
The pair(s) of reagents that yield paramagnetic species is/are :
a.) Na and excess of $N{H_3}$
b.) K and excess of ${O_2}$
c.) Cu and dilute $HN{O_3}$
d.) ${O_2}$ and 2 - ethylanthraquinone
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The species in the options combine to give products. Most of these form the products that have unpaired electrons and are paramagnetic. The aromatic system gives hydrogen peroxide which is diamagnetic in nature. The metals given in above options produce species with unpaired electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
First, let us know about paramagnetic species. These are those species that have unpaired electrons. Now, let us see the options given-
The first option is Na and excess of $N{H_3}$. The Na ion in the liquid ammonia forms solvated electrons. These are unpaired. So, it is paramagnetic.
The second option is K and excess of ${O_2}$. This combination gives superoxide $K{O_2}$. This superoxide has $O_2^ - $ ion which has one unpaired electron. Thus, it is also paramagnetic.
The third option is Cu and dilute $HN{O_3}$. The Cu reacts with nitric acid ($HN{O_3}$) to form cupric nitrate. This cupric nitrate has Copper in +2 oxidation state with one unpaired electron along with NO. So, even these reagents are paramagnetic in nature. The reaction can be given as -
$3Cu + 8HN{O_3}(dil) \to 3Cu{(N{O_3})_2} + 4{H_2}O + 2NO$
The fourth and the last option is ${O_2}$ and 2 - ethyl anthraquinone. This reaction can be written as-
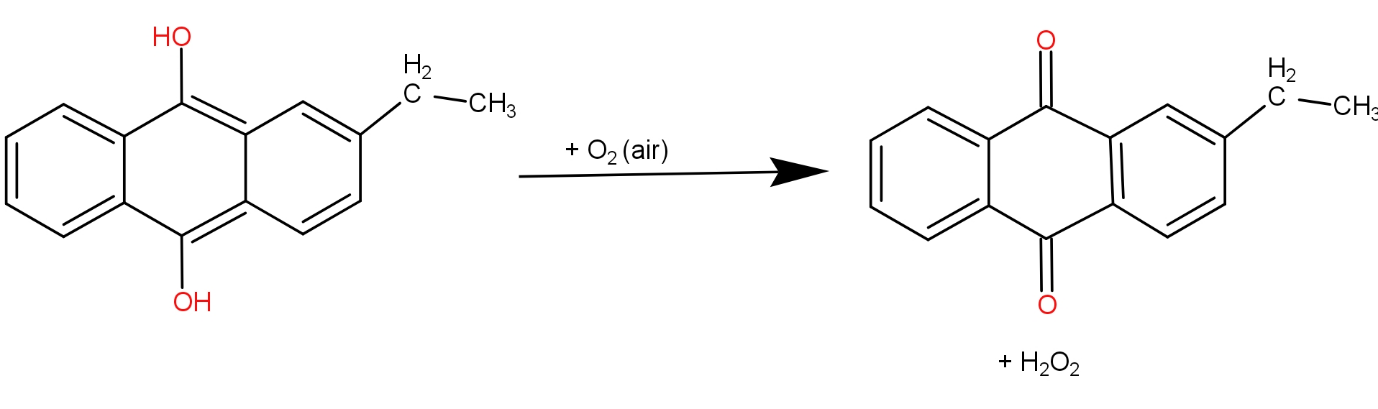
The hydrogen peroxide produced here does not have any unpaired electron. So, it is diamagnetic.
So, the correct answer is “Option A, B and C”.
Note: It must be noted that due to presence of unpaired electrons, the magnetic moment value comes out to be non-zero. These species show colours due to the presence of unpaired electrons that can get excited.
The unpaired electrons in solvated Na and ammonia can also conduct electricity.
Complete step by step answer:
First, let us know about paramagnetic species. These are those species that have unpaired electrons. Now, let us see the options given-
The first option is Na and excess of $N{H_3}$. The Na ion in the liquid ammonia forms solvated electrons. These are unpaired. So, it is paramagnetic.
The second option is K and excess of ${O_2}$. This combination gives superoxide $K{O_2}$. This superoxide has $O_2^ - $ ion which has one unpaired electron. Thus, it is also paramagnetic.
The third option is Cu and dilute $HN{O_3}$. The Cu reacts with nitric acid ($HN{O_3}$) to form cupric nitrate. This cupric nitrate has Copper in +2 oxidation state with one unpaired electron along with NO. So, even these reagents are paramagnetic in nature. The reaction can be given as -
$3Cu + 8HN{O_3}(dil) \to 3Cu{(N{O_3})_2} + 4{H_2}O + 2NO$
The fourth and the last option is ${O_2}$ and 2 - ethyl anthraquinone. This reaction can be written as-

The hydrogen peroxide produced here does not have any unpaired electron. So, it is diamagnetic.
So, the correct answer is “Option A, B and C”.
Note: It must be noted that due to presence of unpaired electrons, the magnetic moment value comes out to be non-zero. These species show colours due to the presence of unpaired electrons that can get excited.
The unpaired electrons in solvated Na and ammonia can also conduct electricity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




