
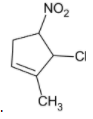
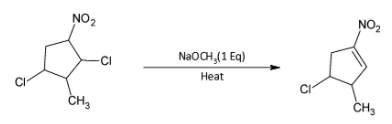
The major product formed in the given reaction is:
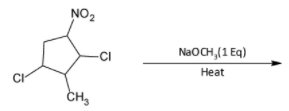
A)
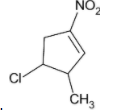
B)
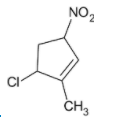
C)
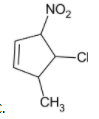
D)





Answer
548.7k+ views
Hint:
This reaction involves the dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halide. The hydrogen and chloride ions are lost from adjacent carbon atoms resulting in the formation of an alkene.
Complete step by step solution:
The attacking species in the reaction is ${\text{NaOC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ which will carry out dehydrohalogenation of the alkyl chloride. A molecule of ${\text{HCl}}$ is lost and ${\text{C = C}}$ double bond is formed.
${\text{NaOC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ breaks into sodium ion and methoxide ion.
Methoxide ion is a strong base and looks to withdraw a hydrogen atom from the $\beta {\text{ - C}}$ atom of the chloride.
To find out the carbon atom which is susceptible to the attack of the base, we need to check whether which carbon has the most acidic hydrogen and will be able to form a stable carbanion transition state.
We know that methyl group is an electron donating group and thus reduces acidity.
Nitro group is an electron withdrawing group. Hence it increases the acidity of the hydrogen atom attached to the carbon bearing the nitro group.
Thus, the removal of hydrogen as a proton becomes easy.
Thus, the product formed will be
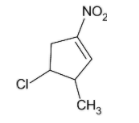
Also, the double bond formed in this product is in conjugation with the double bond in the nitro group thus providing extra stability through delocalization of electrons.
The correct option is A.
Note:
The dehydrohalogenation reaction can also be carried out using ethanolic ${\text{KOH}}$ .
Dehydrohalogenation is easiest to carry out in a tertiary alkyl halide.
If we use alkoxide ion in case of primary alkyl halide, elimination does not occur. Rather we obtain substitution products.
Alkyl iodides are the easiest to dehydrohalogenation followed by alkyl bromides and alkyl chlorides.
This reaction involves the dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halide. The hydrogen and chloride ions are lost from adjacent carbon atoms resulting in the formation of an alkene.
Complete step by step solution:
The attacking species in the reaction is ${\text{NaOC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ which will carry out dehydrohalogenation of the alkyl chloride. A molecule of ${\text{HCl}}$ is lost and ${\text{C = C}}$ double bond is formed.
${\text{NaOC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ breaks into sodium ion and methoxide ion.
Methoxide ion is a strong base and looks to withdraw a hydrogen atom from the $\beta {\text{ - C}}$ atom of the chloride.
To find out the carbon atom which is susceptible to the attack of the base, we need to check whether which carbon has the most acidic hydrogen and will be able to form a stable carbanion transition state.
We know that methyl group is an electron donating group and thus reduces acidity.
Nitro group is an electron withdrawing group. Hence it increases the acidity of the hydrogen atom attached to the carbon bearing the nitro group.
Thus, the removal of hydrogen as a proton becomes easy.
Thus, the product formed will be

Also, the double bond formed in this product is in conjugation with the double bond in the nitro group thus providing extra stability through delocalization of electrons.
The correct option is A.

Note:
The dehydrohalogenation reaction can also be carried out using ethanolic ${\text{KOH}}$ .
Dehydrohalogenation is easiest to carry out in a tertiary alkyl halide.
If we use alkoxide ion in case of primary alkyl halide, elimination does not occur. Rather we obtain substitution products.
Alkyl iodides are the easiest to dehydrohalogenation followed by alkyl bromides and alkyl chlorides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




