
The locus of the centre of a circle which touches externally the circle ${x^2} + {y^2} - 6x - 6y + 14 = 0$ and also touches the y-axis is given by the equation
A) ${x^2} - 6x - 10y + 14 = 0$
B) ${x^2} - 10x - 6y + 14 = 0$
C) ${y^2} - 6x - 10y + 14 = 0$
D) ${y^2} - 10x - 6y + 14 = 0$
Answer
489.6k+ views
Hint: We will first assume a circle that touches the other circle externally. Since, we know, if two circles touch each other externally, then the distance between the centres of the circle is equal to the sum of the radii of the two circles. So, by using this property we will form an equation and further simplifying the equation we will get our desired answer.
Complete answer:
Let the centre of the circle be $\left( {h,k} \right)$ and it is given that it touches the y-axis.
Now, we know, if a circle touches the y-axis, then the radius of the circle is equal to the x-coordinate of the centre of the circle.
That means, the radius of the circle will be $h$.
Now, the equation of the other circle is given to be
${x^2} + {y^2} - 6x - 6y + 14 = 0$
Taking the $x$ terms and $y$ terms together, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 6x + {y^2} - 6y + 14 = 0$
We can write it as,
$ \Rightarrow ({x^2} - 2.3.x + 9) - 9 + ({y^2} - 2.3.y + 9) - 9 + 14 = 0$
Using the formula ${a^2} - 2.a.b + {b^2} = {(a - b)^2}$, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {(x - 3)^2} + {(y - 3)^2} - 4 = 0$
Taking the constant term to the right hand side, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {(x - 3)^2} + {(y - 3)^2} = 4$
$ \Rightarrow {(x - 3)^2} + {(y - 3)^2} = {2^2}$
Therefore, we can say, the centre of this circle is $\left( {3,3} \right)$ and it’s radius is $2$.
Thus, we know, if two circles touch each other externally, then the distance between the centres of the circle is equal to the sum of the radii of the two circles.
By using this property, we can write,
${C_1}{C_{2}} = {r_1} + {r_2}$
Now, substituting the values, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{\left( {h - 3} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {k - 3} \right)}^2}} = h + 2$
[Using the distance formula, that is, $d = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} $]
Now, squaring both sides, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {h - 3} \right)^2} + {\left( {k - 3} \right)^2} = {(h + 2)^2}$
Now, opening the brackets, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {h^2} - 6h + 9 + {k^2} - 6k + 9 = {h^2} + 4h + 4$
Now, taking all the terms to the left hand side and simplifying, we get,
$ \Rightarrow - 10h + {k^2} - 6k + 14 = 0$
Now, substituting $\left( {h,k} \right)$ for $\left( {x,y} \right)$, we get,
${y^2} - 10x - 6y + 14 = 0$
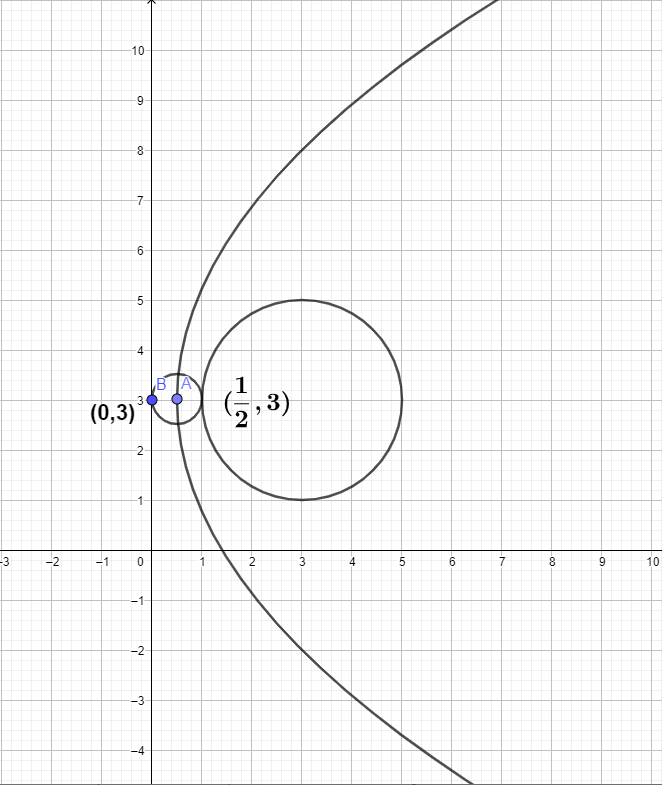
Therefore, the equation of the circle is, ${y^2} - 10x - 6y + 14 = 0$.
The correct option is D.
Note: Here we used the property that, if two circles touch each other externally, the distance between their centres is equal to the sum of the radius. Also, there are properties that say, if two circles overlap each other, the distance between their centres is less than the sum of their radius. Also, if one circle is embedded inside the other circle, then also, the distance between the centres is less than the sum of the radius of the circle.
Complete answer:
Let the centre of the circle be $\left( {h,k} \right)$ and it is given that it touches the y-axis.
Now, we know, if a circle touches the y-axis, then the radius of the circle is equal to the x-coordinate of the centre of the circle.
That means, the radius of the circle will be $h$.
Now, the equation of the other circle is given to be
${x^2} + {y^2} - 6x - 6y + 14 = 0$
Taking the $x$ terms and $y$ terms together, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 6x + {y^2} - 6y + 14 = 0$
We can write it as,
$ \Rightarrow ({x^2} - 2.3.x + 9) - 9 + ({y^2} - 2.3.y + 9) - 9 + 14 = 0$
Using the formula ${a^2} - 2.a.b + {b^2} = {(a - b)^2}$, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {(x - 3)^2} + {(y - 3)^2} - 4 = 0$
Taking the constant term to the right hand side, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {(x - 3)^2} + {(y - 3)^2} = 4$
$ \Rightarrow {(x - 3)^2} + {(y - 3)^2} = {2^2}$
Therefore, we can say, the centre of this circle is $\left( {3,3} \right)$ and it’s radius is $2$.
Thus, we know, if two circles touch each other externally, then the distance between the centres of the circle is equal to the sum of the radii of the two circles.
By using this property, we can write,
${C_1}{C_{2}} = {r_1} + {r_2}$
Now, substituting the values, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{\left( {h - 3} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {k - 3} \right)}^2}} = h + 2$
[Using the distance formula, that is, $d = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} $]
Now, squaring both sides, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {h - 3} \right)^2} + {\left( {k - 3} \right)^2} = {(h + 2)^2}$
Now, opening the brackets, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {h^2} - 6h + 9 + {k^2} - 6k + 9 = {h^2} + 4h + 4$
Now, taking all the terms to the left hand side and simplifying, we get,
$ \Rightarrow - 10h + {k^2} - 6k + 14 = 0$
Now, substituting $\left( {h,k} \right)$ for $\left( {x,y} \right)$, we get,
${y^2} - 10x - 6y + 14 = 0$

Therefore, the equation of the circle is, ${y^2} - 10x - 6y + 14 = 0$.
The correct option is D.
Note: Here we used the property that, if two circles touch each other externally, the distance between their centres is equal to the sum of the radius. Also, there are properties that say, if two circles overlap each other, the distance between their centres is less than the sum of their radius. Also, if one circle is embedded inside the other circle, then also, the distance between the centres is less than the sum of the radius of the circle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




