
The living matter of an organism is
(a Nucleus
(b) Protoplasm
(c) Cell
(d) Nucleoplasm
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: The living matter of an organism is a tough, slimy, semi- fluid, and granular substance in plant cells that surrounds the cell nucleus.
Complete answer:
Protoplasm is the living matter of a cell that's surrounded by a cell wall. Protoplasm may be a gel- like substance present altogether. All the reactions necessary for a cell to sustain occur in protoplasm.
In some definitions, it's a general term for the cytoplasm except for others, it also includes the nucleoplasm. As to the ancient usage, the extranuclear part of the protoplast (the entire cell, excluding the cell wall) was called "protoplasm," but the nucleus is also composed of protoplasm or living matter in its wide sense.
- Similar to the cytoplasm of a cell, the nucleus contains nucleoplasm that is also referred to as karyoplasm or nucleus sap. The nucleoplasm includes the chromosomes and nucleolus. Many matters such as nucleotides (necessary for purposes like DNA replication) and enzymes (which direct activities that happen within the nucleus) are diffuse within the nucleoplasm.
- The cell which means "small room". The cell is a basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known organisms. A cell is the smallest unit of life. Cells are often known as the "building blocks of life".
- In cell biology, the nucleus means ‘seed’. The nucleus is a membrane- bound organelle that is present in eukaryotic cells. It carries all of the cell's genome, aside from a small fragment of mitochondrial DNA, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules during a complex with an outsized sort of proteins, like histones, to make chromosomes.
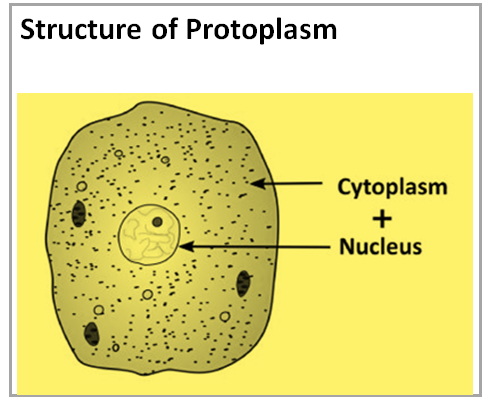
So, the right answer is ‘Protoplasm ‘.
Note: The nucleoplasm is also referred to as the nuclear membrane which is a sort of protoplasm, enveloped by the nuclear envelope. Cells contain cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules like proteins and nucleic acids.
Complete answer:
Protoplasm is the living matter of a cell that's surrounded by a cell wall. Protoplasm may be a gel- like substance present altogether. All the reactions necessary for a cell to sustain occur in protoplasm.
In some definitions, it's a general term for the cytoplasm except for others, it also includes the nucleoplasm. As to the ancient usage, the extranuclear part of the protoplast (the entire cell, excluding the cell wall) was called "protoplasm," but the nucleus is also composed of protoplasm or living matter in its wide sense.
- Similar to the cytoplasm of a cell, the nucleus contains nucleoplasm that is also referred to as karyoplasm or nucleus sap. The nucleoplasm includes the chromosomes and nucleolus. Many matters such as nucleotides (necessary for purposes like DNA replication) and enzymes (which direct activities that happen within the nucleus) are diffuse within the nucleoplasm.
- The cell which means "small room". The cell is a basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known organisms. A cell is the smallest unit of life. Cells are often known as the "building blocks of life".
- In cell biology, the nucleus means ‘seed’. The nucleus is a membrane- bound organelle that is present in eukaryotic cells. It carries all of the cell's genome, aside from a small fragment of mitochondrial DNA, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules during a complex with an outsized sort of proteins, like histones, to make chromosomes.

So, the right answer is ‘Protoplasm ‘.
Note: The nucleoplasm is also referred to as the nuclear membrane which is a sort of protoplasm, enveloped by the nuclear envelope. Cells contain cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules like proteins and nucleic acids.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




