
The mirror image of the curve $\arg \left( {\dfrac{{z - 3}}{{z - i}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6},i = \sqrt { - 1} $in the real axis is:
A.$\arg \left( {\dfrac{{z + 3}}{{z + i}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6}$
B.$\arg \left( {\dfrac{{z - 3}}{{z + i}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6}$
C.$\arg \left( {\dfrac{{z + i}}{{z + 3}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6}$
D.$\arg \left( {\dfrac{{z + 1}}{{z - 3}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6}$
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: Here, we will use the properties of the conjugate of complex numbers for z = a + ib such as $\bar z = a - ib$ and also the property of argument of the complex number like $\arg \left( {\bar z} \right) = - \arg \left( z \right)$ to calculate the mirror image of the given curve.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here, we are given the curve $\arg \left( {\dfrac{{z - 3}}{{z - i}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6},i = \sqrt { - 1} $.
The mirror image of any complex number z = a + ib on the real axis is the conjugate of z i. e., $\bar z = a - ib$. It is because when we draw a curve, for example the given curve is a circle and it lies in the 1st quadrant, then its mirror image will lie in the 4th quadrant. The co – ordinate of x – axis will remain the same but the co – ordinate on the y – axis will change its sign.
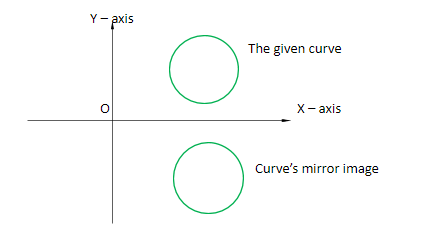
Therefore, the image of z in the real axis is its conjugate $\bar z$.
Now, we have the curve $\arg \left( {\dfrac{{z - 3}}{{z - i}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6}$
For determining the mirror image of the curve, we will substitute z with $\bar z$in the above equation. After this, we get
$ \Rightarrow \arg \left( {\dfrac{{\bar z - 3}}{{\bar z - i}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6}$
We know the property of the argument of conjugate of complex numbers i. e., $\arg \left( {\bar z} \right) = - \arg \left( z \right)$. Therefore, using this property in the above equation, we get
$ \Rightarrow \arg \left( {\dfrac{{ - z - 3}}{{ - z - i}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6}$
$ \Rightarrow \arg \left( {\dfrac{{ - \left( {z + 3} \right)}}{{ - \left( {z + i} \right)}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6}$
$ \Rightarrow \arg \left( {\dfrac{{z + 3}}{{z + i}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6}$
Hence, we get the mirror image of the curve $\arg \left( {\dfrac{{z - 3}}{{z - i}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6},i = \sqrt { - 1} $is found to be $\arg \left( {\dfrac{{z + 3}}{{z + i}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6}$. Therefore, option(A) is correct.
Note: In such problems, you may get confused amongst the properties used. You can also solve this question using the other property of argument of complex numbers like $\arg \left( {\dfrac{{{z_1}}}{{{z_2}}}} \right) = - \arg \left( {\dfrac{{{z_2}}}{{{z_1}}}} \right)$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here, we are given the curve $\arg \left( {\dfrac{{z - 3}}{{z - i}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6},i = \sqrt { - 1} $.
The mirror image of any complex number z = a + ib on the real axis is the conjugate of z i. e., $\bar z = a - ib$. It is because when we draw a curve, for example the given curve is a circle and it lies in the 1st quadrant, then its mirror image will lie in the 4th quadrant. The co – ordinate of x – axis will remain the same but the co – ordinate on the y – axis will change its sign.

Therefore, the image of z in the real axis is its conjugate $\bar z$.
Now, we have the curve $\arg \left( {\dfrac{{z - 3}}{{z - i}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6}$
For determining the mirror image of the curve, we will substitute z with $\bar z$in the above equation. After this, we get
$ \Rightarrow \arg \left( {\dfrac{{\bar z - 3}}{{\bar z - i}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6}$
We know the property of the argument of conjugate of complex numbers i. e., $\arg \left( {\bar z} \right) = - \arg \left( z \right)$. Therefore, using this property in the above equation, we get
$ \Rightarrow \arg \left( {\dfrac{{ - z - 3}}{{ - z - i}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6}$
$ \Rightarrow \arg \left( {\dfrac{{ - \left( {z + 3} \right)}}{{ - \left( {z + i} \right)}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6}$
$ \Rightarrow \arg \left( {\dfrac{{z + 3}}{{z + i}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6}$
Hence, we get the mirror image of the curve $\arg \left( {\dfrac{{z - 3}}{{z - i}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6},i = \sqrt { - 1} $is found to be $\arg \left( {\dfrac{{z + 3}}{{z + i}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{6}$. Therefore, option(A) is correct.
Note: In such problems, you may get confused amongst the properties used. You can also solve this question using the other property of argument of complex numbers like $\arg \left( {\dfrac{{{z_1}}}{{{z_2}}}} \right) = - \arg \left( {\dfrac{{{z_2}}}{{{z_1}}}} \right)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




