
The parallelism condition for two straight lines one of which is specified by the equation $ax+by+c=0$ the other being represented parametrically by $x=\alpha t+\beta ,y=\gamma t+\delta $ is given by
(a) $\alpha \gamma -b\alpha =0,\beta =\delta =c=0$
(b) $a\alpha -b\gamma =0,\beta =\delta =0$
(c) $a\alpha +b\gamma =0$
(d) $a\gamma =b\alpha =0$
Answer
632.1k+ views
Hint: Use parametric equations to find the straight line. Take the slope of both equations to form the required equation.
Given lines are $ax+by+c=0.................\left( 1 \right)$
$x=\alpha t+\beta ................\left( 2 \right)$
$y=\gamma t+\delta .............\left( 3 \right)$
One of the straight line specified is $ax+bx+c=0$
We have to find other straight line by using the equation (2) and (3)
So as to complete the parallelism condition; By cross multiplying:
$\begin{align}
& x=\alpha t+\beta \\
& y=\gamma t+\delta \\
& \dfrac{x}{y}=\dfrac{\alpha t+\beta }{\gamma t+\delta } \\
& \Rightarrow x\left( \gamma t+\delta \right)=y\left( \alpha t+\beta \right) \\
\end{align}$
Divide throughout by $t$
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{x\left( \gamma t+\delta \right)}{t}=\dfrac{y\left( \alpha t+\beta \right)}{t} \\
& \Rightarrow \gamma \alpha +\dfrac{\delta x}{t}=\alpha y+\dfrac{\beta y}{t} \\
\end{align}\]
$\Rightarrow \left( \gamma x-\alpha y \right)+\left( \dfrac{\delta x}{t}-\dfrac{\beta y}{t} \right)=0...................\left( 4 \right)$
Slope ${{m}_{1}}=\alpha =\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{b}_{1}}}=\dfrac{x}{t},$ for equation (1)
Slope ${{m}_{2}}=\gamma =\dfrac{{{a}_{2}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{y}{t}$ , for equation (2)
Substituting the slope on equation (4)
${{\gamma }_{x}}-\alpha y+\alpha \delta -\gamma \beta =0...............\left( 5 \right)$
The equation (5) is the 2nd straight line to fulfil parallelism condition.
$ax+by+c=0$
$\gamma x-\alpha y+\alpha \delta -\gamma \beta =0$ (Equation 5)
$\therefore $ The required equation is found from the slope of the equation.
From this by considering that the slope of both the equations are similar i.e., now comparing the common equation and equation (5).
$\begin{align}
& ax+by+c=0 \\
& \gamma x-\alpha y+\alpha \delta -\gamma \beta \\
& here\text{ }{{\text{a}}_{1}}=a\text{ }{{\text{a}}_{2}}=\gamma \\
& \text{ }{{\text{b}}_{1}}=a\text{ }{{\text{b}}_{2}}=\alpha \text{ } \\
\end{align}$
We can consider that
\[\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}\Rightarrow \dfrac{a}{\gamma }=\dfrac{b}{-\alpha }\]
Now cross multiplying them we get,
\[-a\alpha =b\gamma \Rightarrow a\alpha +b\gamma =0\]
Thus we received the required equation.
So option C is correct.
Note: The slope of a line characterizes the direction of a line. In this question it is important to find the slope to fulfil the conditions of parallelism.
To find the slope, you need to divide the difference of $y$-coordinate of two points on a line by the difference of the $x$-coordinate of those same two points.
$\therefore slope=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}$
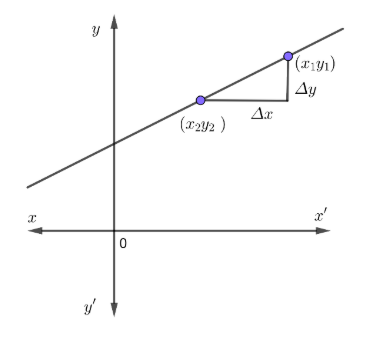
Or, slope can be found also using
$\Delta $ Notation,
$y$-coordinate $=\Delta y$
$x$-coordinate $=\Delta x$
$\therefore slope=\dfrac{\Delta y}{\Delta x}$
$\dfrac{\Delta y}{\Delta x}=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}=$slope of line
Given lines are $ax+by+c=0.................\left( 1 \right)$
$x=\alpha t+\beta ................\left( 2 \right)$
$y=\gamma t+\delta .............\left( 3 \right)$
One of the straight line specified is $ax+bx+c=0$
We have to find other straight line by using the equation (2) and (3)
So as to complete the parallelism condition; By cross multiplying:
$\begin{align}
& x=\alpha t+\beta \\
& y=\gamma t+\delta \\
& \dfrac{x}{y}=\dfrac{\alpha t+\beta }{\gamma t+\delta } \\
& \Rightarrow x\left( \gamma t+\delta \right)=y\left( \alpha t+\beta \right) \\
\end{align}$
Divide throughout by $t$
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{x\left( \gamma t+\delta \right)}{t}=\dfrac{y\left( \alpha t+\beta \right)}{t} \\
& \Rightarrow \gamma \alpha +\dfrac{\delta x}{t}=\alpha y+\dfrac{\beta y}{t} \\
\end{align}\]
$\Rightarrow \left( \gamma x-\alpha y \right)+\left( \dfrac{\delta x}{t}-\dfrac{\beta y}{t} \right)=0...................\left( 4 \right)$
Slope ${{m}_{1}}=\alpha =\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{b}_{1}}}=\dfrac{x}{t},$ for equation (1)
Slope ${{m}_{2}}=\gamma =\dfrac{{{a}_{2}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{y}{t}$ , for equation (2)
Substituting the slope on equation (4)
${{\gamma }_{x}}-\alpha y+\alpha \delta -\gamma \beta =0...............\left( 5 \right)$
The equation (5) is the 2nd straight line to fulfil parallelism condition.
$ax+by+c=0$
$\gamma x-\alpha y+\alpha \delta -\gamma \beta =0$ (Equation 5)
$\therefore $ The required equation is found from the slope of the equation.
From this by considering that the slope of both the equations are similar i.e., now comparing the common equation and equation (5).
$\begin{align}
& ax+by+c=0 \\
& \gamma x-\alpha y+\alpha \delta -\gamma \beta \\
& here\text{ }{{\text{a}}_{1}}=a\text{ }{{\text{a}}_{2}}=\gamma \\
& \text{ }{{\text{b}}_{1}}=a\text{ }{{\text{b}}_{2}}=\alpha \text{ } \\
\end{align}$
We can consider that
\[\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}\Rightarrow \dfrac{a}{\gamma }=\dfrac{b}{-\alpha }\]
Now cross multiplying them we get,
\[-a\alpha =b\gamma \Rightarrow a\alpha +b\gamma =0\]
Thus we received the required equation.
So option C is correct.
Note: The slope of a line characterizes the direction of a line. In this question it is important to find the slope to fulfil the conditions of parallelism.
To find the slope, you need to divide the difference of $y$-coordinate of two points on a line by the difference of the $x$-coordinate of those same two points.
$\therefore slope=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}$

Or, slope can be found also using
$\Delta $ Notation,
$y$-coordinate $=\Delta y$
$x$-coordinate $=\Delta x$
$\therefore slope=\dfrac{\Delta y}{\Delta x}$
$\dfrac{\Delta y}{\Delta x}=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}=$slope of line
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




