosceles triangle with AC = BC and CD is the altitude on the base, we have AD = BD
Hence, we have
AD = 2cm.
We know that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other sides.
Hence, in triangle ADC, we have
$A{{D}^{2}}+D{{C}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}$
Substituting DC = 2 and AC = 5, we get
$C{{D}^{2}}+4=25$
Subtracting 4 on both sides, we get
$C{{D}^{2}}=21$
Hence, we have
$CD=\sqrt{21}$
We know that the area of a triangle is equal to half the product of base and height.
Hence, we have
$ar\left( \Delta ABC \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}CD\times AB=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \sqrt{21}\times 4=2\sqrt{21}$ square centimetres.
Hence option [d] is correct.
Note: Alternative solution: Using heron's formula:
We can also find the area using heron’ s formula.
Here, in triangle ABC, we have
a = 5cm, b = 5cm and c = 4cm
Hence, we have
$s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}=\dfrac{5+5+4}{2}=7$
We know by heron's formula
$\Delta =\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}$
Hence, we have
$ar\left( \Delta ABC \right)=\sqrt{7\left( 7-5 \right)\left( 7-5 \right)\left( 7-3 \right)}=2\sqrt{21}$, which is the same as obtained above
Hence option [d] is correct.
Complete step by step solution:

Given: ABC is an isosceles triangle with AC = BC. The perimeter of the triangle is 14cm and AC: AB = 5:4
To determine: Area of the triangle ABC.
Construction: Draw CD perpendicular to AB
Let AB = x centimeters.
Now, we have
AC:AB = 5:4.
Since in a proportion product of means is equal to the product of extremes, we have
4AC = 5AB
Hence, we have
4AC = 5x
Dividing both sides by 4, we get
$AC=\dfrac{5}{4}x$
Now, we have the perimeter of ABC= AB+BC+AC $=x+\dfrac{5x}{4}+\dfrac{5x}{4}=\dfrac{4x+5x+5x}{4}=\dfrac{7x}{2}$
But given that the perimeter is 14cm.
Hence, we have
$\dfrac{7x}{2}=14$
Multiplying by 2 on both sides, we get
7x= 28
Dividing by 7 on both sides, we get
x = 4cm.
Hence the length of the base AB = 4cm.
Hence, we have
$AC=BC=\dfrac{5x}{4}=5cm$
Since ABC is an isosceles triangle with AC = BC and CD is the altitude on the base, we have AD = BD
Hence, we have
AD = 2cm.
We know that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other sides.
Hence, in triangle ADC, we have
$A{{D}^{2}}+D{{C}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}$
Substituting DC = 2 and AC = 5, we get
$C{{D}^{2}}+4=25$
Subtracting 4 on both sides, we get
$C{{D}^{2}}=21$
Hence, we have
$CD=\sqrt{21}$
We know that the area of a triangle is equal to half the product of base and height.
Hence, we have
$ar\left( \Delta ABC \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}CD\times AB=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \sqrt{21}\times 4=2\sqrt{21}$ square centimetres.
Hence option [d] is correct.
Note: Alternative solution: Using heron's formula:
We can also find the area using heron’ s formula.
Here, in triangle ABC, we have
a = 5cm, b = 5cm and c = 4cm
Hence, we have
$s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}=\dfrac{5+5+4}{2}=7$
We know by heron's formula
$\Delta =\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}$
Hence, we have
$ar\left( \Delta ABC \right)=\sqrt{7\left( 7-5 \right)\left( 7-5 \right)\left( 7-3 \right)}=2\sqrt{21}$, which is the same as obtained above
Hence option [d] is correct.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




