
The number of $${\text{pi }}$$-bonds and $${\text{sigma }}$$-bonds in the Lewis structure of $${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_3}$$ is:
A. $${\text{3sigma ,}}\;{\text{1pi }}$$
B. $${\text{3sigma ,}}\;{\text{2pi }}$$
C. $${\text{3sigma ,}}\;{\text{3pi }}$$
D. None of these
Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: In order to determine sigma $$\left( {\text{sigma }} \right)$$ and pi $$\left( {\text{pi }} \right)$$ bonds in a molecule, first draw its Lewis structure. Lewis structure gives a clear picture of types of bonds present in the molecule. Single bond represents one sigma bond and one double bond indicates one sigma and one pi bond.
Complete step by step solution:
A bond that is formed among two atoms by the overlapping of singly occupied orbitals along their axes (end to end overlap) is called sigma $$\left( {\text{sigma }} \right)$$ bond as shown below.
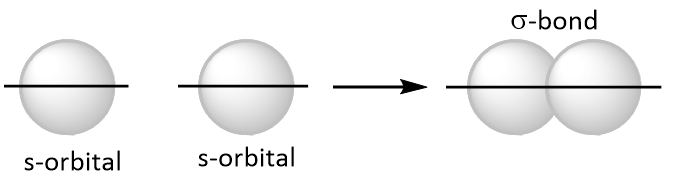
All single bonds are sigma bonds. Single bond is represented by a single line.
$$\left( {\text{pi }} \right)$$-bonds are produced by the sidewise or lateral overlapping of p-orbitals as shown below.
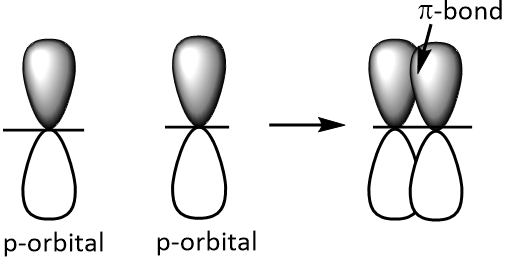
A double bond consists of one sigma and one pi bond. Double bonds are represented by double parallel lines while triple bonds are represented by triple parallel lines.
Lewis structure of $${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_3}$$ can be made by using total number of valence electrons needed by all atoms to attain noble gas configuration (complete octet).
In $${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_3}$$, there is one sulphur atom and three oxygen atoms. Thus the total number of valence electrons (V.E) can be calculated as follows:
$${\text{Total}}\;{\text{valence}}\;{\text{electrons}} = \left( {{\text{1}} \times {\text{V}}{\text{.E}}\;{\text{of}}\;{\text{S}}} \right) + \left( {{\text{3}} \times {\text{V}}{\text{.E}}\;{\text{of}}\;{\text{O}}} \right)$$
The atomic number of sulphur is 16 and its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 6. This shows that there are 6 electrons in the outermost shell. Thus the valence number of sulphur is 6. The atomic number of oxygen is 8 and its electronic configuration is 2, 6. This shows that there are 6 electrons in the outermost shell. Thus the valence number of oxygen is 6.
Hence the total number of valence electrons in $${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_3}$$ can be calculated as:
$$\displaylines{
{\text{Total}}\;{\text{valence}}\;{\text{electrons}} = \left( {1 \times 6} \right) + \left( {3 \times 6} \right) \cr
= 6 + 18 \cr
= 24 \cr} $$
This means that there are a total 24 valence electrons needed by all atoms to acquire noble gas configuration. On the basis of these valence electrons, Lewis structure can be made. When each atom acquires complete octet, Lewis structure of $${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$$ is ready as follows:
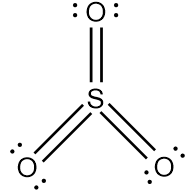
Since we know that single bonds represent one sigma bond and double bonds represent one sigma and one pi bond. Thus,
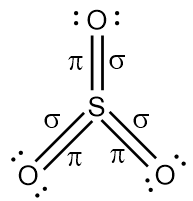
Therefore, there are total $${\text{3sigma }}$$(three sigma) and $${\text{3pi }}$$ (three pi) bonds.
Thus the correction option is C.
Note: Always remember that one double bond represents one sigma and one pi bond while one triple bond consists of one sigma and two pi bonds. Sigma bond is a strong bond while pi bond is a weak bond.
Complete step by step solution:
A bond that is formed among two atoms by the overlapping of singly occupied orbitals along their axes (end to end overlap) is called sigma $$\left( {\text{sigma }} \right)$$ bond as shown below.

All single bonds are sigma bonds. Single bond is represented by a single line.
$$\left( {\text{pi }} \right)$$-bonds are produced by the sidewise or lateral overlapping of p-orbitals as shown below.

A double bond consists of one sigma and one pi bond. Double bonds are represented by double parallel lines while triple bonds are represented by triple parallel lines.
Lewis structure of $${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_3}$$ can be made by using total number of valence electrons needed by all atoms to attain noble gas configuration (complete octet).
In $${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_3}$$, there is one sulphur atom and three oxygen atoms. Thus the total number of valence electrons (V.E) can be calculated as follows:
$${\text{Total}}\;{\text{valence}}\;{\text{electrons}} = \left( {{\text{1}} \times {\text{V}}{\text{.E}}\;{\text{of}}\;{\text{S}}} \right) + \left( {{\text{3}} \times {\text{V}}{\text{.E}}\;{\text{of}}\;{\text{O}}} \right)$$
The atomic number of sulphur is 16 and its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 6. This shows that there are 6 electrons in the outermost shell. Thus the valence number of sulphur is 6. The atomic number of oxygen is 8 and its electronic configuration is 2, 6. This shows that there are 6 electrons in the outermost shell. Thus the valence number of oxygen is 6.
Hence the total number of valence electrons in $${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_3}$$ can be calculated as:
$$\displaylines{
{\text{Total}}\;{\text{valence}}\;{\text{electrons}} = \left( {1 \times 6} \right) + \left( {3 \times 6} \right) \cr
= 6 + 18 \cr
= 24 \cr} $$
This means that there are a total 24 valence electrons needed by all atoms to acquire noble gas configuration. On the basis of these valence electrons, Lewis structure can be made. When each atom acquires complete octet, Lewis structure of $${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$$ is ready as follows:

Since we know that single bonds represent one sigma bond and double bonds represent one sigma and one pi bond. Thus,

Therefore, there are total $${\text{3sigma }}$$(three sigma) and $${\text{3pi }}$$ (three pi) bonds.
Thus the correction option is C.
Note: Always remember that one double bond represents one sigma and one pi bond while one triple bond consists of one sigma and two pi bonds. Sigma bond is a strong bond while pi bond is a weak bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




