
The most useful plasmid for cloning is
Answer
510k+ views
Hint: The process of making multiple copies of a fragment of DNA is called DNA cloning. A plasmid is used as a vector to carry the desired DNA fragment into bacteria which reproduces to produce multiple copies of this DNA which are called clones.
Complete answer:
The plasmid is a small, circular, extrachromosomal DNA molecule. It is single-stranded and has the ability to replicate autonomously and is not under the control of chromosomal DNA. It is found in bacteria and some eukaryotes like yeast.
Because of its ability to replicate, plasmid acts as a cloning vector in recombinant DNA technology for manipulating genes. The most useful plasmid for cloning is pBR322.
Following are the characteristics of pBR322-
- Restriction sites: BamH I, Hind III, Pvu I, Pvu II, Pst I, EcoR I
- Selectable marker: antibiotic resistance genes for ampicillin and tetracycline
- ORI: the origin of replication
- ROP: It codes for proteins involved in the process of replication of plasmid
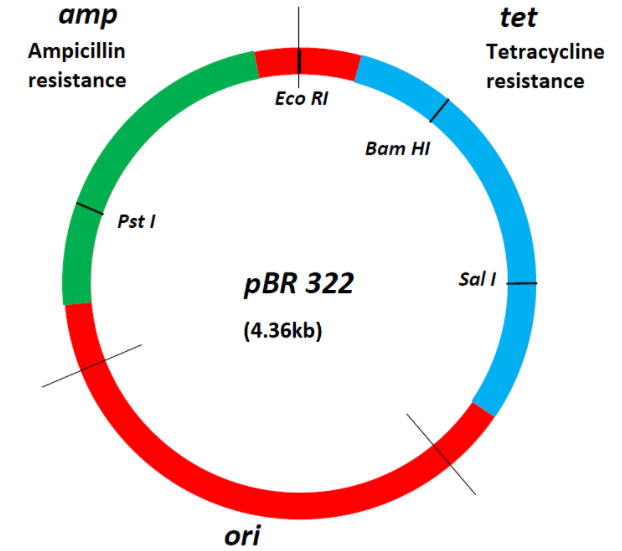
Hence, we can say that the most useful plasmid for cloning is pBR322.
Additional Information: The technology used to produce artificial DNA by combining various DNA fragments having desired genes is called recombinant DNA technology or genetic engineering. It can be accomplished by using specific tools- restriction enzymes, polymerase enzymes, ligases, cloning vectors and the host organism.
Note: Alternative selectable marker help in differentiating recombinants from non-recombinants by producing coloured colonies when reacted with a chromogenic substrate. A recombinant DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of an enzyme, β-galactosidase. This causes the inactivation of the gene for the synthesis of this enzyme. This is referred to as insertional inactivation.
Complete answer:
The plasmid is a small, circular, extrachromosomal DNA molecule. It is single-stranded and has the ability to replicate autonomously and is not under the control of chromosomal DNA. It is found in bacteria and some eukaryotes like yeast.
Because of its ability to replicate, plasmid acts as a cloning vector in recombinant DNA technology for manipulating genes. The most useful plasmid for cloning is pBR322.
Following are the characteristics of pBR322-
- Restriction sites: BamH I, Hind III, Pvu I, Pvu II, Pst I, EcoR I
- Selectable marker: antibiotic resistance genes for ampicillin and tetracycline
- ORI: the origin of replication
- ROP: It codes for proteins involved in the process of replication of plasmid

Hence, we can say that the most useful plasmid for cloning is pBR322.
Additional Information: The technology used to produce artificial DNA by combining various DNA fragments having desired genes is called recombinant DNA technology or genetic engineering. It can be accomplished by using specific tools- restriction enzymes, polymerase enzymes, ligases, cloning vectors and the host organism.
Note: Alternative selectable marker help in differentiating recombinants from non-recombinants by producing coloured colonies when reacted with a chromogenic substrate. A recombinant DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of an enzyme, β-galactosidase. This causes the inactivation of the gene for the synthesis of this enzyme. This is referred to as insertional inactivation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




