
The major product P of the given reaction is:
$C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2} + HOBr \to P$.
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: Markovnikov’s Rule also known as Markownikoff’s rule is used to determine the outcome of some chemical addition reactions. Basically, hydrogen is added to the carbon with the most hydrogens and the halide is added to the carbon with least hydrogens. So, we will apply this rule in the given reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all, let’s discuss Markovnikov's rule. In this, when a protic acid is added to an asymmetric alkene, then the acidic hydrogen attaches itself to the carbon having a greater number of hydrogen substituents whereas the halide group attaches itself to the carbon atom which has a greater number of alkyl substituent.
Now, in the first step, the alkene is protonated and it gives rise to the more stable carbocation. Further, two types of carbocation are formed i.e. primary carbocation and secondary carbocation. We generally prefer secondary carbocation because it is far more stable primary. Then the halide ion i.e. the nucleophile attacks the carbocation. Since, we prefer secondary carbocation so, the major product will be secondary.
So, the addition reaction of hydro bromic acid with propene and the product P is as shown:
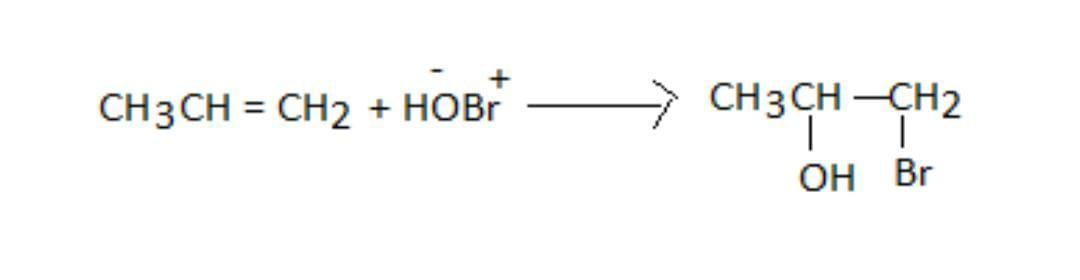
So, we can see that the negative part goes and ads to the carbon bearing the lesser number of hydrogen atoms. As \[ - OH\] is the negative part, it adds to propene.
Note: The free radical addition reactions do not obey Markovnikov’s rule since the regioselectivity of the mechanism of these reactions are not predicted by this rule. These reactions are generally referred to as Anti-Markovnikov addition reactions.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all, let’s discuss Markovnikov's rule. In this, when a protic acid is added to an asymmetric alkene, then the acidic hydrogen attaches itself to the carbon having a greater number of hydrogen substituents whereas the halide group attaches itself to the carbon atom which has a greater number of alkyl substituent.
Now, in the first step, the alkene is protonated and it gives rise to the more stable carbocation. Further, two types of carbocation are formed i.e. primary carbocation and secondary carbocation. We generally prefer secondary carbocation because it is far more stable primary. Then the halide ion i.e. the nucleophile attacks the carbocation. Since, we prefer secondary carbocation so, the major product will be secondary.
So, the addition reaction of hydro bromic acid with propene and the product P is as shown:
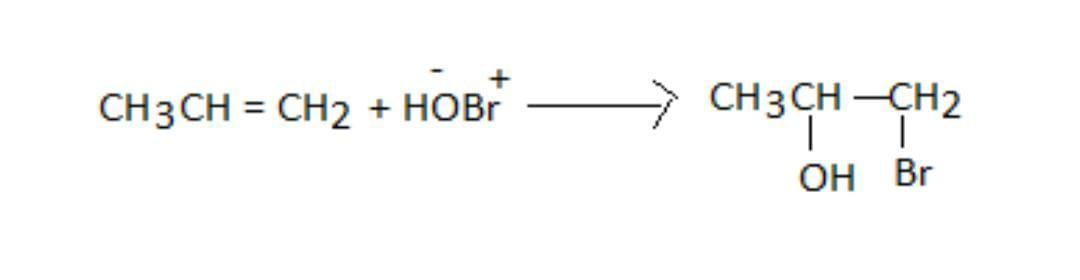
So, we can see that the negative part goes and ads to the carbon bearing the lesser number of hydrogen atoms. As \[ - OH\] is the negative part, it adds to propene.
Note: The free radical addition reactions do not obey Markovnikov’s rule since the regioselectivity of the mechanism of these reactions are not predicted by this rule. These reactions are generally referred to as Anti-Markovnikov addition reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




