
The metal d-orbitals that are directly facing the ligands in ${{K}_{3}}\left[ Co{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}} \right]$ are:
A. ${{d}_{xz}},{{d}_{yx}}\text{ }and\text{ }{{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$
B. ${{d}_{xy}},{{d}_{xz}}\text{ }and\text{ }{{d}_{yz}}$
C. ${{d}_{xy}}\text{ }and\text{ }{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}$
D. $\text{ }{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}\text{ }and\text{ }{{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint:. The d-orbitals of the central metal in coordination complexes are going to split into$~{{e}_{g}}$ and $~{{t}_{2g}}$ orbitals because of the interaction of the d-orbitals of the central metal with the orbitals of the ligands.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the question it is given that the d-orbitals that are directly facing the ligands in ${{K}_{3}}\left[ Co{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}} \right]$ .
- We have to find the d-orbitals of the central metal atom that are in the direction of the cyanide (CN) ligands.
- The given complex is an example of an octahedral because the given complex contains six cyanide ligands in its structure.
- We know that cyanide is a strong ligand.
- In octahedral complexes the ligands are going to approach the central metal atom along the axis.
- Then the d-orbitals along the axis are going to face the ligands.
- Now we have to find the d-orbitals which are along the axis.
- The structure of the d-orbitals is as follows.
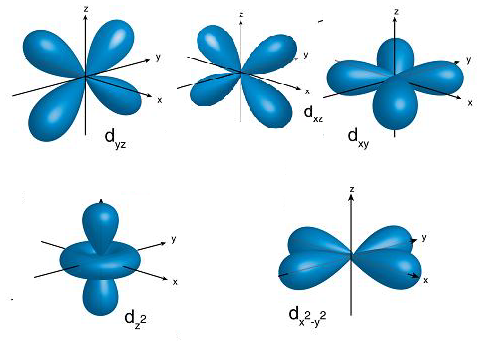
- From the above structures of d-orbitals we can say that the orbitals $\text{ }{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}\text{ }and\text{ }{{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$ are along the axis.
- Therefore the metal d-orbitals metal d-orbitals that are directly facing the ligands in ${{K}_{3}}\left[ Co{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}} \right]$ are $\text{ }{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}\text{ }and\text{ }{{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: We have to know the structure of the given complex then only we can find the metal d-orbitals which are in the direction of ligands and metal d-orbitals which are not the direction of ligands. In a square planar complex the metal d-orbitals are not in the direction of ligands.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the question it is given that the d-orbitals that are directly facing the ligands in ${{K}_{3}}\left[ Co{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}} \right]$ .
- We have to find the d-orbitals of the central metal atom that are in the direction of the cyanide (CN) ligands.
- The given complex is an example of an octahedral because the given complex contains six cyanide ligands in its structure.
- We know that cyanide is a strong ligand.
- In octahedral complexes the ligands are going to approach the central metal atom along the axis.
- Then the d-orbitals along the axis are going to face the ligands.
- Now we have to find the d-orbitals which are along the axis.
- The structure of the d-orbitals is as follows.

- From the above structures of d-orbitals we can say that the orbitals $\text{ }{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}\text{ }and\text{ }{{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$ are along the axis.
- Therefore the metal d-orbitals metal d-orbitals that are directly facing the ligands in ${{K}_{3}}\left[ Co{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}} \right]$ are $\text{ }{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}\text{ }and\text{ }{{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: We have to know the structure of the given complex then only we can find the metal d-orbitals which are in the direction of ligands and metal d-orbitals which are not the direction of ligands. In a square planar complex the metal d-orbitals are not in the direction of ligands.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




