
The locus of the foot of the perpendicular from the origin to chords of the circle ${x^2} + {y^2} - 4x - 6y - 3 = 0$ which subtend a right angle at the origin is
A. $2({x^2} + {y^2}) - 4x - 6y - 3 = 0$
B. ${x^2} + {y^2} - 4x - 6y - 3 = 0$
C. $2({x^2} + {y^2}) + 4x + 6y - 3 = 0$
D. $2({x^2} + {y^2}) + 4x + 6y + 3 = 0$
Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: At first, we’ll find the equation of chord by assuming a point with the center of the chord, as it is given perpendicular to the line joining the point and the origin.
Now using this equation of chord we’ll homogenize the equation of the circle to get the pair of the line joining the origin and the endpoints of chords. Then using the property, the in pair of the straight line of perpendicular lines the sum of the coefficient of ${x^2}$ and ${y^2}$ is zero, we’ll get the required equation.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given data: Equation of the circle ${x^2} + {y^2} - 4x - 6y - 3 = 0$
Let the foot of the perpendicular from origin to chord be $(h,k)$
As we know the slope of the line joining the points $(a,b)$ and $(c,d)$ have a slope $\dfrac{{d - b}}{{c - a}}$
Therefore, the slope of the perpendicular line will be $\dfrac{{k - 0}}{{h - 0}}$
$ = \dfrac{k}{h}$
Now, we know that the product of the slopes of two perpendicular lines is -1.
So, we can say that the slope of the chord would be $ - \dfrac{h}{k}$.
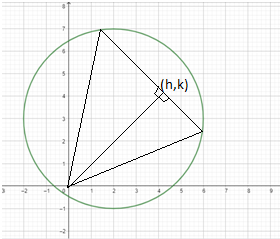
Now, we will find the equation of the chord to find the equation of the pair of lines joining the end-points of the chord with the origin.
Equation of any line passing through $({x_1},{y_1})$ and having slope ‘m’ is given by
$ \Rightarrow (y - {y_1}) = m(x - {x_1})$
Therefore, the equation of chord is $ \Rightarrow (y - k) = - \dfrac{h}{k}(x - h)$
$ \Rightarrow (y - k) = - \dfrac{h}{k}(x - h)$
On cross multiplication
$ \Rightarrow yk - {k^2} = {h^2} - hx$
$ \Rightarrow yk + hx = {h^2} + {k^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{yk + hx}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}} = 1$ ….(i)
Now we know that ${x^2} + {y^2} - 4x - 6y - 3 = 0$ is also a pair of the equation of two lines and homogenizing it with the help of the equation of chord, we will get the pair of lines joining the endpoint of the chord and origin
We can write the equation of pair of the line as
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - (1)(4x + 6y) - 3{(1)^2} = 0\]
Substituting the value of 1 from equation(i)
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - \left( {\dfrac{{yk + hx}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}}} \right)(4x + 6y) - 3{\left( {\dfrac{{yk + hx}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}}} \right)^2} = 0\]
Since it is an equation of two perpendicular lines
Hence the sum of the coefficient of ${x^2}$ and ${y^2}$ will be equal to zero
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {1 - \dfrac{{4h}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}} - \dfrac{{3{h^2}}}{{{{\left( {{h^2} + {k^2}} \right)}^2}}}} \right) + \left( {1 - \dfrac{{6k}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}} - \dfrac{{3{k^2}}}{{{{\left( {{h^2} + {k^2}} \right)}^2}}}} \right) = 0\]
By combining the like terms
\[ \Rightarrow 1 + 1 - \dfrac{{4h + 6k}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}} - 3\left[ {\dfrac{{{h^2} + {k^2}}}{{{{\left( {{h^2} + {k^2}} \right)}^2}}}} \right] = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow 1 + 1 - \dfrac{{4h + 6k}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}} - \dfrac{3}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}} = 0\]
On multiplying the whole equation by \[\left( {{h^2} + {k^2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\left( {{h^2} + {k^2}} \right) - 4h - 6k - 3 = 0\]
Now $(h,k)$ is the point whose locus is to be found
Substituting it with the $(x,y)$
Therefore, the required equation is \[2\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) - 4x - 6y - 3 = 0\]
Option(i) is correct.
