
The order of acidic strength of HOCl, \[HCl{O_2}\], \[HCl{O_3}\] and \[HCl{O_4}\] are:
(A) \[HCl{O_4}\] > \[HCl{O_3}\] > \[HCl{O_2}\] > HClO
(B) HClO > \[HCl{O_2}\] > \[HCl{O_3}\] > \[HCl{O_4}\]
(C) \[HCl{O_3}\] > \[HCl{O_4}\] > \[HCl{O_2}\] > HClO
(D) \[HCl{O_3}\] > \[HCl{O_2}\] > HClO > \[HCl{O_4}\]
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: .We can use the concept of stability of conjugate base of the particular acid in order to compare their acidic strength. We can say that more stable the conjugate base, more will be the acidic strength of the related acid. Conjugate base can be stabilized by effects like inductive effect and hyperconjugation.
Complete answer:
- To estimate the acidic strength of the given acids, we will need to draw the structures of all the given acids and then we will compare its acidity.
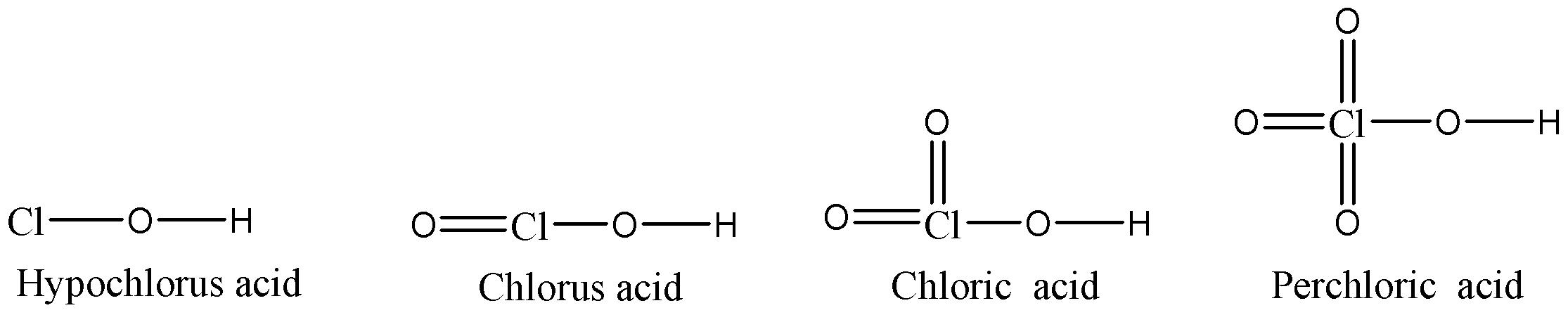
- We can see that chlorine atom in Hypochlorous acid only have any oxygen atom bonded with chlorine atom but Chlorous acid, Chloric acid and Perchloric acid have one, two and three oxygen atoms doubly bonded with chlorine atom respectively in addition to the singly bonded oxygen atom. These oxygen atoms that are doubly bonded with chlorine will withdraw the electron density from the chlorine atom because oxygen is more electronegative than chlorine.

We can see the conjugate bases that will be formed as the dissociation of hydrogen atoms will take place in aqueous medium. Now depending upon the stability of the conjugate bases, the stability of acids will be decided because as the conjugate base is more stable, it will be in dissociated state and allow to give protons which are responsible for the acidic character of the acid.
- In Hypochlorous acid, the negative charge on oxygen atom will not be stabilised by inductive effect as chlorine atoms do not have any substituents. So, this conjugate base will be the most unstable of them all and so that hypochlorous acid will be having the least acidic strength of them all.
- In Chlorous acid, Cl=O bond will withdraw the electron density from the negatively charged oxygen atom in the conjugate base, so the conjugate base will be more stable and hence the overall acidic strength of Chlorous acid will be more compared to Hypochlorous acid.
- Chloric acid has two Cl=O bonds, so the conjugate base of this acid will be more stable than the conjugate base of Chlorous acid because there will be two oxygen atoms withdrawing the electron density from the negatively charged oxygen atom. So, the acidic strength of Chloric acid will be more than Chlorous acid.
- Perchloric acid has three Cl=O bonds and hence three oxygen atoms will withdraw the electron density from the negatively charged oxygen atom, so in this case the conjugate base will be most stable. Hence we can say that the acidic strength of Perchloric acid will be the highest amongst all.
So, correct answer is (A) \[HCl{O_4}\] > \[HCl{O_3}\] > \[HCl{O_2}\] > HClO
Note: In order to compare the stability of conjugate bases of these acids, first we need to identify the structures of acid but in these cases, make sure that your imagined structure of the acid is proper and follows the rules of chemistry. One can have difficulty to assign structure as Cl-O bonds are rarely seen. Note that any acid that can donate a proton has a O-H single bond and only those protons are responsible for the acidity of acid.
Complete answer:
- To estimate the acidic strength of the given acids, we will need to draw the structures of all the given acids and then we will compare its acidity.

- We can see that chlorine atom in Hypochlorous acid only have any oxygen atom bonded with chlorine atom but Chlorous acid, Chloric acid and Perchloric acid have one, two and three oxygen atoms doubly bonded with chlorine atom respectively in addition to the singly bonded oxygen atom. These oxygen atoms that are doubly bonded with chlorine will withdraw the electron density from the chlorine atom because oxygen is more electronegative than chlorine.

We can see the conjugate bases that will be formed as the dissociation of hydrogen atoms will take place in aqueous medium. Now depending upon the stability of the conjugate bases, the stability of acids will be decided because as the conjugate base is more stable, it will be in dissociated state and allow to give protons which are responsible for the acidic character of the acid.
- In Hypochlorous acid, the negative charge on oxygen atom will not be stabilised by inductive effect as chlorine atoms do not have any substituents. So, this conjugate base will be the most unstable of them all and so that hypochlorous acid will be having the least acidic strength of them all.
- In Chlorous acid, Cl=O bond will withdraw the electron density from the negatively charged oxygen atom in the conjugate base, so the conjugate base will be more stable and hence the overall acidic strength of Chlorous acid will be more compared to Hypochlorous acid.
- Chloric acid has two Cl=O bonds, so the conjugate base of this acid will be more stable than the conjugate base of Chlorous acid because there will be two oxygen atoms withdrawing the electron density from the negatively charged oxygen atom. So, the acidic strength of Chloric acid will be more than Chlorous acid.
- Perchloric acid has three Cl=O bonds and hence three oxygen atoms will withdraw the electron density from the negatively charged oxygen atom, so in this case the conjugate base will be most stable. Hence we can say that the acidic strength of Perchloric acid will be the highest amongst all.
So, correct answer is (A) \[HCl{O_4}\] > \[HCl{O_3}\] > \[HCl{O_2}\] > HClO
Note: In order to compare the stability of conjugate bases of these acids, first we need to identify the structures of acid but in these cases, make sure that your imagined structure of the acid is proper and follows the rules of chemistry. One can have difficulty to assign structure as Cl-O bonds are rarely seen. Note that any acid that can donate a proton has a O-H single bond and only those protons are responsible for the acidity of acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




