
The other name of glycolysis is
(a) EMP-pathway
(b) TCA-pathway
(c) HMS-pathway
(d) Carbon -pathway
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: The other name of glycolysis is associated with the name of its discoverers that is Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas.
Complete step by step answer:
The other name of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP) pathway because it was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. The glycolysis is a metallic pathway that converts glucose into two molecules of pyruvate through a series of reactions. This results in the production of ATP and NADH in a small amount during the reactions. This pathway occurs under aerobic conditions.
Additional Information:
Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
In the first step of glycolysis phosphorylation of glucose is done by ATP in the presence of catalyst enzyme hexokinase to form glucose 6-phosphate.
In the second step of glycolysis isomerization of glucose, 6-phosphate is done to fructose 6-phosphate in the presence of catalyst enzyme phosphoglucose isomerase. (Here 6 membered pyranose is converted into five-membered furanose and also aldose is converted into ketose.)
In the third step of glycolysis phosphorylation of fructose 6-phosphate is done to form fructose 1,6-bisphosphate in the presence of catalyst enzyme phosphofructokinase.
Till the third step of glycolysis, no energy is produced or generated in the form of ATP. In the next step of glycolysis cleavage of the fructose 1,6 -bisphosphate (6-carbon unit) is done to three carbon units i.e., dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. The reaction was catalyzed by the enzyme aldolase.
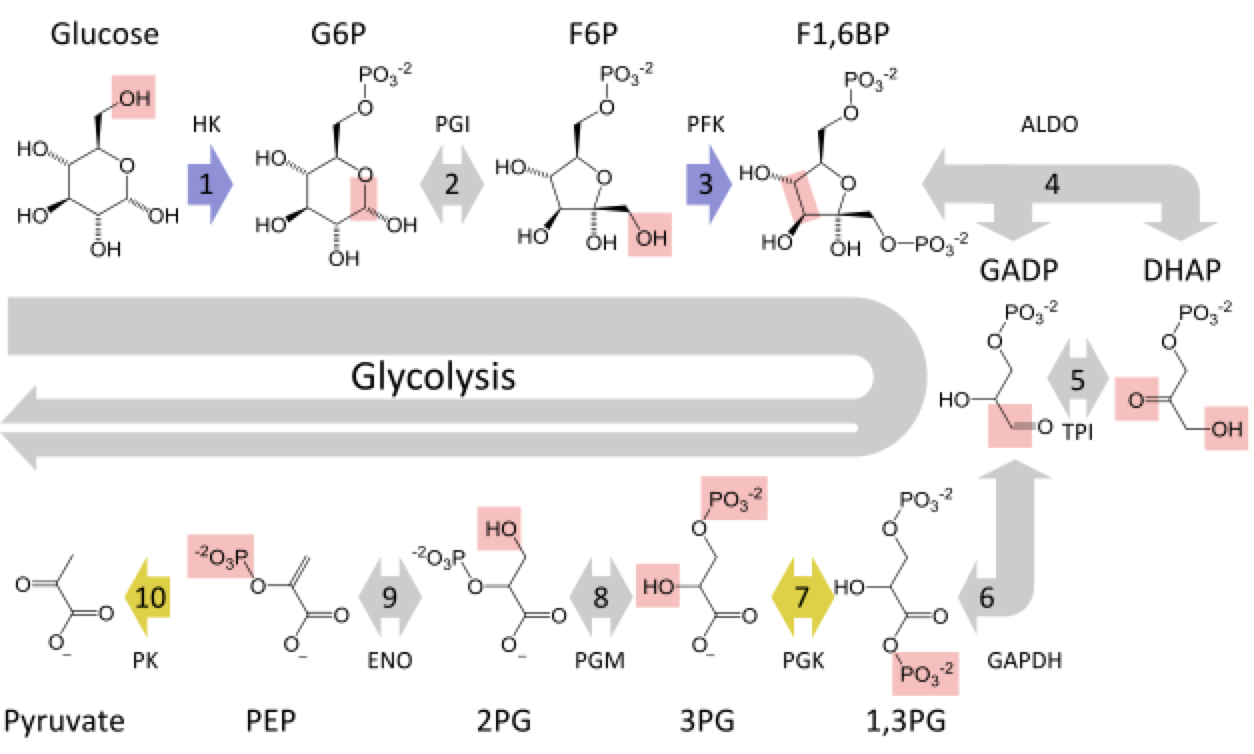
The glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate will continue in this glycolytic pathway but the dihydroxyacetone phosphate has to be converted into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to continue on this pathway. This conversion will be done by the isomerization process in the presence of catalyst enzyme triose phosphate isomerase.
