
The most characteristic feature of carbocations is that they undergo rearrangement readily forming the major product of the reaction. The migrating aptitude of various groups are:
A.

B.
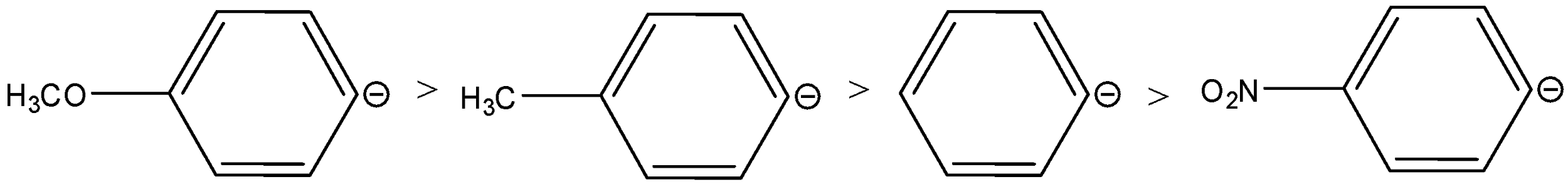
C.
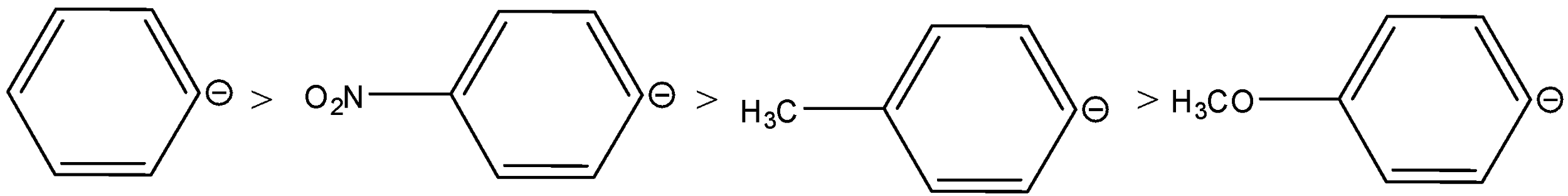
D.
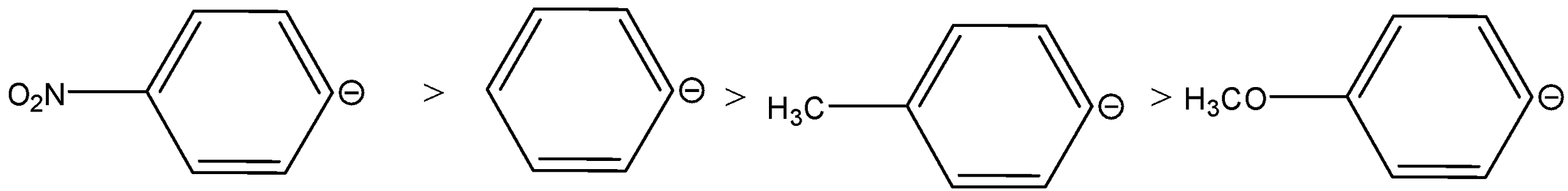



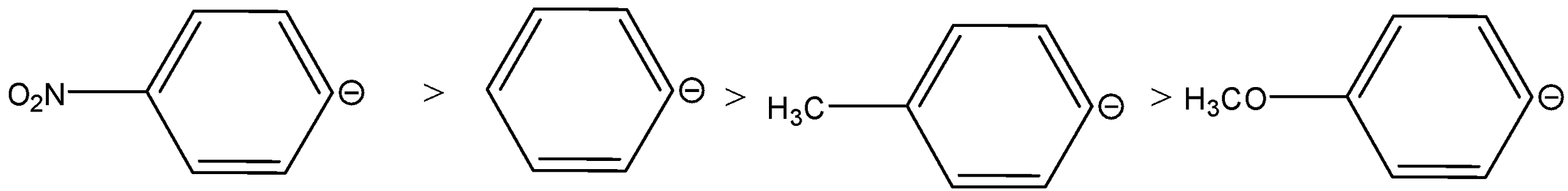
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Stability of the carbocation depends upon the number of the electron-donating groups. The higher the number of the electron-donating group higher will be the stability of the carbocation and vice versa. The migrating ability of the anion depends upon the stability of the carbanion. The higher the stability of the anion lower will be the migrating ability and vice-versa.
Complete step by step answer:
The rearrangement occurs in carbocation stability. The +I and +M accelerate the shifts of the anion. As the +I and +M decrease the stability of the carbanion. Therefore, considering the electronic effects of the groups, the order of stability of the anions is,

Therefore, the order of migrating ability will be reversed, the order is,
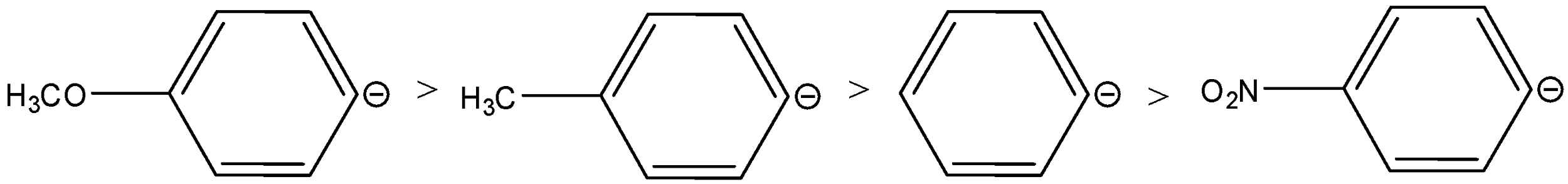
So, the correct option is B.
Additional information:
The stability of carbocations can be determined by understanding the following rules:
By increasing the number of adjacent carbon atoms to the carbocation, we can increase its stability. This means that the greater number of adjacent carbon atoms, the higher is the stability.
The stability of carbocations can be increased by delocalization through resonance. This means that adjacent pi bonds that allow the p – orbital of the carbocation to be a part of a conjugated pi – system, increases the stability of the carbocation.
Also, a greater number of lone pairs on the neighboring atoms of the carbocation increases its stability.
Note: Formation of a Carbocation is often the Rate-Limiting Step in a reaction mechanism. So, by understanding how carbocations are stabilized, you can understand the effect of substituents on reaction rates.
Complete step by step answer:
The rearrangement occurs in carbocation stability. The +I and +M accelerate the shifts of the anion. As the +I and +M decrease the stability of the carbanion. Therefore, considering the electronic effects of the groups, the order of stability of the anions is,

Therefore, the order of migrating ability will be reversed, the order is,

So, the correct option is B.
Additional information:
The stability of carbocations can be determined by understanding the following rules:
By increasing the number of adjacent carbon atoms to the carbocation, we can increase its stability. This means that the greater number of adjacent carbon atoms, the higher is the stability.
The stability of carbocations can be increased by delocalization through resonance. This means that adjacent pi bonds that allow the p – orbital of the carbocation to be a part of a conjugated pi – system, increases the stability of the carbocation.
Also, a greater number of lone pairs on the neighboring atoms of the carbocation increases its stability.
Note: Formation of a Carbocation is often the Rate-Limiting Step in a reaction mechanism. So, by understanding how carbocations are stabilized, you can understand the effect of substituents on reaction rates.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




