
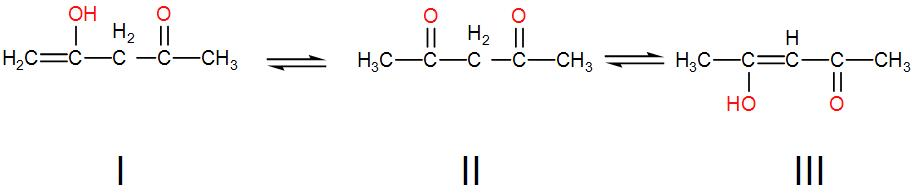
The order of stability of the following tautomeric compounds is:
[A] I > II > III
[B] III > II> I
[C] II > I > III
[D] II > III > I

Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Tautomerism is a kind of isomerism. In this, there is an interconversion between the two possible chemical forms of the same species. There are sometimes tautomers which are more stable than the other one but an equilibrium is maintained between the forms.
Complete step by step answer:
We can define tautomers as the structural isomers of chemical compounds which they readily interconvert into each other. Generally, it’s the proton that relocates and thus there exists equilibrium between the two forms.
We call this process of interconverting of protons as tautomerization and the species undergoing the process are called the tautomers.
Here in the given compound we have keto – enol tautomerism. In this tautomerism, a compounds containing ketone groups i.e. –CO can undergo enol formation i.e. –CO converts to –COH even though Keto forms are considered more stable.
Now, let us see the structures given to us one by one.
In the third tautomer we have conjugated double bonds which give extra stability so III is the most stable.
Among the first and second tautomers, the first tautomer is the enol form and the second is the keto form. We know that keto is more stable than enol tautomer so structure II is more stable than structure I.
We can understand from the above discussion that the order of stability is III > II > I.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: We should remember that tautomers are not similar to the canonical forms of resonance stabilised species. We can chemically distinguish tautomers and they can be identified by their different spectroscopic data. On the other hand resonance canonical structures do not physically exist and are just a hypothetical concept to understand theory of chemical compounds better.
Complete step by step answer:
We can define tautomers as the structural isomers of chemical compounds which they readily interconvert into each other. Generally, it’s the proton that relocates and thus there exists equilibrium between the two forms.
We call this process of interconverting of protons as tautomerization and the species undergoing the process are called the tautomers.
Here in the given compound we have keto – enol tautomerism. In this tautomerism, a compounds containing ketone groups i.e. –CO can undergo enol formation i.e. –CO converts to –COH even though Keto forms are considered more stable.
Now, let us see the structures given to us one by one.
In the third tautomer we have conjugated double bonds which give extra stability so III is the most stable.
Among the first and second tautomers, the first tautomer is the enol form and the second is the keto form. We know that keto is more stable than enol tautomer so structure II is more stable than structure I.
We can understand from the above discussion that the order of stability is III > II > I.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: We should remember that tautomers are not similar to the canonical forms of resonance stabilised species. We can chemically distinguish tautomers and they can be identified by their different spectroscopic data. On the other hand resonance canonical structures do not physically exist and are just a hypothetical concept to understand theory of chemical compounds better.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




