
The locus of the midpoints of all chords of the parabola ${y^2} = 4ax$ through its vertex is another parabola with directrix
$\left( a \right)x = - a$
$\left( b \right)x = a$
$\left( c \right)x = 0$
$\left( d \right)x = - \dfrac{a}{2}$

Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: In this particular question use the concept that first finds out the midpoint of the chord of the parabola then try to eliminate the t from the midpoint of the parabola, so use these concepts to reach the solution of the question.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given data:
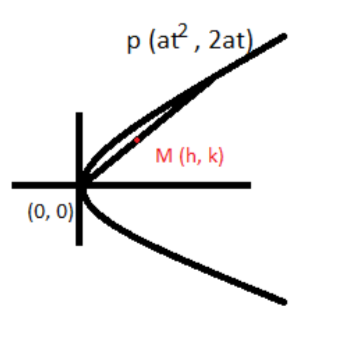
Coordinates of point P and origin are $\left( {a{t^2},2at} \right),\left( {0,0} \right)$.
Now as we know that the midpoint ($x,y$) of the line joining the points $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$ is given as,
$ \Rightarrow \left( {x,y} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {y_1}}}{2},\dfrac{{{x_2} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$
So the midpoint of the chord of the parabola (h, k) whose endpoints are $\left( {a{t^2},2at} \right),\left( {0,0} \right)$ is,
Let, $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right){\text{ = }}\left( {a{t^2},2at} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = \left( {0,0} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {h,k} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{a{t^2} + 0}}{2},\dfrac{{2at + 0}}{2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {h,k} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{a{t^2}}}{2},at} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{a{t^2}}}{2},k = at$
$ \Rightarrow 2h = a{t^2}$................ (1)
$ \Rightarrow k = at..............(2)$
Now from equation (2)
$ \Rightarrow t = \dfrac{k}{a}$
Now substitute this value in equation (1) we have,
$ \Rightarrow 2h = a{\left( {\dfrac{k}{a}} \right)^2}$
Now simplify it we have,
$ \Rightarrow 2h = \dfrac{{{k^2}}}{a}$
$ \Rightarrow {k^2} = 2ah$
Now replace ‘h’ by ‘x’ and ‘k’ by ‘y’ so we have,
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = 2ax$
Now the above equation represents the parabola.
Now we have to find out the directrix of the above equation.
Now as we know the equation of directrix of ${y^2} = 4ax$ is, x = -a behind the vertex (0, 0), where ‘a’ is the length of the focus from the vertex of the parabola.
So, in equation ${y^2} = 2ax$ the length of the focus from the vertex is $\dfrac{a}{2}$ so the equation of the directrix is,
$ \Rightarrow x = - \dfrac{a}{2}$ behind the vertex.
So this is the required answer.
Hence option (d) is the correct answer.
Note: This type of question requires a basic knowledge of parabola. In mathematics, a parabola is a plane curve which is mirror-symmetrical and is roughly U-shaped. It matches many other superficially different mathematical definitions, which can all be proven to describe exactly the same curves. One definition of a parabola includes a point (the focus) and a line (the directrix). The emphasis does not lie on the directrix. The parabola is the locus of points in that plane that are equidistant from both the directrix and the focus. Another definition of a parabola is as a conic segment, formed from the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane parallel to another plane that is tangential to the conical surface.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given data:
Coordinates of point P and origin are $\left( {a{t^2},2at} \right),\left( {0,0} \right)$.
Now as we know that the midpoint ($x,y$) of the line joining the points $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$ is given as,
$ \Rightarrow \left( {x,y} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {y_1}}}{2},\dfrac{{{x_2} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$
So the midpoint of the chord of the parabola (h, k) whose endpoints are $\left( {a{t^2},2at} \right),\left( {0,0} \right)$ is,
Let, $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right){\text{ = }}\left( {a{t^2},2at} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = \left( {0,0} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {h,k} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{a{t^2} + 0}}{2},\dfrac{{2at + 0}}{2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {h,k} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{a{t^2}}}{2},at} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{a{t^2}}}{2},k = at$
$ \Rightarrow 2h = a{t^2}$................ (1)
$ \Rightarrow k = at..............(2)$
Now from equation (2)
$ \Rightarrow t = \dfrac{k}{a}$
Now substitute this value in equation (1) we have,
$ \Rightarrow 2h = a{\left( {\dfrac{k}{a}} \right)^2}$
Now simplify it we have,
$ \Rightarrow 2h = \dfrac{{{k^2}}}{a}$
$ \Rightarrow {k^2} = 2ah$
Now replace ‘h’ by ‘x’ and ‘k’ by ‘y’ so we have,
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = 2ax$
Now the above equation represents the parabola.
Now we have to find out the directrix of the above equation.
Now as we know the equation of directrix of ${y^2} = 4ax$ is, x = -a behind the vertex (0, 0), where ‘a’ is the length of the focus from the vertex of the parabola.
So, in equation ${y^2} = 2ax$ the length of the focus from the vertex is $\dfrac{a}{2}$ so the equation of the directrix is,
$ \Rightarrow x = - \dfrac{a}{2}$ behind the vertex.
So this is the required answer.
Hence option (d) is the correct answer.
Note: This type of question requires a basic knowledge of parabola. In mathematics, a parabola is a plane curve which is mirror-symmetrical and is roughly U-shaped. It matches many other superficially different mathematical definitions, which can all be proven to describe exactly the same curves. One definition of a parabola includes a point (the focus) and a line (the directrix). The emphasis does not lie on the directrix. The parabola is the locus of points in that plane that are equidistant from both the directrix and the focus. Another definition of a parabola is as a conic segment, formed from the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane parallel to another plane that is tangential to the conical surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




