
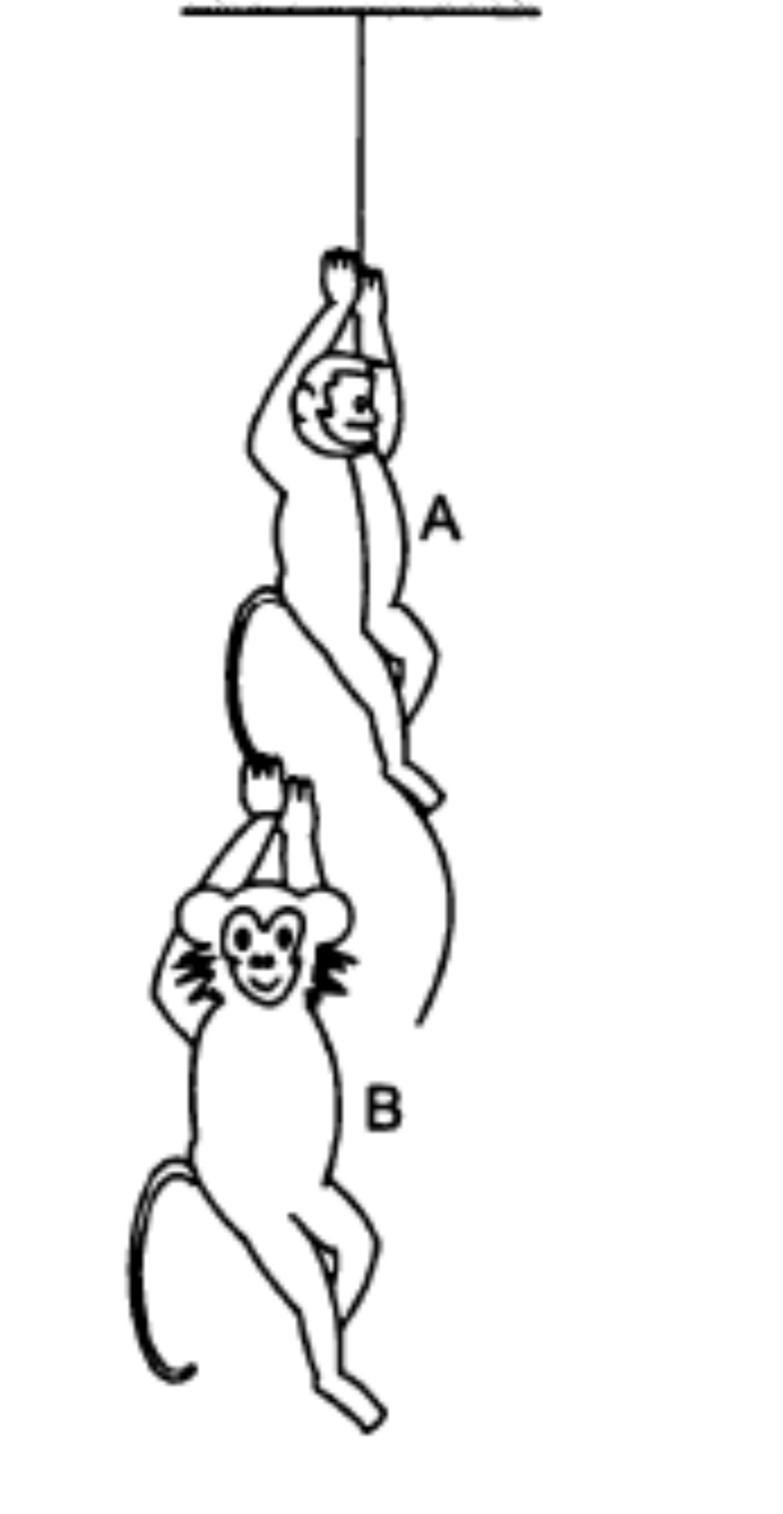
The monkey B shown in figure is holding on to the tail of monkey A which is climbing up a rope. The masses of the monkeys A and B are 5 kg and 2 kg respectively. If A can tolerate a tension of 30 N in its tail , what force should it apply on the rope in order to carry monkey B with it ? Take $ g = 10m{s^{ - 2}} $

Answer
502.2k+ views
Hint :The net acceleration given to objects owing to the combined influence of gravitation and centrifugal force is indicated by g, the gravity of Earth. This acceleration is measured in metres per second squared or newtons per kilogram in SI units. To answer this question, we use F = mg.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The monkey B (the kid of monkey A) is immobile in relation to monkey A, and they both move at the same rate,a. Now, the force that should be used to pull monkey B upwards in order for him to be raised with acceleration a must be equal to m(g+a), where m is the mass of monkey B. Because monkey A's tail has a maximum tension of 30N.
So, 30=m(g+a)=2(10+a)
Hence, $ \Rightarrow a = 5m{s^{ - 2}} $
This is the greatest upward acceleration that both systems can achieve as a combined system. The tail of monkey A will break if the acceleration exceeds this amount. Now, the force that monkey A must apply to the rope in order for this force to be performed onto him as the reaction force must be adequate to raise both the monkey A and the kid monkey B at a common acceleration of $ a = 5m{s^{ - 2}} $ .
Now, $ {F_{max}} $ =(M+m)(g+a)=7×15=105N
This is the maximum force that monkey A should apply to the rope in order for the entire system to travel at maximum speed. When both the monkey and the child go up at the same speed, the situation of minimal force acting on the combined system of the monkey and the child will occur. If that's the case, $ {F_{min}} = (M + m)g = 70N. $
To go up with maximal acceleration, monkey A should pull the rope with a force of 70N, so that the strain on his tail is just equal to the breaking strength of the tail.
Hence option C is correct.
Note :
Do be careful where you add up the masses and where you subtract the given two masses.
It asserts that an object's rate of change of velocity is directly proportional to the force applied and occurs in the force's direction. The equation is as follows: force (N) = mass (kg) x acceleration ( $ m{s^{ - 2}} $ ). As a result, the acceleration of a constant mass object is proportional to the force applied.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The monkey B (the kid of monkey A) is immobile in relation to monkey A, and they both move at the same rate,a. Now, the force that should be used to pull monkey B upwards in order for him to be raised with acceleration a must be equal to m(g+a), where m is the mass of monkey B. Because monkey A's tail has a maximum tension of 30N.
So, 30=m(g+a)=2(10+a)
Hence, $ \Rightarrow a = 5m{s^{ - 2}} $
This is the greatest upward acceleration that both systems can achieve as a combined system. The tail of monkey A will break if the acceleration exceeds this amount. Now, the force that monkey A must apply to the rope in order for this force to be performed onto him as the reaction force must be adequate to raise both the monkey A and the kid monkey B at a common acceleration of $ a = 5m{s^{ - 2}} $ .
Now, $ {F_{max}} $ =(M+m)(g+a)=7×15=105N
This is the maximum force that monkey A should apply to the rope in order for the entire system to travel at maximum speed. When both the monkey and the child go up at the same speed, the situation of minimal force acting on the combined system of the monkey and the child will occur. If that's the case, $ {F_{min}} = (M + m)g = 70N. $
To go up with maximal acceleration, monkey A should pull the rope with a force of 70N, so that the strain on his tail is just equal to the breaking strength of the tail.
Hence option C is correct.
Note :
Do be careful where you add up the masses and where you subtract the given two masses.
It asserts that an object's rate of change of velocity is directly proportional to the force applied and occurs in the force's direction. The equation is as follows: force (N) = mass (kg) x acceleration ( $ m{s^{ - 2}} $ ). As a result, the acceleration of a constant mass object is proportional to the force applied.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




