
The lines ${L_1}:y - x = 0$ and ${L_2}:2x + y = 0$ intersect the line ${L_3}:y + 2 = 0$ at P and Q respectively. The bisector of the acute angle between ${L_1}$ and ${L_2}$ intersects ${L_3}$ at R.
Statement - 1: The ratio $PR:RQ$ equals $2\sqrt 2 :\sqrt 5 $.
Statement - 2: In any triangle, the bisector of an angle divides the triangle into two similar triangles.
A) Statement – 1 is true, Statement – 2 is false.
B) Statement – 1 is false, Statement – 2 is true.
C) Statement – 1 is true, Statement – 2 is true; Statement – 1 is a correct explanation for Statement – 1.
D) Statement – 1 is true, Statement – 2 is true; Statement – 1 is not a correct explanation for Statement – 1.
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: First construct the graph based on the equation provided in the question. All the lines will form a triangle. Find the points P, Q, R. Then find the distances PQ and RQ. As OR is an angle bisector. Then, the ratio of OP and OQ is the same as the ratio of PR and RQ. So, we can find OP and OQ by distance formula.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given: - ${L_1}:y - x = 0,{L_2}:2x + y = 0$ and ${L_3}:y + 2 = 0$.
The graph of the lines ${L_1}:y - x = 0,{L_2}:2x + y = 0$ and ${L_3}:y + 2 = 0$.
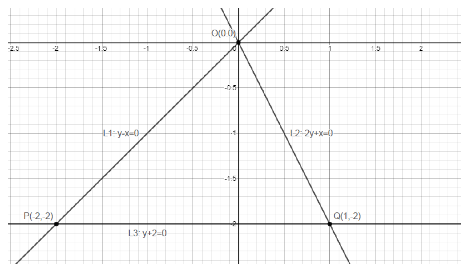
As we know that P is the intersection point of the lines ${L_1}:y - x = 0$ and ${L_3}:y = - 2$.
For the coordinates of P, substitute the value of y in the equation, $y - x = 0$,
$ - 2 - x = 0$
Move x to the right hand of the equation,
$x = - 2$
So, the coordinates of point P is $\left( { - 2, - 2} \right)$.
Also, Q is the intersection point of the lines ${L_2}:2x + y = 0$ and ${L_3}:y = - 2$.
For the coordinates of Q, substitute the value of y in the equation, $2x + y = 0$,
$2x - 2 = 0$
Move 2 to the right hand of the equation,
$2x = 2$
Divide both sides by 2,
$x = 1$
So, the coordinates of point Q is $\left( {1, - 2} \right)$.
As we know that the internal angular bisector divides the side in the ratio of opposite sides and R is the angle bisector. Then,
$\dfrac{{PR}}{{QR}} = \dfrac{{OP}}{{OQ}}$ …… (1)
Use distance formula $d = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_1} - {x_2}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)}^2}} $ to find the value of OP and OQ.
For OP, ${x_1} = 0,{y_1} = 0,{x_2} = - 2,{y_2} = - 2$. Then,
$\begin{gathered}
OP = \sqrt {{{\left( {0 - \left( { - 2} \right)} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {0 - \left( { - 2} \right)} \right)}^2}} \\
= \sqrt {{{\left( 2 \right)}^2} + {{\left( 2 \right)}^2}} \\
= \sqrt {4 + 4} \\
= \sqrt 8 \\
= 2\sqrt 2 \\
\end{gathered} $
For OQ, ${x_1} = 0,{y_1} = 0,{x_2} = 1,{y_2} = - 2$. Then,
$\begin{gathered}
OQ = \sqrt {{{\left( {0 - \left( 1 \right)} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {0 - \left( { - 2} \right)} \right)}^2}} \\
= \sqrt {{{\left( { - 1} \right)}^2} + {{\left( 2 \right)}^2}} \\
= \sqrt {1 + 4} \\
= \sqrt 5 \\
\end{gathered} $
Substitute the values of OP and OQ in equation (1),
$\dfrac{{PR}}{{QR}} = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 }}{{\sqrt 5 }}$
So, Statement – 1 is true.
Also, the angle bisector does not give similar triangles in this case.
So, Statement – 2 is false.
Hence, option (2) is the correct answer.
Note: The students might make mistakes while taking the ratio of the corresponding sides. As bisectors divide in the ratio of corresponding sides.
The sum of all the internal angles of a triangle is always 180o no matter how the triangle is constructed.
The length of any side of a triangle is shorter than the sum of the other two sides.
A triangle can always be split into two right triangles no matter how the triangle is constructed.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given: - ${L_1}:y - x = 0,{L_2}:2x + y = 0$ and ${L_3}:y + 2 = 0$.
The graph of the lines ${L_1}:y - x = 0,{L_2}:2x + y = 0$ and ${L_3}:y + 2 = 0$.

As we know that P is the intersection point of the lines ${L_1}:y - x = 0$ and ${L_3}:y = - 2$.
For the coordinates of P, substitute the value of y in the equation, $y - x = 0$,
$ - 2 - x = 0$
Move x to the right hand of the equation,
$x = - 2$
So, the coordinates of point P is $\left( { - 2, - 2} \right)$.
Also, Q is the intersection point of the lines ${L_2}:2x + y = 0$ and ${L_3}:y = - 2$.
For the coordinates of Q, substitute the value of y in the equation, $2x + y = 0$,
$2x - 2 = 0$
Move 2 to the right hand of the equation,
$2x = 2$
Divide both sides by 2,
$x = 1$
So, the coordinates of point Q is $\left( {1, - 2} \right)$.
As we know that the internal angular bisector divides the side in the ratio of opposite sides and R is the angle bisector. Then,
$\dfrac{{PR}}{{QR}} = \dfrac{{OP}}{{OQ}}$ …… (1)
Use distance formula $d = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_1} - {x_2}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)}^2}} $ to find the value of OP and OQ.
For OP, ${x_1} = 0,{y_1} = 0,{x_2} = - 2,{y_2} = - 2$. Then,
$\begin{gathered}
OP = \sqrt {{{\left( {0 - \left( { - 2} \right)} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {0 - \left( { - 2} \right)} \right)}^2}} \\
= \sqrt {{{\left( 2 \right)}^2} + {{\left( 2 \right)}^2}} \\
= \sqrt {4 + 4} \\
= \sqrt 8 \\
= 2\sqrt 2 \\
\end{gathered} $
For OQ, ${x_1} = 0,{y_1} = 0,{x_2} = 1,{y_2} = - 2$. Then,
$\begin{gathered}
OQ = \sqrt {{{\left( {0 - \left( 1 \right)} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {0 - \left( { - 2} \right)} \right)}^2}} \\
= \sqrt {{{\left( { - 1} \right)}^2} + {{\left( 2 \right)}^2}} \\
= \sqrt {1 + 4} \\
= \sqrt 5 \\
\end{gathered} $
Substitute the values of OP and OQ in equation (1),
$\dfrac{{PR}}{{QR}} = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 }}{{\sqrt 5 }}$
So, Statement – 1 is true.
Also, the angle bisector does not give similar triangles in this case.
So, Statement – 2 is false.
Hence, option (2) is the correct answer.
Note: The students might make mistakes while taking the ratio of the corresponding sides. As bisectors divide in the ratio of corresponding sides.
The sum of all the internal angles of a triangle is always 180o no matter how the triangle is constructed.
The length of any side of a triangle is shorter than the sum of the other two sides.
A triangle can always be split into two right triangles no matter how the triangle is constructed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