In the next step, 1,3-biphosphoglycerate has formed from glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate by the action of enzyme glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, here NAD+ will serve as the electron acceptor.
Then by the action of enzyme phosphoglycerate kinase, 1,3-biphosphoglycerate is used to produce ATP from ADP and also of NADH.
The final step of glycolysis involves the formation of pyruvate and more molecules of ATP in the presence of enzyme pyruvate kinase. This is accomplished by rearrangement of 3-phosphoglycerate to 2-phosphoglycerate.
So, the correct answer is ’EMP-Pathway’.
Note:
- Glycolysis consists of a sequence of 10 chemical reactions.
- If enough oxygen is present the pyruvate enters into the tricarboxylic acid cycle or is fermented into lactic acid or ethanol if oxygen is absent.
- The dihydroxyacetone phosphate has to go through an isomerization process in the presence of catalyst enzyme triose phosphate isomerase to be converted into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
- Glycolysis produces both ATP for cellular energy requirements and building blocks for the synthesis of other cellular products.
Complete step by step answer:
The other name of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP) pathway because it was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. The glycolysis is a metallic pathway that converts glucose into two molecules of pyruvate through a series of reactions. This results in the production of ATP and NADH in a small amount during the reactions. This pathway occurs under aerobic conditions.
Additional Information:
Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
In the first step of glycolysis phosphorylation of glucose is done by ATP in the presence of catalyst enzyme hexokinase to form glucose 6-phosphate.
In the second step of glycolysis isomerization of glucose, 6-phosphate is done to fructose 6-phosphate in the presence of catalyst enzyme phosphoglucose isomerase. (Here 6 membered pyranose is converted into five-membered furanose and also aldose is converted into ketose.)
In the third step of glycolysis phosphorylation of fructose 6-phosphate is done to form fructose 1,6-bisphosphate in the presence of catalyst enzyme phosphofructokinase.
Till the third step of glycolysis, no energy is produced or generated in the form of ATP. In the next step of glycolysis cleavage of the fructose 1,6 -bisphosphate (6-carbon unit) is done to three carbon units i.e., dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. The reaction was catalyzed by the enzyme aldolase.

The glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate will continue in this glycolytic pathway but the dihydroxyacetone phosphate has to be converted into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to continue on this pathway. This conversion will be done by the isomerization process in the presence of catalyst enzyme triose phosphate isomerase.
In the next step, 1,3-biphosphoglycerate has formed from glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate by the action of enzyme glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, here NAD+ will serve as the electron acceptor.
Then by the action of enzyme phosphoglycerate kinase, 1,3-biphosphoglycerate is used to produce ATP from ADP and also of NADH.
The final step of glycolysis involves the formation of pyruvate and more molecules of ATP in the presence of enzyme pyruvate kinase. This is accomplished by rearrangement of 3-phosphoglycerate to 2-phosphoglycerate.
So, the correct answer is ’EMP-Pathway’.
Note:
- Glycolysis consists of a sequence of 10 chemical reactions.
- If enough oxygen is present the pyruvate enters into the tricarboxylic acid cycle or is fermented into lactic acid or ethanol if oxygen is absent.
- The dihydroxyacetone phosphate has to go through an isomerization process in the presence of catalyst enzyme triose phosphate isomerase to be converted into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
- Glycolysis produces both ATP for cellular energy requirements and building blocks for the synthesis of other cellular products.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




