
The major product in the following reaction is:
${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}} - {\text{C}} \equiv {\text{C}} - {\text{H}}\,\,{\text{ + }}\,{\text{HBr}}\,{\text{(excess)}}\,\,\longrightarrow$
A.
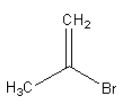
B.
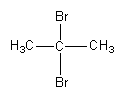
C.
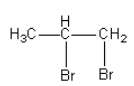
D.
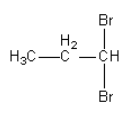




Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint:Hydrogen bromide gives an addition reaction on alkyne. Nucleophilic alkyne gets protonated. Then at carbocation halide attacks. In excess of hydrogen halide, gem product forms.
Complete step by step solution:
The alkyne reacts with hydrogen bromide to give a halogenated alkene. Alkynes are nucleophilic so they attack the hydrogen of hydrogen bromide and get protonated. So, a secondary carbocation forms. Then bromide attacks the carbocation and gets attached.
The formation of alkene is shown as follows:
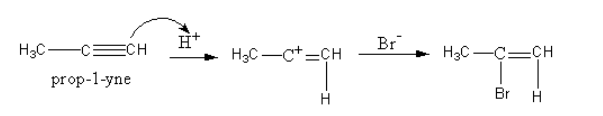
As the hydrogen bromide is present in excess, a further reaction takes place. This time the alkene bromide gets reduced to give alkyl bromide.
The hydrogen bromide similarly adds on the alkene as the hydrogen bromide was added to the alkyne.
The reaction for the formation of alkyl bromide is shown as follows:
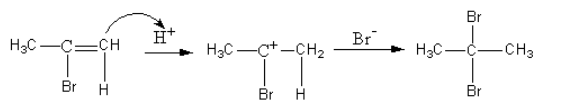
So, the major product formed by the reaction of propyne with hydrogen bromide which is present in excess is $2,2 - $dibromopropane.
As both the bromine atoms are present at the same carbon so, the product is known as gem-dihalide.
Therefore, option (B) is correct.
Note:
The reaction of hydrogen bromide with alkyne is an example of an addition reaction. In the first step, the electrophilic addition takes place. In the second step, the nucleophilic addition takes place. If the hydrogen bromide is not present in excess then the reaction stops at the formation of $2 - $ bromopropene. The hydrogen attached to the triple bond in alkyne is very acidic. The acidity increases as the electron-donating group increases. So, the alkyne works as a nucleophile. If both the halogen atoms are present at different carbon atoms then the product is known as vicinal-dihalide.
Complete step by step solution:
The alkyne reacts with hydrogen bromide to give a halogenated alkene. Alkynes are nucleophilic so they attack the hydrogen of hydrogen bromide and get protonated. So, a secondary carbocation forms. Then bromide attacks the carbocation and gets attached.
The formation of alkene is shown as follows:

As the hydrogen bromide is present in excess, a further reaction takes place. This time the alkene bromide gets reduced to give alkyl bromide.
The hydrogen bromide similarly adds on the alkene as the hydrogen bromide was added to the alkyne.
The reaction for the formation of alkyl bromide is shown as follows:

So, the major product formed by the reaction of propyne with hydrogen bromide which is present in excess is $2,2 - $dibromopropane.
As both the bromine atoms are present at the same carbon so, the product is known as gem-dihalide.
Therefore, option (B) is correct.
Note:
The reaction of hydrogen bromide with alkyne is an example of an addition reaction. In the first step, the electrophilic addition takes place. In the second step, the nucleophilic addition takes place. If the hydrogen bromide is not present in excess then the reaction stops at the formation of $2 - $ bromopropene. The hydrogen attached to the triple bond in alkyne is very acidic. The acidity increases as the electron-donating group increases. So, the alkyne works as a nucleophile. If both the halogen atoms are present at different carbon atoms then the product is known as vicinal-dihalide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




