
The moment of inertia of an elliptical disc of uniform mass distribution of mass 'm', semi major axis 'r', semi minor axis 'd' about its axis is
(A) $= \dfrac{mr^2}{2}$
(B) $= \dfrac{md^2}{2}$
(C) $> \dfrac{mr^2}{2}$
(D) $< \dfrac{mr^2}{2}$
Answer
535.8k+ views
Hint: A rough comparison of the moment of inertia of the given elliptical disc has to be made with the moment of inertia of the circular disc. Moment of inertia depends on the product of mass and the square of distance of separation from the axis of the ellipse.
Formula used:
The moment of inertia of a circular disc of uniform mass is given as:
$I = \dfrac{MR^2}{2}$.
Complete answer:
For the given ellipse, the semi-major axis has been given to have a value of r and semi-minor axis has been given to have a value of d.
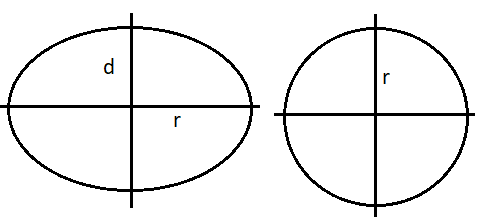
Now, we have to compare all the options one by one:
(A) $=\dfrac{mr^2}{2}$
Now, if we take the semi-major axis of the ellipse and draw a disc from it, we get this value as the moment of inertia. Therefore, this option clearly does not fit our description of the case of ellipse.
(B) $=\dfrac{md^2}{2}$
This option too is for the case when we take the semi-minor axis and make a disc from it.
(C) $>\dfrac{mr^2}{2}$
Moment of inertia depends on distance from the axis. In a circular disc, the distance of all points is more from the axis as compared to the ellipse.
(D) $< \dfrac{mr^2}{2}$
This means that the circular disc drawn from the semi-major axis will have more moment of inertia from the ellipse under consideration.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (D).
Additional information:
The moment of inertia is calculated for a uniform circular body by considering a small mass element and multiplying it with the square of separation from the axis and then an integration is performed over the whole body.
Note:
The semi-major axis of an ellipse is the longer side and semi-minor axis, as the name suggests is the smaller side. The term semi clearly rules out the conflict. When we talk about semi-major axis, we take half the distance of the major axis.
Formula used:
The moment of inertia of a circular disc of uniform mass is given as:
$I = \dfrac{MR^2}{2}$.
Complete answer:
For the given ellipse, the semi-major axis has been given to have a value of r and semi-minor axis has been given to have a value of d.

Now, we have to compare all the options one by one:
(A) $=\dfrac{mr^2}{2}$
Now, if we take the semi-major axis of the ellipse and draw a disc from it, we get this value as the moment of inertia. Therefore, this option clearly does not fit our description of the case of ellipse.
(B) $=\dfrac{md^2}{2}$
This option too is for the case when we take the semi-minor axis and make a disc from it.
(C) $>\dfrac{mr^2}{2}$
Moment of inertia depends on distance from the axis. In a circular disc, the distance of all points is more from the axis as compared to the ellipse.
(D) $< \dfrac{mr^2}{2}$
This means that the circular disc drawn from the semi-major axis will have more moment of inertia from the ellipse under consideration.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (D).
Additional information:
The moment of inertia is calculated for a uniform circular body by considering a small mass element and multiplying it with the square of separation from the axis and then an integration is performed over the whole body.
Note:
The semi-major axis of an ellipse is the longer side and semi-minor axis, as the name suggests is the smaller side. The term semi clearly rules out the conflict. When we talk about semi-major axis, we take half the distance of the major axis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




