
The optically inactive amino acid is
A) Lysine
B) Glycine
C) Arginine
D) Alanine
Answer
546.6k+ views
Hint:
To answer this question, you should recall the concept of optical isomerism. To identify resolvable and non-resolvable isomers you need to know about the presence of a chiral carbon and should not contain any symmetry.
Complete step by step solution:
For any chemical entity to be optically active it should have a chiral carbon and should not contain any symmetry. Resolving means conversion of an optically inactive compound to the optically active compound. Make sure you remember that meso compounds will never be resolved. Amino acids are very small biomolecules and exist naturally in a zwitterion state where the carboxylic acid moiety is ionized and the basic amino group is protonated. The entire class of amino acids has a common backbone of an organic carboxylic acid group and an amino group attached to a saturated carbon atom.
The structures of the aforementioned options can be drawn as:
A. Lysine
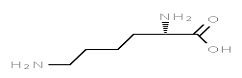
B. Glycine:
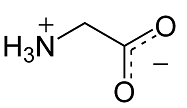
The simplest of all amino acids, Glycine which has \[H\] as a functional group lacks optical activity, as the saturated alpha carbon is unsubstituted.
C. Arginine:
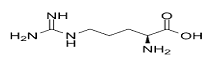
D. Alanine:
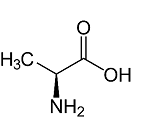
Therefore the correct answer to this question is option B.
Note:
Meso compounds will never be resolved. In general, a meso compound should contain two or more identical substituted stereocenters. This molecule also has an internal symmetry plane that divides the compound in half. These two halves reflect each other by the internal mirror. This results in the stereochemistry being cancelled out by the two stereocenters hence resulting in an optically inactive mixture. If A is a meso compound, it should have two or more stereocenters, an internal plane, and the stereochemistry should be R and S:
Look for an internal plane, or internal mirror, that lies in between the compound.
R cancels S out in a meso compound with two stereo centres making it optically inactive.
To answer this question, you should recall the concept of optical isomerism. To identify resolvable and non-resolvable isomers you need to know about the presence of a chiral carbon and should not contain any symmetry.
Complete step by step solution:
For any chemical entity to be optically active it should have a chiral carbon and should not contain any symmetry. Resolving means conversion of an optically inactive compound to the optically active compound. Make sure you remember that meso compounds will never be resolved. Amino acids are very small biomolecules and exist naturally in a zwitterion state where the carboxylic acid moiety is ionized and the basic amino group is protonated. The entire class of amino acids has a common backbone of an organic carboxylic acid group and an amino group attached to a saturated carbon atom.
The structures of the aforementioned options can be drawn as:
A. Lysine

B. Glycine:

The simplest of all amino acids, Glycine which has \[H\] as a functional group lacks optical activity, as the saturated alpha carbon is unsubstituted.
C. Arginine:

D. Alanine:

Therefore the correct answer to this question is option B.
Note:
Meso compounds will never be resolved. In general, a meso compound should contain two or more identical substituted stereocenters. This molecule also has an internal symmetry plane that divides the compound in half. These two halves reflect each other by the internal mirror. This results in the stereochemistry being cancelled out by the two stereocenters hence resulting in an optically inactive mixture. If A is a meso compound, it should have two or more stereocenters, an internal plane, and the stereochemistry should be R and S:
Look for an internal plane, or internal mirror, that lies in between the compound.
R cancels S out in a meso compound with two stereo centres making it optically inactive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




