
The monkey has a mass twice that of the block which has the plane mirror on the monkey’s side as shown in the figure. Initially the system is at rest and the vertical separation of the monkey and the mirror is 2 m. The speed of the monkey when he looks at himself is:
A. \[\sqrt{\dfrac{2g}{3}}\]
B. \[\sqrt{\dfrac{g}{3}}\]
C. \[2\sqrt{\dfrac{g}{3}}\]
D. \[\sqrt{\dfrac{g}{3}}\]

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: In this question we are asked to calculate the speed of the monkey when he will see his image in the mirror. Now, we know that after a certain time the monkey and the block will have travelled a certain distance. Therefore, we will be calculating the distance travelled by the monkey as well as the block having the plane mirror. Later, we will calculate the time required for monkeys to travel this distance. And as we know, speed is given by distance travelled over the time required. To solve all this question, we will be using kinematic equations and Newton’s laws of motion.
Formula used:
\[{{v}^{2}}={{u}^{2}}+2as\]
Complete answer:
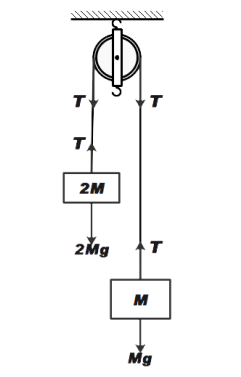
We will draw the FBD of the given condition as shown in the figure below.
From the diagram we can write the equation of motion for the monkey and the block containing the mirror.
Therefore,
Equation of motion for monkey
\[2mg-T=2ma\] ……………… (1)
Similarly, writing for the block
We get,
\[T-mg=ma\] ………………….. (2)
Therefore, from (1) and (2)
\[mg=3ma\]
Therefore,
\[a=\dfrac{g}{3}\] ………………….. (4)
Now using the kinematics equation
We get,
\[{{v}^{2}}={{u}^{2}}+2as\]
It is given that the distance travelled by the monkey is 2 m and the monkey is initially at rest.
Therefore,
After substituting the given values
We get,
\[{{v}^{2}}=0+2\dfrac{g}{3}\times 2\]
Therefore,
\[v=2\sqrt{\dfrac{g}{3}}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Newton’s laws of motion are the fundamental laws of classical mechanics. They describe the motion of the object and the forces exerted by these motions. There are three basic laws of motion. The three laws are: 1) An object will continue to move in a straight line until an external force is applied. 2) The acceleration of an object is directly forced and inversely to the mass of the object. 3) For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Formula used:
\[{{v}^{2}}={{u}^{2}}+2as\]
Complete answer:
We will draw the FBD of the given condition as shown in the figure below.
From the diagram we can write the equation of motion for the monkey and the block containing the mirror.
Therefore,
Equation of motion for monkey
\[2mg-T=2ma\] ……………… (1)
Similarly, writing for the block
We get,
\[T-mg=ma\] ………………….. (2)
Therefore, from (1) and (2)
\[mg=3ma\]
Therefore,
\[a=\dfrac{g}{3}\] ………………….. (4)
Now using the kinematics equation
We get,
\[{{v}^{2}}={{u}^{2}}+2as\]
It is given that the distance travelled by the monkey is 2 m and the monkey is initially at rest.
Therefore,
After substituting the given values
We get,
\[{{v}^{2}}=0+2\dfrac{g}{3}\times 2\]
Therefore,
\[v=2\sqrt{\dfrac{g}{3}}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Newton’s laws of motion are the fundamental laws of classical mechanics. They describe the motion of the object and the forces exerted by these motions. There are three basic laws of motion. The three laws are: 1) An object will continue to move in a straight line until an external force is applied. 2) The acceleration of an object is directly forced and inversely to the mass of the object. 3) For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




