
The monomers of Buna-S are:
(A) Vinyl chloride and sulphur
(B) Butadiene
(C) Styrene and butadiene
(D) Isoprene and butadiene
Answer
547.5k+ views
Hint: Polymers are classified into four categories :
- Thermoplastic
- Thermosetting
- Fibres
- Elastomer
Now the order of strength in these different types of polymers is :
Elastomers $ < $ Thermoplastic $ < $ Fibres $ < $ Thermosetting.
Complete step by step solution:
Polymers are materials made of long, repeating chains of molecules. The materials have unique properties, depending on the type of molecules being bonded and how they are bonded.
Monomers: The smallest unit of polymer from which the whole polymer is formed, is known as monomers.
We can define all these four types of polymer as follows:
Elastomers: These are the molecules which have the weak intermolecular forces.They are very elastic.
Examples are: Natural rubber, neoprene, Buna-S
Thermoplastic: All the plastic material which can be softened and melted by heating but they set again when cool, are called thermoplastic polymers.
Examples are: Polyethylene, Polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride
Thermosetting: They are generally a liquid at room temperature which hardens irreversibly on heating.
Examples are: Polyurethane , Bakelite
Fibres: These are the polymers which have the strong intermolecular force between the chains.
Examples are: Polyvinyl chloride, phenol formaldehyde.
In this question we are asked with the monomers of Buna-S. The monomers of Buna-S are styrene and butadiene. The formation is as follows:
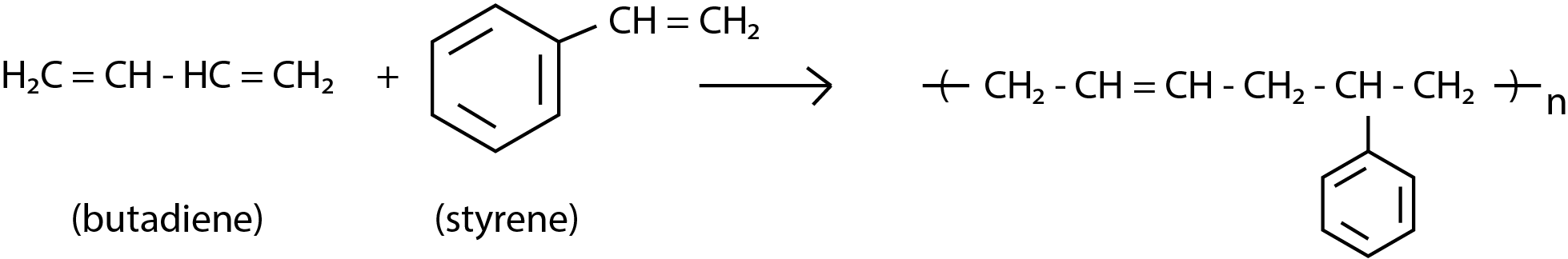
So option c is the correct answer.
Note:
Free radical: They are defined as the molecular species which are capable of independent existence and which contains an unpaired electron in an atomic orbital. They are generally unstable and highly reactive.
Radical polymerisation: It is defined as the polymerisation in which the formation of stable free radical takes place.
- Thermoplastic
- Thermosetting
- Fibres
- Elastomer
Now the order of strength in these different types of polymers is :
Elastomers $ < $ Thermoplastic $ < $ Fibres $ < $ Thermosetting.
Complete step by step solution:
Polymers are materials made of long, repeating chains of molecules. The materials have unique properties, depending on the type of molecules being bonded and how they are bonded.
Monomers: The smallest unit of polymer from which the whole polymer is formed, is known as monomers.
We can define all these four types of polymer as follows:
Elastomers: These are the molecules which have the weak intermolecular forces.They are very elastic.
Examples are: Natural rubber, neoprene, Buna-S
Thermoplastic: All the plastic material which can be softened and melted by heating but they set again when cool, are called thermoplastic polymers.
Examples are: Polyethylene, Polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride
Thermosetting: They are generally a liquid at room temperature which hardens irreversibly on heating.
Examples are: Polyurethane , Bakelite
Fibres: These are the polymers which have the strong intermolecular force between the chains.
Examples are: Polyvinyl chloride, phenol formaldehyde.
In this question we are asked with the monomers of Buna-S. The monomers of Buna-S are styrene and butadiene. The formation is as follows:
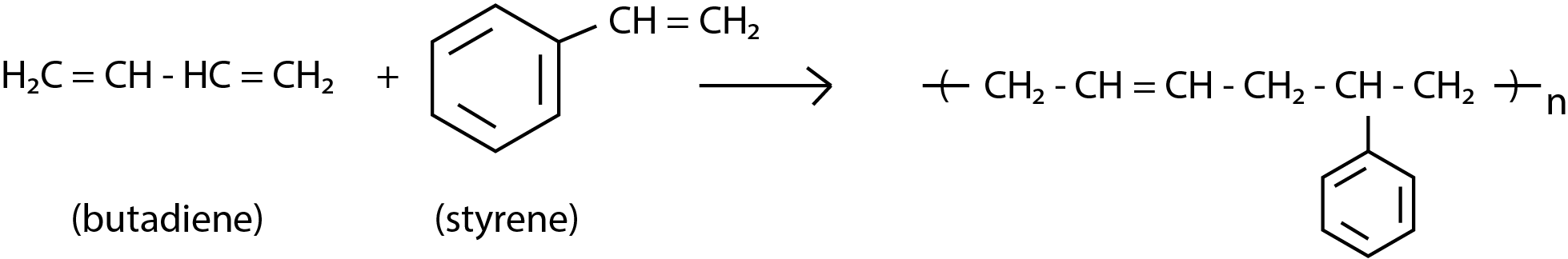
So option c is the correct answer.
Note:
Free radical: They are defined as the molecular species which are capable of independent existence and which contains an unpaired electron in an atomic orbital. They are generally unstable and highly reactive.
Radical polymerisation: It is defined as the polymerisation in which the formation of stable free radical takes place.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




