
The lower window of a house is at height 2m above the ground and its upper window is 4m vertically above the lower window. At a certain instant, the angles of elevation of a balloon from these windows are observed to be \[{{60}^{\circ }}\] and \[{{30}^{\circ }}\] respectively. Find the height of the balloon above the ground.
Answer
627.6k+ views
Hint: Use the fact that the vertical line representing the windows and the balloon are perpendicular to the ground. Use values of tangent of \[{{30}^{\circ }}\] and \[{{60}^{\circ }}\] to relate the length of the base to the height of the balloon. Simplify the equations to calculate the height of the balloon.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have two windows; one is at height 2m above the ground and the other is 4m above the lower window. We have a balloon in the air whose angle of elevation from the two windows is \[{{60}^{\circ }}\] and \[{{30}^{\circ }}\]. We have to calculate the height of the balloon above the ground.
Let’s assume that the base of ground is represented by line AB. The lower window is represented by BC and is of height 2m above the ground. The height of the upper window from the ground is represented by BD. The balloon is represented by AE and is x m above the ground. We have to calculate the value of x, as shown in the figure.
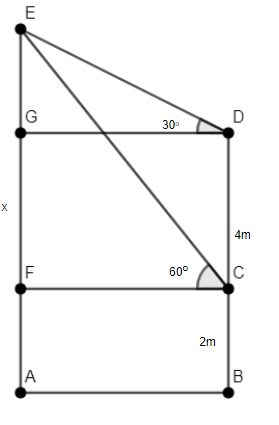
We observe that the base AB is perpendicular to line BD and AE.
We will consider the triangle \[\Delta EGD\]. We observe that \[EG\bot GD\] and \[\angle EDG={{30}^{\circ }}\].
Thus, we have \[\tan \left( \angle EDG \right)=\tan \left( {{30}^{\circ }} \right)\].
We know that tangent of any angle is the ratio of height of the perpendicular and the base of the right angled triangle.
Thus, we have \[\tan \left( \angle EDG \right)=\dfrac{EG}{GD}=\tan \left( {{30}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\].
Rearranging the terms, we have \[EG=\dfrac{GD}{\sqrt{3}}.....\left( 1 \right)\].
Now, we will consider the triangle \[\Delta ECF\]. We observe that \[EF\bot FC\] and \[\angle ECF={{60}^{\circ }}\].
Thus, we have \[\tan \left( \angle ECF \right)=\tan \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)\].
We know that tangent of any angle is the ratio of height of the perpendicular and the base of the right angled triangle.
Thus, we have \[\tan \left( \angle ECF \right)=\dfrac{EF}{FC}=\tan \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\sqrt{3}\].
Rearranging the terms, we have \[EF=\sqrt{3}FC....\left( 2 \right)\].
As \[GDCF\] is a rectangle, we have \[GD=CF.....\left( 3 \right)\] and \[GF=CD=4m.....\left( 4 \right)\].
We observe that \[GF=EF-EG.....\left( 5 \right)\].
Substituting equation (1), (2) and (4) in equation (5), we have \[4=\sqrt{3}FC-\dfrac{GD}{\sqrt{3}}.....\left( 6 \right)\].
Substituting equation (3) in equation (6), we have \[4=\sqrt{3}FC-\dfrac{FC}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{3FC-FC}{\sqrt{3}}\].
Simplifying the above equation by rearranging the terms, we have \[4=\dfrac{2FC}{\sqrt{3}}\Rightarrow FC=2\sqrt{3}m.....\left( 7 \right)\].
Substituting equation (7) in equation (1), we have \[EG=\dfrac{GD}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{FC}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}=2m\].
Thus, we have \[EG=2m,GF=4m.....\left( 8 \right)\].
We observe that \[ABCF\] is a rectangle. Thus, we have \[AF=BC=2m.....\left( 9 \right)\].
We know that \[AE=x=AF+FG+EG\].
Substituting equation (8) and (9) in above equation, we have \[AE=x=AF+FG+EG=2+4+2=8m\].
Hence, the height of the balloon above the ground is 8m.
Note: One must observe that all the angles are in degrees and not in radians. We must also keep in mind that the height of one window is from the ground and the height of the other window is from the first window. It’s important to consider that the balloon is not in the same line as that of the windows.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have two windows; one is at height 2m above the ground and the other is 4m above the lower window. We have a balloon in the air whose angle of elevation from the two windows is \[{{60}^{\circ }}\] and \[{{30}^{\circ }}\]. We have to calculate the height of the balloon above the ground.
Let’s assume that the base of ground is represented by line AB. The lower window is represented by BC and is of height 2m above the ground. The height of the upper window from the ground is represented by BD. The balloon is represented by AE and is x m above the ground. We have to calculate the value of x, as shown in the figure.

We observe that the base AB is perpendicular to line BD and AE.
We will consider the triangle \[\Delta EGD\]. We observe that \[EG\bot GD\] and \[\angle EDG={{30}^{\circ }}\].
Thus, we have \[\tan \left( \angle EDG \right)=\tan \left( {{30}^{\circ }} \right)\].
We know that tangent of any angle is the ratio of height of the perpendicular and the base of the right angled triangle.
Thus, we have \[\tan \left( \angle EDG \right)=\dfrac{EG}{GD}=\tan \left( {{30}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\].
Rearranging the terms, we have \[EG=\dfrac{GD}{\sqrt{3}}.....\left( 1 \right)\].
Now, we will consider the triangle \[\Delta ECF\]. We observe that \[EF\bot FC\] and \[\angle ECF={{60}^{\circ }}\].
Thus, we have \[\tan \left( \angle ECF \right)=\tan \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)\].
We know that tangent of any angle is the ratio of height of the perpendicular and the base of the right angled triangle.
Thus, we have \[\tan \left( \angle ECF \right)=\dfrac{EF}{FC}=\tan \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\sqrt{3}\].
Rearranging the terms, we have \[EF=\sqrt{3}FC....\left( 2 \right)\].
As \[GDCF\] is a rectangle, we have \[GD=CF.....\left( 3 \right)\] and \[GF=CD=4m.....\left( 4 \right)\].
We observe that \[GF=EF-EG.....\left( 5 \right)\].
Substituting equation (1), (2) and (4) in equation (5), we have \[4=\sqrt{3}FC-\dfrac{GD}{\sqrt{3}}.....\left( 6 \right)\].
Substituting equation (3) in equation (6), we have \[4=\sqrt{3}FC-\dfrac{FC}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{3FC-FC}{\sqrt{3}}\].
Simplifying the above equation by rearranging the terms, we have \[4=\dfrac{2FC}{\sqrt{3}}\Rightarrow FC=2\sqrt{3}m.....\left( 7 \right)\].
Substituting equation (7) in equation (1), we have \[EG=\dfrac{GD}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{FC}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}=2m\].
Thus, we have \[EG=2m,GF=4m.....\left( 8 \right)\].
We observe that \[ABCF\] is a rectangle. Thus, we have \[AF=BC=2m.....\left( 9 \right)\].
We know that \[AE=x=AF+FG+EG\].
Substituting equation (8) and (9) in above equation, we have \[AE=x=AF+FG+EG=2+4+2=8m\].
Hence, the height of the balloon above the ground is 8m.
Note: One must observe that all the angles are in degrees and not in radians. We must also keep in mind that the height of one window is from the ground and the height of the other window is from the first window. It’s important to consider that the balloon is not in the same line as that of the windows.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




