
The number of tarsals per limb of human beings is
(a) 5
(b) 6
(c) 7
(d) 8
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: Tarsal is a bone-forming part of the ankle or heel. The number of tarsals per limb of a human being is a prime number. The number count is the same as the number that corresponds to the wonders of the world and the colors present in the rainbow.
Complete answer:
The tarsus is a grouping of seven articulated bones situated between the lower end of the tibia and the lower leg fibula and the metatarsus at each foot of the human body. It is composed of the midfoot (cuboid, medial, intermediate, and lateral cuneiform, and navicular) and hindfoot (talus and calcaneus).
The talus (astragalus) articulates with the lower leg bones to form the ankle joint. The other six tarsals act as a solid weight-bearing base, closely bound together by ligaments below the talus. The calcaneus is the biggest tarsal, or heel bone, which forms the prominence at the back of the foot. The remaining tarsals include the three cuneiforms, navicular and the cuboid. The cuboid and cuneiforms adjoin the bones of the metatarsal in a strong, almost immovable joint.
Additional Information: The tarsals of the upper limb refer to the carpal bones. In humans, the tarsals form a longitudinal arch in the foot in conjunction with the metatarsal bones, a shape well suited to bear and move weight in bipedal locomotion.
So, the correct answer is, ‘7’.
Note: The tarsus articulates with the metatarsus bones, which articulate in turn with the proximal phalanges of the toes. The joint between the tibia and fibula above and the tarsus underneath is called the ankle joint. The largest bone in the tarsus is the calcaneus in humans, which is the weight-bearing bone within the foot's heel. The foot bones provide the soft tissues with mechanical support; helping the foot to withstand the body's weight when standing and in motion.
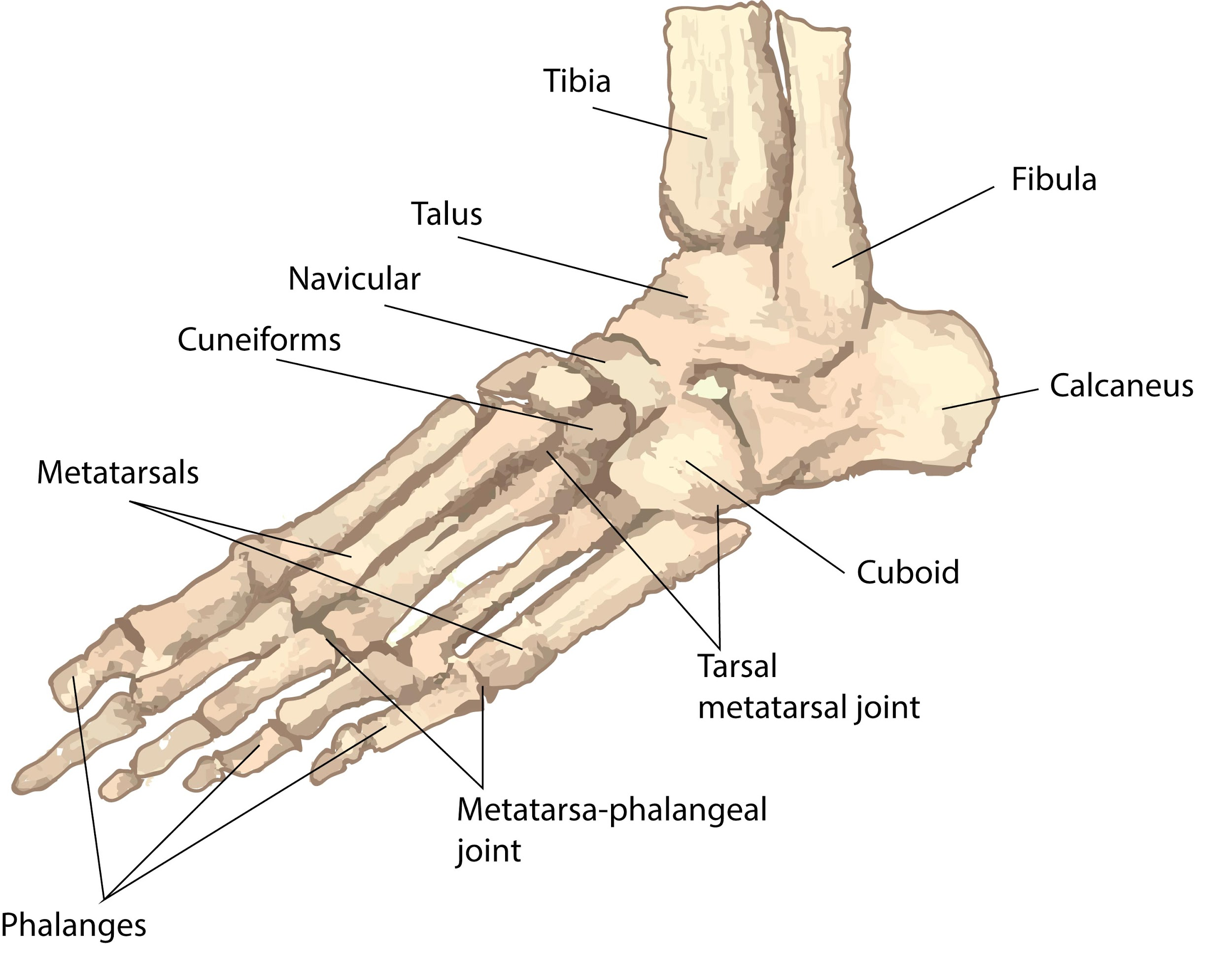
Complete answer:
The tarsus is a grouping of seven articulated bones situated between the lower end of the tibia and the lower leg fibula and the metatarsus at each foot of the human body. It is composed of the midfoot (cuboid, medial, intermediate, and lateral cuneiform, and navicular) and hindfoot (talus and calcaneus).
The talus (astragalus) articulates with the lower leg bones to form the ankle joint. The other six tarsals act as a solid weight-bearing base, closely bound together by ligaments below the talus. The calcaneus is the biggest tarsal, or heel bone, which forms the prominence at the back of the foot. The remaining tarsals include the three cuneiforms, navicular and the cuboid. The cuboid and cuneiforms adjoin the bones of the metatarsal in a strong, almost immovable joint.
Additional Information: The tarsals of the upper limb refer to the carpal bones. In humans, the tarsals form a longitudinal arch in the foot in conjunction with the metatarsal bones, a shape well suited to bear and move weight in bipedal locomotion.
So, the correct answer is, ‘7’.
Note: The tarsus articulates with the metatarsus bones, which articulate in turn with the proximal phalanges of the toes. The joint between the tibia and fibula above and the tarsus underneath is called the ankle joint. The largest bone in the tarsus is the calcaneus in humans, which is the weight-bearing bone within the foot's heel. The foot bones provide the soft tissues with mechanical support; helping the foot to withstand the body's weight when standing and in motion.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




