
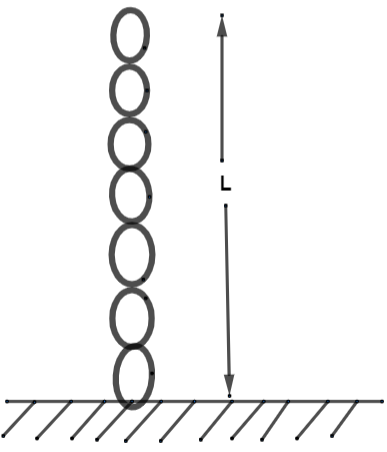
What will be the loss in potential energy of the chain (mass m) when half of its length is generated.

Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: As the question asks about the potential energy which is grounded so, by the use of the formula of potential energy we will solve the problem. We will also consider the potential energy of the part as 0 which is grounded. After that we will subtract half of the potential energy of the chain from its total.
Formula used:
$P.E.=mgh$ where m is mass, g is gravitational force, h is height and P.E. is called potential energy.
Complete answer:
Potential energy: As the name suggests it is the energy which tells about the capability of the potential of an object. Either it is stored into the object or it is just present due to gravitational force. For example if we understand it with the help of an example, we consider an example of a spring whose potential energy is generated by either stretching it or compressing it. Also, if we consider any object that is under rest then, in that case also, we will say that the object will exert potential energy but in the form of gravitation. The formula of potential energy is $P.E.=mgh$.
According to the question, we have the mass of the chain is m. Its length is an L unit which is given to us. We need to find out the loss in its potential energy if in case the half length of the chain made to grounded.
As we can clearly see that the chain is vertically linear and is uniform, so if the half length gets into the ground then its length will change into half. This means that the length or height of the chain now changes into $\dfrac{L}{2}$.
Thus, by the formula of potential energy we have that $P.E.=mg\dfrac{L}{2}$ which is the potential energy for the part of the chain which is not grounded and the for the rest of the height of the chain which is grounded has $P.E.=0$. So, now the loss in potential energy can be carried out by subtracting the potential energy of the upper half of the chain from the whole potential energy. Therefore, we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Delta P.E.=mgL-\dfrac{mgL}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \Delta P.E.=\dfrac{mgL}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the loss in potential energy is $\dfrac{mgL}{2}$.
Note:
Take the following points into consideration:
(1) The formula of potential energy: $P.E.=mgh$.
(2) The potential energy of the part of the chain which is grounded is taken as 0.
(3)For the total potential energy we will just replace the height by the length of an object in the formula of potential energy.
Formula used:
$P.E.=mgh$ where m is mass, g is gravitational force, h is height and P.E. is called potential energy.
Complete answer:
Potential energy: As the name suggests it is the energy which tells about the capability of the potential of an object. Either it is stored into the object or it is just present due to gravitational force. For example if we understand it with the help of an example, we consider an example of a spring whose potential energy is generated by either stretching it or compressing it. Also, if we consider any object that is under rest then, in that case also, we will say that the object will exert potential energy but in the form of gravitation. The formula of potential energy is $P.E.=mgh$.
According to the question, we have the mass of the chain is m. Its length is an L unit which is given to us. We need to find out the loss in its potential energy if in case the half length of the chain made to grounded.
As we can clearly see that the chain is vertically linear and is uniform, so if the half length gets into the ground then its length will change into half. This means that the length or height of the chain now changes into $\dfrac{L}{2}$.
Thus, by the formula of potential energy we have that $P.E.=mg\dfrac{L}{2}$ which is the potential energy for the part of the chain which is not grounded and the for the rest of the height of the chain which is grounded has $P.E.=0$. So, now the loss in potential energy can be carried out by subtracting the potential energy of the upper half of the chain from the whole potential energy. Therefore, we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Delta P.E.=mgL-\dfrac{mgL}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \Delta P.E.=\dfrac{mgL}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the loss in potential energy is $\dfrac{mgL}{2}$.
Note:
Take the following points into consideration:
(1) The formula of potential energy: $P.E.=mgh$.
(2) The potential energy of the part of the chain which is grounded is taken as 0.
(3)For the total potential energy we will just replace the height by the length of an object in the formula of potential energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




