
The main function of phloem is the translocation of
(a)Food
(b)Water
(c)Mineral
(d)Air
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Transport in biology means carrying substance absorbed or made in the body of an organism to all other parts of its body. In plants, it is only water and minerals that need to be transported to its other parts. Another thing that needs to be transported to other parts of the plants is the food prepared in leaves.
Complete answer:
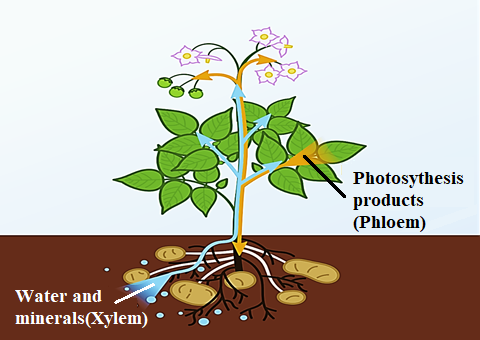
Phloem is an elongated, tubular shape with thin-walled sieve tubes vascular tissue. Its function is the transportation of food and nutrients such as sugar from leaves to other parts of the plant. This movement of substances is called translocation.
Additional Information:
Phloem is the food transporting component of the plant. It includes 4 component and they are:
1. Sieve tube elements:
-They are long tube-like structures arranged longitudinally.
-They are found in association with companion cells.
-The end walls are perforated in a sieve manner to form sieve plates.
-Each cell lacks a nucleus.
- It has a large vacuole and a peripheral cytoplasm.
2. Companion Cells:
-Companion cells are specialised parenchymatous cells.
-They help in maintaining the pressure gradient in the sieve tubes.
-Nuclei of the companion cells control the function of the sieve tubes.
3. Phloem Parenchyma:
-The cells are cylindrical, elongated with tapering ends and dense cytoplasm and nucleus. The cells are connected to each other by plasmodesmata connections.
-The cell wall is composed of cellulose.
-It is absent in monocotyledons.
4. Phloem Fibres:
-They are also called bast fibres.
-They are made of sclerenchymatous cells.
-Phloem fibres are absent in the primary phloem but present in the secondary phloem.
-Fibres are elongated, unbranded and bear pointed apices.
-The cell walls are thick.
-They lose their protoplasm at maturity and become dead.
-The fibres of jute, hemp and flax are of commercial use.
So, the correct answer, “food.”
Note: The two important translocating tools of plants are Xylem and Phloem.
Xylem transports water and soluble mineral nutrients from roots to various parts of the plant. It is responsible for replacing water lost through transpiration and photosynthesis. Phloem translocates sugars made by photosynthetic areas of plants to storage organs like roots, tubers or bulbs.
Complete answer:
Phloem is an elongated, tubular shape with thin-walled sieve tubes vascular tissue. Its function is the transportation of food and nutrients such as sugar from leaves to other parts of the plant. This movement of substances is called translocation.
Additional Information:
Phloem is the food transporting component of the plant. It includes 4 component and they are:
1. Sieve tube elements:
-They are long tube-like structures arranged longitudinally.
-They are found in association with companion cells.
-The end walls are perforated in a sieve manner to form sieve plates.
-Each cell lacks a nucleus.
- It has a large vacuole and a peripheral cytoplasm.
2. Companion Cells:
-Companion cells are specialised parenchymatous cells.
-They help in maintaining the pressure gradient in the sieve tubes.
-Nuclei of the companion cells control the function of the sieve tubes.
3. Phloem Parenchyma:
-The cells are cylindrical, elongated with tapering ends and dense cytoplasm and nucleus. The cells are connected to each other by plasmodesmata connections.
-The cell wall is composed of cellulose.
-It is absent in monocotyledons.
4. Phloem Fibres:
-They are also called bast fibres.
-They are made of sclerenchymatous cells.
-Phloem fibres are absent in the primary phloem but present in the secondary phloem.
-Fibres are elongated, unbranded and bear pointed apices.
-The cell walls are thick.
-They lose their protoplasm at maturity and become dead.
-The fibres of jute, hemp and flax are of commercial use.

So, the correct answer, “food.”
Note: The two important translocating tools of plants are Xylem and Phloem.
Xylem transports water and soluble mineral nutrients from roots to various parts of the plant. It is responsible for replacing water lost through transpiration and photosynthesis. Phloem translocates sugars made by photosynthetic areas of plants to storage organs like roots, tubers or bulbs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




