
The missing structures A and B in the reaction sequence are given by the set:
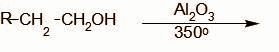
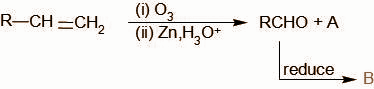
A.${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}},{\text{RCOOH}}$
B.Methanal, ${\text{RC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$
C.Ethanal, ${\text{RCOOH}}$
D.Methanal, ${\text{RCHOHR'}}$
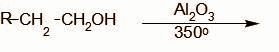
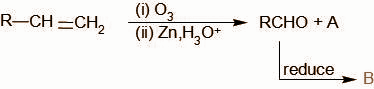
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you must recall the various reactions of oxygen containing organic compounds. Aluminum oxide is a lewis acid and converts alcohols to alkenes.
Complete step by step solution:
A is formed as a by- product along with an aldehyde when an alkene undergoes ozonolysis reaction.
We know that, ozonolysis reaction involves the breaking of a carbon carbon double bond wherever present with the addition of an oxygen atom on the carbon atom which forms a double bond with the carbon atom. As a result, carboxylic compounds are obtained (aldehydes or ketones). In the question, the ozonolysis of the given alkene gives${\text{RCHO}}$. Thus it is evident that the other product formed is${\text{HCHO}}$.
In the next step, the aldehyde is reduced. The mild reduction of an aldehyde leads to the formation of an alcohol. We can see it as the addition of a hydrogen molecule over the carbon oxygen double bond.
Thus, the product formed is ${\text{RC}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}}$
Therefore we know A is ${\text{HCHO}}$(methanal) and B is ${\text{RC}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}}$.
The correct option is B.
Note: Alkenes are oxidized with ozone to form aldehydes or ketones, or carboxylic acids. Generally, ozone is bubbled through a solution of the alkene at low temperature till the solution takes on a characteristic blue color, which indicates complete consumption of the alkene.
In the next step, a reagent is added to convert the intermediate ozonide formed in the first step to a carbonyl derivative. The reagent added is generally a reducing agent. The use of zinc dust, or dimethyl sulfide produces aldehydes and ketones while the use of hydrogen peroxide produces carboxylic acids.
Complete step by step solution:
A is formed as a by- product along with an aldehyde when an alkene undergoes ozonolysis reaction.
We know that, ozonolysis reaction involves the breaking of a carbon carbon double bond wherever present with the addition of an oxygen atom on the carbon atom which forms a double bond with the carbon atom. As a result, carboxylic compounds are obtained (aldehydes or ketones). In the question, the ozonolysis of the given alkene gives${\text{RCHO}}$. Thus it is evident that the other product formed is${\text{HCHO}}$.
In the next step, the aldehyde is reduced. The mild reduction of an aldehyde leads to the formation of an alcohol. We can see it as the addition of a hydrogen molecule over the carbon oxygen double bond.
Thus, the product formed is ${\text{RC}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}}$
Therefore we know A is ${\text{HCHO}}$(methanal) and B is ${\text{RC}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}}$.
The correct option is B.
Note: Alkenes are oxidized with ozone to form aldehydes or ketones, or carboxylic acids. Generally, ozone is bubbled through a solution of the alkene at low temperature till the solution takes on a characteristic blue color, which indicates complete consumption of the alkene.
In the next step, a reagent is added to convert the intermediate ozonide formed in the first step to a carbonyl derivative. The reagent added is generally a reducing agent. The use of zinc dust, or dimethyl sulfide produces aldehydes and ketones while the use of hydrogen peroxide produces carboxylic acids.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




