
The medians of a right triangle which are drawn from the vertices of the acute angles are $ 5 $ and $ \sqrt {40} $ . The value of the hypotenuse is:
A. $ 10 $
B. $ 2\sqrt {40} $
C. $ \sqrt {13} $
D. $ 2\sqrt {13} $
E.None of these
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: Here, one medium is given as $ 5{\rm{ cm}} $ and another medium is given as $ 2\sqrt 6 {\rm{ cm}} $ . Then we know that the medium is that segment which is drawn from the vertex of the triangle and bisect the opposite side. Using Pythagoras theorem, we obtain the hypotenuse of the right triangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The following is the schematic diagram for the triangle ABD.
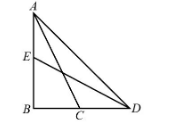
By observing the diagram, we obtained that,
Medium $ {\rm{AC}} $ is $ 5{\rm{ cm}} $ .
Medium $ {\rm{ED}} $ is $ 2\sqrt 6 {\rm{ cm}} $ .
We know that medium is the segment which is drawn from the vertex of the triangle and bisect opposite sides.
Let us assume that $ {\rm{BC}} = x $ and $ {\rm{AE}} = y $ , $ {\rm{BD}} = 2x $ .
Since, it is known from the triangle that,
$ {\rm{AE}} = {\rm{EB}} = y $
$ {\rm{AB}} = 2y $
The Pythagoras theorem tells that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to sum of square of perpendicular side and square of base.
$ {\left( {{\rm{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\rm{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\rm{Base}}} \right)^2} $
In the triangle $ {\rm{EBD}} $ , apply Pythagoras theorem, we get,
$ {\rm{E}}{{\rm{D}}^2} = {\rm{E}}{{\rm{B}}^2} + {\rm{B}}{{\rm{D}}^2} $
On substituting the values of hypotenuse, perpendicular and base in the above expression, we get,
$ \begin{array}{l}
{\left( {2\sqrt {10} } \right)^2} = 4{x^2} + {y^2}\\
4{x^2} + {y^2} = 40
\end{array} $ …..(1)
In right angle triangle $ {\rm{ABC}} $ , apply Pythagoras theorem, we get,
$ {\rm{A}}{{\rm{C}}^2} = {\rm{A}}{{\rm{B}}^2} + {\rm{B}}{{\rm{C}}^2} $
On substituting the values $ {\rm{AB}} $ , $ {\rm{BC}} $ and $ {\rm{AC}} $ in the above expression we get,
$ \begin{array}{l}
{5^2} = {\left( {2y} \right)^2} + {x^2}\\
{x^2} + 4{y^2} = 25
\end{array} $
In equation $ 4{x^2} + {y^2} = 40 $ , multiply it by $ 4 $ and then subtract from equation 1 we get,
$ \begin{array}{c}
- 15{x^2} = - 135\\
{x^2} = 9\\
x = \sqrt 9
\end{array} $
The length of the side is always positive.
On substituting the value of $ x $ in $ 4{x^2} + {y^2} = 40 $ then we get,
$ \begin{array}{c}
4{\left( 3 \right)^2} + {y^2} = 40\\
36 + {y^2} = 40\\
{y^2} = 4\\
y = 2
\end{array} $
Then the value of $ y $ is $ 2 $ .
The values of $ {\rm{AB}} $ and $ {\rm{BD}} $ are $ 4{\rm{ cm}} $ and $ 6{\rm{ cm}} $ .
In triangle $ {\rm{ABD}} $ , apply Pythagoras theorem, we get,
$ {\rm{A}}{{\rm{D}}^2} = {\rm{A}}{{\rm{B}}^2} + {\rm{B}}{{\rm{D}}^2} $
On substitute the values of $ {\rm{AB}} $ and $ {\rm{BD}} $ we get,
$ \begin{array}{c}
{\rm{A}}{{\rm{D}}^2} = {\left( 4 \right)^2} + {\left( 6 \right)^2}\\
= 52{\rm{ cm}}
\end{array} $
Taking square root on both sides we get,
\[\begin{array}{l}
{\rm{AD}} = \sqrt {52} \\
{\rm{AD}} = 2\sqrt {13} {\rm{ cm}}
\end{array}\]
Hence, the hypotenuse of the right triangle is $ 2\sqrt {13} {\rm{ cm}} $ .