Note: Some of the students try to homogenize the equation of circle using itself which is not correct, since we require the pair of the line joining the origin and the point of the chord so the equation of chord is used to homogenize the equation of the circle, so keep it in mind.
Now using this equation of chord we’ll homogenize the equation of the circle to get the pair of the line joining the origin and the endpoints of chords. Then using the property, the in pair of the straight line of perpendicular lines the sum of the coefficient of ${x^2}$ and ${y^2}$ is zero, we’ll get the required equation.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given data: Equation of the circle ${x^2} + {y^2} - 4x - 6y - 3 = 0$

Let the foot of the perpendicular from origin to chord be $(h,k)$
As we know the slope of the line joining the points $(a,b)$ and $(c,d)$ have a slope $\dfrac{{d - b}}{{c - a}}$
Therefore, the slope of the perpendicular line will be $\dfrac{{k - 0}}{{h - 0}}$
$ = \dfrac{k}{h}$
Now, we know that the product of the slopes of two perpendicular lines is -1.
So, we can say that the slope of the chord would be $ - \dfrac{h}{k}$.
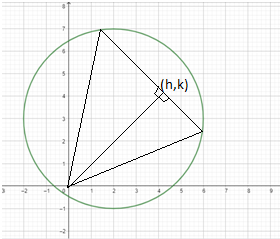
Now, we will find the equation of the chord to find the equation of the pair of lines joining the end-points of the chord with the origin.
Equation of any line passing through $({x_1},{y_1})$ and having slope ‘m’ is given by
$ \Rightarrow (y - {y_1}) = m(x - {x_1})$
Therefore, the equation of chord is $ \Rightarrow (y - k) = - \dfrac{h}{k}(x - h)$
$ \Rightarrow (y - k) = - \dfrac{h}{k}(x - h)$
On cross multiplication
$ \Rightarrow yk - {k^2} = {h^2} - hx$
$ \Rightarrow yk + hx = {h^2} + {k^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{yk + hx}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}} = 1$ ….(i)
Now we know that ${x^2} + {y^2} - 4x - 6y - 3 = 0$ is also a pair of the equation of two lines and homogenizing it with the help of the equation of chord, we will get the pair of lines joining the endpoint of the chord and origin
We can write the equation of pair of the line as
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - (1)(4x + 6y) - 3{(1)^2} = 0\]
Substituting the value of 1 from equation(i)
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - \left( {\dfrac{{yk + hx}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}}} \right)(4x + 6y) - 3{\left( {\dfrac{{yk + hx}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}}} \right)^2} = 0\]
Since it is an equation of two perpendicular lines
Hence the sum of the coefficient of ${x^2}$ and ${y^2}$ will be equal to zero
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {1 - \dfrac{{4h}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}} - \dfrac{{3{h^2}}}{{{{\left( {{h^2} + {k^2}} \right)}^2}}}} \right) + \left( {1 - \dfrac{{6k}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}} - \dfrac{{3{k^2}}}{{{{\left( {{h^2} + {k^2}} \right)}^2}}}} \right) = 0\]
By combining the like terms
\[ \Rightarrow 1 + 1 - \dfrac{{4h + 6k}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}} - 3\left[ {\dfrac{{{h^2} + {k^2}}}{{{{\left( {{h^2} + {k^2}} \right)}^2}}}} \right] = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow 1 + 1 - \dfrac{{4h + 6k}}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}} - \dfrac{3}{{{h^2} + {k^2}}} = 0\]
On multiplying the whole equation by \[\left( {{h^2} + {k^2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\left( {{h^2} + {k^2}} \right) - 4h - 6k - 3 = 0\]
Now $(h,k)$ is the point whose locus is to be found
Substituting it with the $(x,y)$
Therefore, the required equation is \[2\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) - 4x - 6y - 3 = 0\]
Option(i) is correct.
Note: Some of the students try to homogenize the equation of circle using itself which is not correct, since we require the pair of the line joining the origin and the point of the chord so the equation of chord is used to homogenize the equation of the circle, so keep it in mind.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




