
The number of linkage group(s) present in Escherichia coli is
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Four
(d) Seven
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: The linkage group is the presence of genes on a single chromosome.
Complete answer:
The total number of linkage groups in an organism equals the number of autosomes in its haploid cell. The total number of linkage groups in prokaryotes is one, this is because bacteria being prokaryotes have only a single circular chromosome.
Additional information:
1. Linkage of genes on a chromosome that is not altered and is inherited as such from generation to generation without any crossover.
2. In linkage, genes are closely associated and tend to remain together.
3. The number of linkage groups equals the number of chromosomes in the basic set. The number of linkage groups I’m an organism is equal to the haploid number of its chromosomes.
4. The linkage group is a set of genes at different loci on the same chromosome that except for crossing over tend to act as a single pair of genes in meiosis instead of undergoing independent assortment.
5. Linkage is of two types
Complete linkage - the genes located on the same chromosome do not separate and are inherited together over the generations due to the absence of crossing over.
Incomplete linkage – genes present in the same chromosome have a tendency to separate due to crossing over and hence produce recombinant progeny besides the parental type.
So, the correct answer is ‘One’.
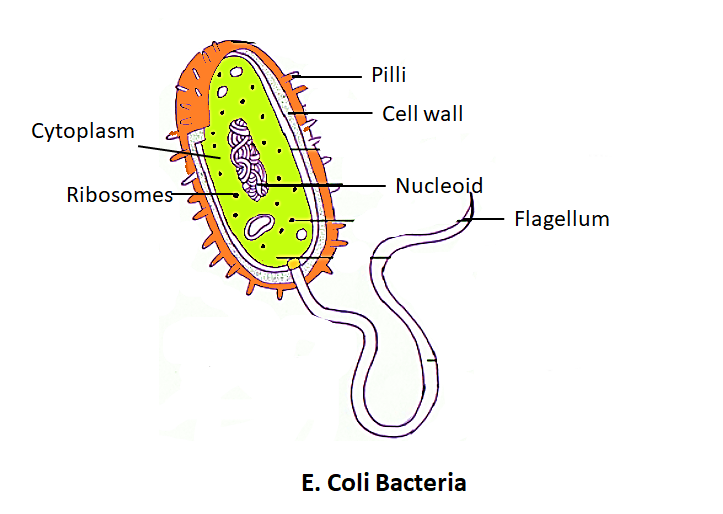
Note: Thomas Hunt Morgan expanded the idea of linkage after noticing that in some instances the observed rate of crossing over events differed from the expected rate of crossing over events. The unit of measurement describing the distance between two linkage groups is the Centimorgan and is named after T. H. Morgan.
Complete answer:
The total number of linkage groups in an organism equals the number of autosomes in its haploid cell. The total number of linkage groups in prokaryotes is one, this is because bacteria being prokaryotes have only a single circular chromosome.
Additional information:
1. Linkage of genes on a chromosome that is not altered and is inherited as such from generation to generation without any crossover.
2. In linkage, genes are closely associated and tend to remain together.
3. The number of linkage groups equals the number of chromosomes in the basic set. The number of linkage groups I’m an organism is equal to the haploid number of its chromosomes.
4. The linkage group is a set of genes at different loci on the same chromosome that except for crossing over tend to act as a single pair of genes in meiosis instead of undergoing independent assortment.
5. Linkage is of two types
Complete linkage - the genes located on the same chromosome do not separate and are inherited together over the generations due to the absence of crossing over.
Incomplete linkage – genes present in the same chromosome have a tendency to separate due to crossing over and hence produce recombinant progeny besides the parental type.
So, the correct answer is ‘One’.

Note: Thomas Hunt Morgan expanded the idea of linkage after noticing that in some instances the observed rate of crossing over events differed from the expected rate of crossing over events. The unit of measurement describing the distance between two linkage groups is the Centimorgan and is named after T. H. Morgan.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




