
The nature of $ \pi - $ bonds in perchlorate is
(A) $ O(d\pi ) - Cl(p\pi ) $
(B) $ O(p\pi ) - Cl(d\pi ) $
(C) $ O(d\pi ) - Cl(d\pi ) $
(D) $ O(p\pi ) - Cl(p\pi ) $
Answer
546.3k+ views
Hint: Perchlorate is $ Cl{O_4}^ - $ . In this compound there is one chlorine atom and four oxygen atoms are present. The three oxygen atoms are linked with chlorine by double bonds and one oxygen atom is linked with chlorine by a single atom and it is negatively charged.
Complete step by step solution:
First of all let us understand the structure of perchlorate.
The molecular formula of perchlorate is $ Cl{O_4}^ - $ and its structure is as
.
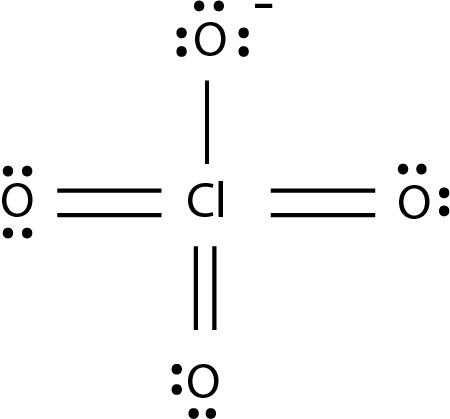
By the structure it is clear that in this compound there is one chlorine atom and four oxygen atoms are present. The three oxygen atoms are linked with chlorine by double bonds and one oxygen atom is linked with chlorine by a single atom and it is negatively charged.
Now we know that the atomic number of chlorine is $ 17 $ so its electronic configuration in its valence shell is $ 3{s^2}3{p^5}3{d^0} $ means it has vacant d-orbitals. So it can increase its valency. Now the atomic number of oxygen is $ 8 $ . So its electronic configuration in its valence shell is $ 2{s^2}2{p^4} $ and there is no vacant orbital because there are no d-orbitals for the second orbit. Hence the bond formed between chlorine and oxygen in this molecule will be of type $ O(p\pi ) - Cl(d\pi ) $ . The bond will be of type $ 2p\pi - 3d\pi $ because the orbitals involved in the molecule is $ 2p $ of oxygen and $ 3d $ of chlorine.
Hence option b is the correct option for this question.
Note:
We know that the electrons which are present in the outermost orbit of the atom is responsible for the formation of bonds in the molecule. And the valency of the atom is also decided by the outermost orbital only.
Complete step by step solution:
First of all let us understand the structure of perchlorate.
The molecular formula of perchlorate is $ Cl{O_4}^ - $ and its structure is as
.

By the structure it is clear that in this compound there is one chlorine atom and four oxygen atoms are present. The three oxygen atoms are linked with chlorine by double bonds and one oxygen atom is linked with chlorine by a single atom and it is negatively charged.
Now we know that the atomic number of chlorine is $ 17 $ so its electronic configuration in its valence shell is $ 3{s^2}3{p^5}3{d^0} $ means it has vacant d-orbitals. So it can increase its valency. Now the atomic number of oxygen is $ 8 $ . So its electronic configuration in its valence shell is $ 2{s^2}2{p^4} $ and there is no vacant orbital because there are no d-orbitals for the second orbit. Hence the bond formed between chlorine and oxygen in this molecule will be of type $ O(p\pi ) - Cl(d\pi ) $ . The bond will be of type $ 2p\pi - 3d\pi $ because the orbitals involved in the molecule is $ 2p $ of oxygen and $ 3d $ of chlorine.
Hence option b is the correct option for this question.
Note:
We know that the electrons which are present in the outermost orbit of the atom is responsible for the formation of bonds in the molecule. And the valency of the atom is also decided by the outermost orbital only.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




