
The mass of the earth is 81 times the mass of the Moon and the distance between the earth and the Moon is 60 times the radius of earth. If R is the radius of the earth, then the distance between the Moon and the point on the line joining the Moon and the earth where the gravitational force becomes zero is
A. 30R
B. 15R
C. 6R
D. 5R
Answer
528.3k+ views
Hint: Define gravitational force. Obtain the mathematical expression for gravitational force. To find the solution to this question consider a point where the gravitational force will be zero. Find the force on a particle at the point due to earth and moon. Then equate these two forces to find the answer to the question.
Formula used:
Gravitational force between two mass M and M at a distance R apart is given as,
$F=\dfrac{GMm}{{{R}^{2}}}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
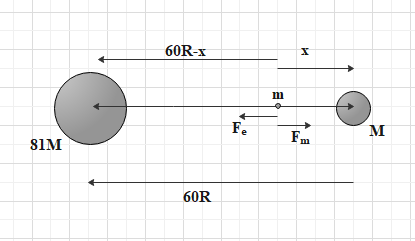
Consider the mass of the moon is M.
So, the mass of the earth is $81M$ .
Again, the radius of earth is R.
So, the distance between the moon and earth is $r=60R$.
The gravitational force at a point on the line joining the moon and earth is zero. Let, the point is at a distance x from the moon. So, the distance of the point from the earth is $60R-x$ .
Since, the gravitational force at that point is zero, if we put a mass m at that point it will not feel any force. The gravitational force on the mass m due to earth and moon will be balanced i.e. these two forces will be equal and opposite to each other.
Now, let the force on the particle of mass m due to earth is, ${{F}_{e}}$
So,
${{F}_{e}}=\dfrac{G\times 81M\times m}{{{\left( 60R-x \right)}^{2}}}$
Again, let the force on the particle of mass m due to moon is, ${{F}_{m}}$
So,
${{F}_{m}}=\dfrac{GMm}{{{x}^{2}}}$
For the gravitational force to be zero the force ${{F}_{e}}$ and ${{F}_{m}}$ should be equal and opposite.
So, we can write,
$\begin{align}
& {{F}_{m}}={{F}_{e}} \\
& \dfrac{G\times 81Mm}{{{\left( 60R-x \right)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{GMm}{{{x}^{2}}} \\
& \dfrac{81}{{{\left( 60R-x \right)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{x}^{2}}} \\
& {{\left( 60R-x \right)}^{2}}=81{{x}^{2}} \\
& 60R-x=9x \\
& 10x=60R \\
& x=6R \\
\end{align}$
So, the point at which the gravitational force is zero will be 6R
The correct option is (C)
Note: The value of the gravitational constant G is $6.67\times {{10}^{-11}}N{{m}^{2}}k{{g}^{-2}}$.
In the particle of mass m, the total force is zero. There will be always gravitational force due to earth and moon. At that point these forces are equal and hence the total force or the gravitational force becomes zero at that point.
Formula used:
Gravitational force between two mass M and M at a distance R apart is given as,
$F=\dfrac{GMm}{{{R}^{2}}}$
Complete step-by-step answer:

Consider the mass of the moon is M.
So, the mass of the earth is $81M$ .
Again, the radius of earth is R.
So, the distance between the moon and earth is $r=60R$.
The gravitational force at a point on the line joining the moon and earth is zero. Let, the point is at a distance x from the moon. So, the distance of the point from the earth is $60R-x$ .
Since, the gravitational force at that point is zero, if we put a mass m at that point it will not feel any force. The gravitational force on the mass m due to earth and moon will be balanced i.e. these two forces will be equal and opposite to each other.
Now, let the force on the particle of mass m due to earth is, ${{F}_{e}}$
So,
${{F}_{e}}=\dfrac{G\times 81M\times m}{{{\left( 60R-x \right)}^{2}}}$
Again, let the force on the particle of mass m due to moon is, ${{F}_{m}}$
So,
${{F}_{m}}=\dfrac{GMm}{{{x}^{2}}}$
For the gravitational force to be zero the force ${{F}_{e}}$ and ${{F}_{m}}$ should be equal and opposite.
So, we can write,
$\begin{align}
& {{F}_{m}}={{F}_{e}} \\
& \dfrac{G\times 81Mm}{{{\left( 60R-x \right)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{GMm}{{{x}^{2}}} \\
& \dfrac{81}{{{\left( 60R-x \right)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{x}^{2}}} \\
& {{\left( 60R-x \right)}^{2}}=81{{x}^{2}} \\
& 60R-x=9x \\
& 10x=60R \\
& x=6R \\
\end{align}$
So, the point at which the gravitational force is zero will be 6R
The correct option is (C)
Note: The value of the gravitational constant G is $6.67\times {{10}^{-11}}N{{m}^{2}}k{{g}^{-2}}$.
In the particle of mass m, the total force is zero. There will be always gravitational force due to earth and moon. At that point these forces are equal and hence the total force or the gravitational force becomes zero at that point.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




