
The locus of a point at the tip of a minute hand of a clock moving from \[3:15PM\] to \[3:45PM\] on a particular day is
A. A circle
B. A horizontal line
C. A quadrant
D. A semicircle
Answer
516.6k+ views
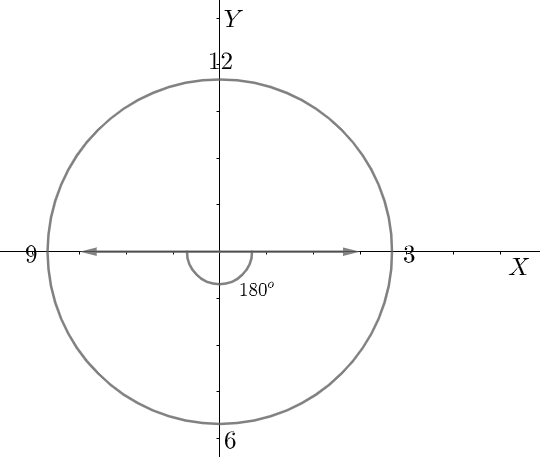
Hint: We first note what is the starting point and finishing point of the minute hand. Then, we compare the clock to Cartesian coordinate axes. The number $3$ on the clock shows the positive x axis, the number $9$ on the clock shows the negative x axis, the number $12$ on the clock shows the positive y axis and the number $6$ on the clock shows the negative y axis. As the minute hand moves from the positive x axis to the negative x axis, it completes a ${{180}^{\circ }}$ turn, which is half a complete turn, from which we get our final answer.
Complete step-by-step solution:
A locus is the path traversed by a point given that the point moves satisfying an underline equation or condition. It is the set of all the points that satisfy a given equation or condition. For example, the locus of a point such that the point is at a constant distance from a fixed point is a circle.
Now, if we compare a clock with Cartesian coordinate axes, then the number $3$ on the clock shows the positive x axis, the number $9$ on the clock shows the negative x axis, the number $12$ on the clock shows the positive y axis and the number $6$ on the clock shows the negative y axis. Now, since the length of the minute hand is constant, we can say that the locus of any particular point on it is a circular arc in general. As the minute hand moves from the positive x axis to the negative x axis, it completes a ${{180}^{\circ }}$ turn, which is half a complete turn, or half a circle.
Thus, we can conclude that the locus of a point at the tip of a minute hand of a clock moving from \[3:15PM\] to \[3:45PM\] on a particular day is a semicircle which is Option D.
Note: These problems are easy if we can visualize the clock completely. Students often mistakenly write the answer as a circle though they know that it is a semicircle. These mistakes should be avoided. Also, it's better if we draw a rough sketch of a clock and then solve it.
Complete step-by-step solution:
A locus is the path traversed by a point given that the point moves satisfying an underline equation or condition. It is the set of all the points that satisfy a given equation or condition. For example, the locus of a point such that the point is at a constant distance from a fixed point is a circle.
Now, if we compare a clock with Cartesian coordinate axes, then the number $3$ on the clock shows the positive x axis, the number $9$ on the clock shows the negative x axis, the number $12$ on the clock shows the positive y axis and the number $6$ on the clock shows the negative y axis. Now, since the length of the minute hand is constant, we can say that the locus of any particular point on it is a circular arc in general. As the minute hand moves from the positive x axis to the negative x axis, it completes a ${{180}^{\circ }}$ turn, which is half a complete turn, or half a circle.
Thus, we can conclude that the locus of a point at the tip of a minute hand of a clock moving from \[3:15PM\] to \[3:45PM\] on a particular day is a semicircle which is Option D.

Note: These problems are easy if we can visualize the clock completely. Students often mistakenly write the answer as a circle though they know that it is a semicircle. These mistakes should be avoided. Also, it's better if we draw a rough sketch of a clock and then solve it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