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The length, area and breath will never be negative. For a single point the length will be zero and the square root of any number will be positive and negative. Since, the length is always positive we took positive value.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The following is the schematic diagram for the triangle ABD.

By observing the diagram, we obtained that,
Medium $ {\rm{AC}} $ is $ 5{\rm{ cm}} $ .
Medium $ {\rm{ED}} $ is $ 2\sqrt 6 {\rm{ cm}} $ .
We know that medium is the segment which is drawn from the vertex of the triangle and bisect opposite sides.
Let us assume that $ {\rm{BC}} = x $ and $ {\rm{AE}} = y $ , $ {\rm{BD}} = 2x $ .
Since, it is known from the triangle that,
$ {\rm{AE}} = {\rm{EB}} = y $
$ {\rm{AB}} = 2y $
The Pythagoras theorem tells that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to sum of square of perpendicular side and square of base.
$ {\left( {{\rm{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\rm{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\rm{Base}}} \right)^2} $
In the triangle $ {\rm{EBD}} $ , apply Pythagoras theorem, we get,
$ {\rm{E}}{{\rm{D}}^2} = {\rm{E}}{{\rm{B}}^2} + {\rm{B}}{{\rm{D}}^2} $
On substituting the values of hypotenuse, perpendicular and base in the above expression, we get,
$ \begin{array}{l}
{\left( {2\sqrt {10} } \right)^2} = 4{x^2} + {y^2}\\
4{x^2} + {y^2} = 40
\end{array} $ …..(1)
In right angle triangle $ {\rm{ABC}} $ , apply Pythagoras theorem, we get,
$ {\rm{A}}{{\rm{C}}^2} = {\rm{A}}{{\rm{B}}^2} + {\rm{B}}{{\rm{C}}^2} $
On substituting the values $ {\rm{AB}} $ , $ {\rm{BC}} $ and $ {\rm{AC}} $ in the above expression we get,
$ \begin{array}{l}
{5^2} = {\left( {2y} \right)^2} + {x^2}\\
{x^2} + 4{y^2} = 25
\end{array} $
In equation $ 4{x^2} + {y^2} = 40 $ , multiply it by $ 4 $ and then subtract from equation 1 we get,
$ \begin{array}{c}
- 15{x^2} = - 135\\
{x^2} = 9\\
x = \sqrt 9
\end{array} $
The length of the side is always positive.
On substituting the value of $ x $ in $ 4{x^2} + {y^2} = 40 $ then we get,
$ \begin{array}{c}
4{\left( 3 \right)^2} + {y^2} = 40\\
36 + {y^2} = 40\\
{y^2} = 4\\
y = 2
\end{array} $
Then the value of $ y $ is $ 2 $ .
The values of $ {\rm{AB}} $ and $ {\rm{BD}} $ are $ 4{\rm{ cm}} $ and $ 6{\rm{ cm}} $ .
In triangle $ {\rm{ABD}} $ , apply Pythagoras theorem, we get,
$ {\rm{A}}{{\rm{D}}^2} = {\rm{A}}{{\rm{B}}^2} + {\rm{B}}{{\rm{D}}^2} $
On substitute the values of $ {\rm{AB}} $ and $ {\rm{BD}} $ we get,
$ \begin{array}{c}
{\rm{A}}{{\rm{D}}^2} = {\left( 4 \right)^2} + {\left( 6 \right)^2}\\
= 52{\rm{ cm}}
\end{array} $
Taking square root on both sides we get,
\[\begin{array}{l}
{\rm{AD}} = \sqrt {52} \\
{\rm{AD}} = 2\sqrt {13} {\rm{ cm}}
\end{array}\]
Hence, the hypotenuse of the right triangle is $ 2\sqrt {13} {\rm{ cm}} $ .
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The length, area and breath will never be negative. For a single point the length will be zero and the square root of any number will be positive and negative. Since, the length is always positive we took positive value.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




