
The natural rubber is the polymer of:
A. 1,3-butadiene
B. Polyamide
C. Isoprene
D. None of the above.
Answer
606.6k+ views
Hint: The monomer of natural rubber is chemically known as 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene.
Complete answer:
Natural rubber is a polymer of isoprene. The chemical name of isoprene is 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene and its chemical formula is ${ CH }_{ 2 }=C\left( { CH }_{ 3 } \right) -CH={ CH }_{ 2 }$. Isoprene is a liquid that is colourless and volatile. As we can see from the formula it has two double bonds. Thus, it is an unsaturated hydrocarbon. The main sources of isoprene are plants and animals. The structure of isoprene is given below.
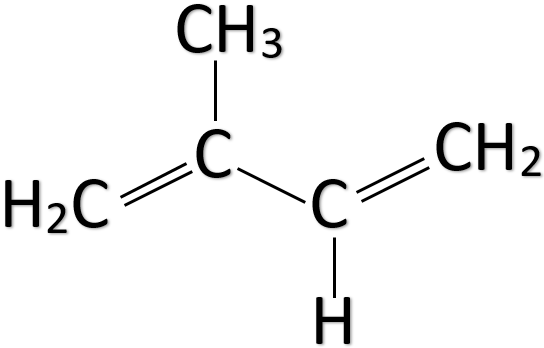
Natural rubber is also known as latex, Caucho, Indian rubber, caoutchouc, and Amazonian rubber. The major source of natural rubber which is used commercially is the Amazonian rubber tree. Previously natural rubber was mostly extracted from the Congo rubber tree.
Additional Information: Natural rubber is an example of elastomer. Elastomer, as the name suggests is a polymer that has elastic properties. That is, it can return to its original shape after it is deformed or stretched. This property of elastomers comes from the ability of the rubber to stretch apart the chains and when the tension is released, the chain can come back to its original position.
As we know that isoprene has two double bonds, when it is polymerised it retains one of the double bonds. By mixing sulphur and rubber, the properties of rubber such as toughness, elasticity, heat, and cold resistance are increased. This process is known as vulcanization. The vulcanization of rubber causes the shorter chains to link in a crossed way with the longer chains through the sulphur.
Note: Don’t confuse isoprene with 1,3-butadiene as given in option A. Isoprene is 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene and as we can see, it has an extra methyl group linked with the second carbon of 1,3-butadiene.
Complete answer:
Natural rubber is a polymer of isoprene. The chemical name of isoprene is 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene and its chemical formula is ${ CH }_{ 2 }=C\left( { CH }_{ 3 } \right) -CH={ CH }_{ 2 }$. Isoprene is a liquid that is colourless and volatile. As we can see from the formula it has two double bonds. Thus, it is an unsaturated hydrocarbon. The main sources of isoprene are plants and animals. The structure of isoprene is given below.

Natural rubber is also known as latex, Caucho, Indian rubber, caoutchouc, and Amazonian rubber. The major source of natural rubber which is used commercially is the Amazonian rubber tree. Previously natural rubber was mostly extracted from the Congo rubber tree.
Additional Information: Natural rubber is an example of elastomer. Elastomer, as the name suggests is a polymer that has elastic properties. That is, it can return to its original shape after it is deformed or stretched. This property of elastomers comes from the ability of the rubber to stretch apart the chains and when the tension is released, the chain can come back to its original position.
As we know that isoprene has two double bonds, when it is polymerised it retains one of the double bonds. By mixing sulphur and rubber, the properties of rubber such as toughness, elasticity, heat, and cold resistance are increased. This process is known as vulcanization. The vulcanization of rubber causes the shorter chains to link in a crossed way with the longer chains through the sulphur.
Note: Don’t confuse isoprene with 1,3-butadiene as given in option A. Isoprene is 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene and as we can see, it has an extra methyl group linked with the second carbon of 1,3-butadiene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




