
The locus of the midpoints of chords of the circle \[{x^2} + {y^2} = 1\]which subtends a right angle at the origin is
A.\[{x^2} + {y^2} = \dfrac{1}{4}\]
B.\[{x^2} + {y^2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
C.\[xy = 0\]
D.\[{x^2} - {y^2} = 0\]

Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: In this question equation of the circle is given, and the coordinate of center and vertex is also given, so we will find the radius of the circle by comparing it with the length of the cord, and then the chord equation is found.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given the center of the circle, C is at \[(0,0)\]
R is the radius of the circle
Equation of the circle \[{x^2} + {y^2} = 1\]
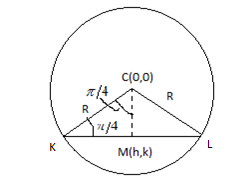
In the figure, we can see line CM is perpendicular to the KL; hence we apply the right-angled property in\[\Delta CKM\]; therefore, the length of line CM will be
\[CM = R\sin \dfrac{\pi }{4} = \dfrac{R}{{\sqrt 2 }} - - (i)\] [Since\[\sin \dfrac{\pi }{4} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]]
By squaring both sides of the equation (i), we can further write
\[
{\left( {CM} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{R}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)^2} \\
{\Rightarrow \left( {CM} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{{R^2}}}{2} - - (ii) \\
\]
Now apply the distance formula in the line CM whose vertices are given as (0, 0) and (h, k), respectively
\[
{\left( {CM} \right)^2} = {\left( {h - 0} \right)^2} + {\left( {k - 0} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow { \left( {CM} \right)^2} = {h^2} + {k^2} - - (iii) \\
\]
Where \[{\left( {CM} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{{R^2}}}{2}\] from equation (ii)
Hence by comparing equation (ii) and (iii), we can write
\[{h^2} + {k^2} = \dfrac{{{R^2}}}{2} - - (iv)\]
Since the equation of the circle is given hence by replacing h, k by x, y and radius R with 1 in equation (iv), we get the equation as
\[
{x^2} + {y^2} = \dfrac{{{1^2}}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\]
Hence the locus of the midpoints \[{x^2} + {y^2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
Option (B) is correct.
Note: A chord of a circle is the straight line drawn between the ends point of the circle, where the diameter is the longest chord passing through the center, joining both endpoints at the circumference.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given the center of the circle, C is at \[(0,0)\]
R is the radius of the circle
Equation of the circle \[{x^2} + {y^2} = 1\]

In the figure, we can see line CM is perpendicular to the KL; hence we apply the right-angled property in\[\Delta CKM\]; therefore, the length of line CM will be
\[CM = R\sin \dfrac{\pi }{4} = \dfrac{R}{{\sqrt 2 }} - - (i)\] [Since\[\sin \dfrac{\pi }{4} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]]
By squaring both sides of the equation (i), we can further write
\[
{\left( {CM} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{R}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)^2} \\
{\Rightarrow \left( {CM} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{{R^2}}}{2} - - (ii) \\
\]
Now apply the distance formula in the line CM whose vertices are given as (0, 0) and (h, k), respectively
\[
{\left( {CM} \right)^2} = {\left( {h - 0} \right)^2} + {\left( {k - 0} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow { \left( {CM} \right)^2} = {h^2} + {k^2} - - (iii) \\
\]
Where \[{\left( {CM} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{{R^2}}}{2}\] from equation (ii)
Hence by comparing equation (ii) and (iii), we can write
\[{h^2} + {k^2} = \dfrac{{{R^2}}}{2} - - (iv)\]
Since the equation of the circle is given hence by replacing h, k by x, y and radius R with 1 in equation (iv), we get the equation as
\[
{x^2} + {y^2} = \dfrac{{{1^2}}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\]
Hence the locus of the midpoints \[{x^2} + {y^2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
Option (B) is correct.
Note: A chord of a circle is the straight line drawn between the ends point of the circle, where the diameter is the longest chord passing through the center, joining both endpoints at the circumference.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




