
The number of aromatic isomers possible for $ {C_7}{H_8}O\; $ is:
Answer
559.5k+ views
Hint: Isomerism is a phenomenon of organic chemistry in which more than one species has the same chemical formula but different structures. Those compounds that have the same chemical formula but different properties and the arrangement of atoms in their molecule are called isomers.
Complete answer:
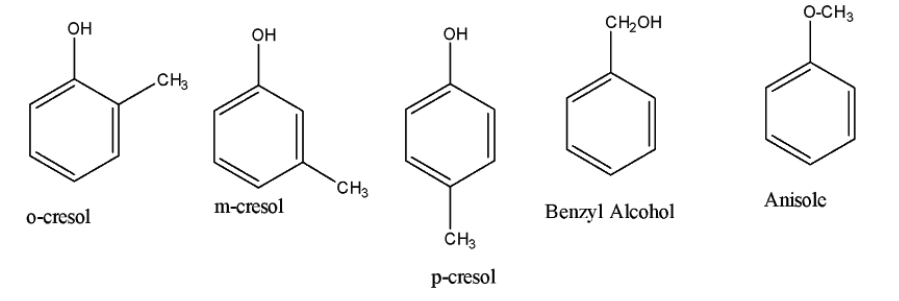
In aromatic isomerism, the basic structure is benzene whose molecular formula is ${C_6}{H_6}$ and the rest of the atoms are placed differently on the ring forming different isomers with the same atoms. Here we are given the molecular formula $ {C_7}{H_8}O\; $ and the benzene ring formula which is ${C_6}{H_6}$, so the remaining atoms we have is $1 $ C$, $2 $ H$ and $1$ $O$ atom. ${C_7}{H_8}$ is toluene. It’s the only benzenoid isomer that is possible. Now we have to insert $1$ $O$ atom into the ring. We can do that in five ways.
we can arrange the $C{H_3}$ and $O$ atom on the ortho, para, and meta position, that will get us $ 2 - methylphenol $ , $ 3 - methylphenol $ and $ 4 - methylphenol $ . The common names of these compounds are $o - cresol,\,m - cresol$ and $p - cresol$. One way is that if we place the oxygen atom with the methyl group which will lead to the formation of methyl phenyl ether also known as anisole. The fifth isomer could be benzyl alcohol in which $ - OH$ group is attached to the $C{H_2}$ group. Hence, in this way, we can say that the possible isomers for the molecular formula $ {C_7}{H_8}O\; $ will be five. These are:
Note:
Isomerism is of two types (a) Structural and (b) Stereo. Aromatic isomerism is a type of structural isomerism. In structural isomerism, the molecular formula of every compound is the same but has different placement of bonds and atoms in the molecule.
Complete answer:
In aromatic isomerism, the basic structure is benzene whose molecular formula is ${C_6}{H_6}$ and the rest of the atoms are placed differently on the ring forming different isomers with the same atoms. Here we are given the molecular formula $ {C_7}{H_8}O\; $ and the benzene ring formula which is ${C_6}{H_6}$, so the remaining atoms we have is $1 $ C$, $2 $ H$ and $1$ $O$ atom. ${C_7}{H_8}$ is toluene. It’s the only benzenoid isomer that is possible. Now we have to insert $1$ $O$ atom into the ring. We can do that in five ways.
we can arrange the $C{H_3}$ and $O$ atom on the ortho, para, and meta position, that will get us $ 2 - methylphenol $ , $ 3 - methylphenol $ and $ 4 - methylphenol $ . The common names of these compounds are $o - cresol,\,m - cresol$ and $p - cresol$. One way is that if we place the oxygen atom with the methyl group which will lead to the formation of methyl phenyl ether also known as anisole. The fifth isomer could be benzyl alcohol in which $ - OH$ group is attached to the $C{H_2}$ group. Hence, in this way, we can say that the possible isomers for the molecular formula $ {C_7}{H_8}O\; $ will be five. These are:

Note:
Isomerism is of two types (a) Structural and (b) Stereo. Aromatic isomerism is a type of structural isomerism. In structural isomerism, the molecular formula of every compound is the same but has different placement of bonds and atoms in the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




